Boundless Study Slides
advertisement

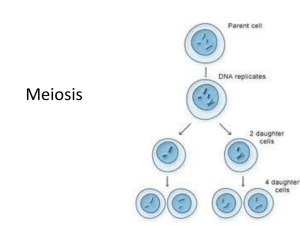
Boundless Lecture Slides Available on the Boundless Teaching Platform Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless Teaching Platform Boundless empowers educators to engage their students with affordable, customizable textbooks and intuitive teaching tools. The free Boundless Teaching Platform gives educators the ability to customize textbooks in more than 20 subjects that align to hundreds of popular titles. Get started by using high quality Boundless books, or make switching to our platform easier by building from Boundless content pre-organized to match the assigned textbook. This platform gives educators the tools they need to assign readings and assessments, monitor student activity, and lead their classes with pre-made teaching resources. Using Boundless Presentations The Appendix The appendix is for you to use to add depth and breadth to your lectures. You can simply drag and drop slides from the appendix into the main presentation to make for a richer lecture experience. Get started now at: http://boundless.com/teaching-platform Free to edit, share, and copy Feel free to edit, share, and make as many copies of the Boundless presentations as you like. We encourage you to take these presentations and make them your own. If you have any questions or problems please email: educators@boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com About Boundless Boundless is an innovative technology company making education more affordable and accessible for students everywhere. The company creates the world’s best open educational content in 20+ subjects that align to more than 1,000 popular college textbooks. Boundless integrates learning technology into all its premium books to help students study more efficiently at a fraction of the cost of traditional textbooks. The company also empowers educators to engage their students more effectively through customizable books and intuitive teaching tools as part of the Boundless Teaching Platform. More than 2 million learners access Boundless free and premium content each month across the company’s wide distribution platforms, including its website, iOS apps, Kindle books, and iBooks. To get started learning or teaching with Boundless, visit boundless.com. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction > The Process of Meiosis The Process of Meiosis • Introduction • Meiosis I • Meiosis II • Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction > The Process of Meiosis Introduction • Sexual reproduction is the production of haploid cells and the fusion of two of those cells to form a diploid cell. • Before sexual reproduction can occur, the number of chromosomes in a diploid cell must decrease by half. • Meiosis produces cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. • Haploid cells used in sexual reproduction, gametes, are formed during meiosis, which consists of one round of chromosome replication and two rounds of nuclear division. • Meiosis I is the first round of meiotic division, while meiosis II is the second round. Offspring Closely Resemble Their Parents View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/meiosis-and-sexual-reproduction-11/the-process-of-meiosis-92/introduction403-11630 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction > The Process of Meiosis Meiosis I • Meiosis is preceded by interphase which consists of the G1 phase (growth), the S phase (DNA replication), and the G2 phase. • During prophase I, the homologous chromosomes condense and become visible as the x shape we know, pair up to form a tetrad, and exchange genetic material by crossing over. • During prometaphase I, microtubules attach at the chromosomes' kinetochores and the nuclear envelope breaks down. • In metaphase I, the tetrads line themselves up at the metaphase plate and homologous pairs orient themselves randomly. • In anaphase I, centromeres break down and homologous chromosomes separate. Crossover between homologous chromosomes View on Boundless.com • In telophase I, chromosomes move to opposite poles; during cytokinesis the cell separates into two haploid cells. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/meiosis-and-sexual-reproduction-11/the-process-of-meiosis-92/meiosis-i-40411631 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction > The Process of Meiosis Meiosis II • During prophase II, chromsomes condense again, centrosomes that were duplicated during interphase I move away from each other toward opposite poles, and new spindles are formed. • During prometaphase II, the nuclear envelopes are completely broken down, and each sister chromatid forms an individual kinetochore that attaches to microtubules from opposite poles. • During metaphase II, sister chromatids are condensed and aligned at the equator of the cell. • During anaphase II sister chromatids are pulled apart by the kinetochore microtubules and move toward opposite poles. Meiosis I vs. Meiosis II View on Boundless.com • During telophase II and cytokinesis, chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense; the two cells divide into four unique haploid cells. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/meiosis-and-sexual-reproduction-11/the-process-of-meiosis-92/meiosis-ii-40511632 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction > The Process of Meiosis Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis • For the most part, in mitosis, diploid cells are partitioned into two new diploid cells, while in meiosis, diploid cells are partitioned into four new haploid cells. • In mitosis, the daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while in meiosis, the daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes as the parent. • The daughter cells produced by mitosis are identical, whereas the daughter cells produced by meiosis are different because crossing over has occurred. • The events that occur in meiosis but not mitosis include homologous chromosomes pairing up, crossing over, and lining up along the metaphase plate Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis in tetrads. View on Boundless.com • Meiosis II and mitosis are not reduction division like meiosis I because the number of chromosomes remains the same; therefore, meiosis II is referred to as equatorial division. • When the homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles during meiosis I, the ploidy level is reduced from two to one, which is referred to as a reduction division. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/meiosis-and-sexual-reproduction-11/the-process-of-meiosis-92/comparingmeiosis-and-mitosis-406-11633 Appendix Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Key terms • chromatid either of the two strands of a chromosome that separate during meiosis • crossing over the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that results in recombinant chromosomes • diploid of a cell, having a pair of each type of chromosome, one of the pair being derived from the ovum and the other from the spermatozoon • equatorial division a process of nuclear division in which each chromosome divides equally such that the number of chromosomes remains the same from parent to daughter cells • gamete a reproductive cell, male (sperm) or female (egg), that has only half the usual number of chromosomes • haploid of a cell having a single set of unpaired chromosomes • meiosis II the second part of the meiotic process; the end result is production of four haploid cells from the two haploid cells produced in meiosis I • ploidy the number of homologous sets of chromosomes in a cell • reduction division the first of the two divisions of meiosis, a type of cell division • tetrad two pairs of sister chromatids (a dyad pair) aligned in a certain way and often on the equatorial plane during the meiosis process Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Offspring Closely Resemble Their Parents <em>In kind</em> means that the offspring of any organism closely resemble their parent or parents.The hippopotamus gives birth to hippopotamus calves (a).Joshua trees produce seeds from which Joshua tree seedlings emerge (b).Adult flamingos lay eggs that hatch into flamingo chicks (c). Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Print ." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44468/latest/Figure_07_00_02abc.jpg View on Boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Crossover between homologous chromosomes Crossover occurs between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.The result is an exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Print%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/Figure_11_01_02.jpg View on Boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Synapsis holds pairs of homologous chromosomes together Early in prophase I, homologous chromosomes come together to form a synapse.The chromosomes are bound tightly together and in perfect alignment by a protein lattice called a synaptonemal complex and by cohesin proteins at the centromere. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Print%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/Figure_11_01_01.jpg View on Boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Meiosis I ensures unique gametes Random, independent assortment during metaphase I can be demonstrated by considering a cell with a set of two chromosomes (n = 2).In this case, there are two possible arrangements at the equatorial plane in metaphase I.The total possible number of different gametes is 2n, where n equals the number of chromosomes in a set.In this example, there are four possible genetic combinations for the gametes.With n = 23 in human cells, there are over 8 million possible combinations of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Print%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/Figure_11_01_03.jpg View on Boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Meiosis I vs. Meiosis II The process of chromosome alignment differs between meiosis I and meiosis II.In prometaphase I, microtubules attach to the fused kinetochores of homologous chromosomes, and the homologous chromosomes are arranged at the midpoint of the cell in metaphase I.In anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are separated.In prometaphase II, microtubules attach to the kinetochores of sister chromatids, and the sister chromatids are arranged at the midpoint of the cells in metaphase II.In anaphase II, the sister chromatids are separated. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Print ." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/Figure_11_01_04.jpg View on Boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Complete Stages of Meiosis An animal cell with a diploid number of four (2n = 4) proceeds through the stages of meiosis to form four haploid daughter cells. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Print ." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/Figure_11_01_05.jpg View on Boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis Meiosis and mitosis are both preceded by one round of DNA replication; however, meiosis includes two nuclear divisions.The four daughter cells resulting from meiosis are haploid and genetically distinct.The daughter cells resulting from mitosis are diploid and identical to the parent cell. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Print ." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/Figure_11_01_06.jpg View on Boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Which of the following explains why meiosis is an integral part of sexual reproduction? A) Meiosis results in a reduction of chromosomes. B) Meiosis produces diploid cells from haploid cells. C) Meiosis fertilizes a sperm and an egg cell. D) Meiosis doubles the number of chromosomes in a cell. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Which of the following explains why meiosis is an integral part of sexual reproduction? A) Meiosis results in a reduction of chromosomes. B) Meiosis produces diploid cells from haploid cells. C) Meiosis fertilizes a sperm and an egg cell. D) Meiosis doubles the number of chromosomes in a cell. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction How is genetic material exchanged during meiosis? A) Following telophase, cytokinesis seperates the cell into two daughter cells. B) Microtubules attach to fused homologous chromosomes. C) Chromosomes are replicated and produce identical copies during DNA replication. D) Segments of homologous chromosomes recombine, creating recombinant chromosomes Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction How is genetic material exchanged during meiosis? A) Following telophase, cytokinesis seperates the cell into two daughter cells. B) Microtubules attach to fused homologous chromosomes. C) Chromosomes are replicated and produce identical copies during DNA replication. D) Segments of homologous chromosomes recombine, creating recombinant chromosomes Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction At what stage do homologous chromosomes separate? A) Metaphase I B) Telophase I C) Anaphase I D) Prometaphase I Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction At what stage do homologous chromosomes separate? A) Metaphase I B) Telophase I C) Anaphase I D) Prometaphase I Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Which of the following is a result of meiosis II? A) Homologous chromosomes separate and four haploid cells are created. B) Homologous chromosomes separate and four diploid cells are created. C) Sister chromatids separate and four haploid cells are created. D) Sister chromatids separate and two diploid cells are created. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Which of the following is a result of meiosis II? A) Homologous chromosomes separate and four haploid cells are created. B) Homologous chromosomes separate and four diploid cells are created. C) Sister chromatids separate and four haploid cells are created. D) Sister chromatids separate and two diploid cells are created. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Which of the following occurs in both mitosis and meiosis? A) movement of sister chromatids to opposite poles B) crossing over between sister chromatids C) formation of two diploid cells D) two nuclear cell divisions Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Which of the following occurs in both mitosis and meiosis? A) movement of sister chromatids to opposite poles B) crossing over between sister chromatids C) formation of two diploid cells D) two nuclear cell divisions Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Attribution • Connexions. "Introduction." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44468/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "diploid." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/diploid • Wiktionary. "gamete." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/gamete • Wiktionary. "haploid." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/haploid • Connexions. "The Process of Meiosis." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/ • Wikipedia. "crossing over." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/crossing%20over • Connexions. "The Process of Meiosis." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "chromatid." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/chromatid • Wiktionary. "tetrad." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/tetrad • Connexions. "The Process of Meiosis." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wikipedia. "meiosis II." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/meiosis%20II • Connexions. "The Process of Meiosis." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44469/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/equatorial-division • Wiktionary. "ploidy." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/ploidy • Wiktionary. "reduction division." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/reduction+division Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com