Meiosis Phases Worksheet: Biology, Genetics
advertisement

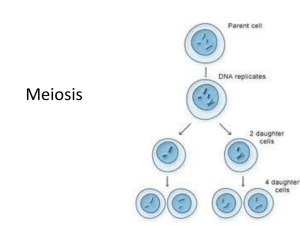
Phases of Meiosis Name of Phase Description 1. Homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrad 2. Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides 3. Nuclear membrane reforms, cytoplasm divides, 4 daughter cells formed 4. Chromosomes line up along equator, not in homologous pairs 5. Crossing-over occurs 6. Chromatids separate 7. Homologs line up alone equator 8. Cytoplasm divides, 2 daughter cells are formed Identifying Processes On the lines provided, order the different stages of meiosis I THROUGH meiosis II, including interphase in the proper sequence. 1. _____________ 2. ______________ 3. _____________ 4. _____________ 5. ______________ 6. _____________ 7. ______________ 8. _____________ 9. ______________ homologous chromosome line up in the center of the cell spindle fibers pull homologous pairs to ends of the cell 4 haploid (N) daughter cells form cells undergo a round of DNA replication sister chromatids separate from each other 2 haploid (N) daughter cells form spindle fibers attach to the homologous chromosome pairs individual chromatids move to each end of the cell crossing-over (if any) occurs Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 10. Compare the number and type of cells that result from meiosis vs mitosis. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 11. How do the genetic contents of cells resulting from mitosis and meiosis differ? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 12. Comparing and Contrasting Describe a similarity and a difference between meiosis I and meiosis II. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 13 Applying Concepts If a diploid cell containing 28 chromosomes undergoes meiosis, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 14 Compare and Contrast: How are mitosis and meiosis similar and different? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Read each statement, then on the line write down the phase of mitosis or meiosis that the action occurs. IF the action occurs in both, write both. The first one is done for you. 1. metaphase I of meiosis I____________ 2. ___________________________________________ 3. ___________________________________________ Homologous chromosome line up in the center of the cell The individual chromosomes move apart. 4. ___________________________________________ Spindle fibers pull homologous pairs to ends of the cell 4 haploid (N) daughter cells form 5. ___________________________________________ Cells undergo a round of DNA replication 6. ___________________________________________ 7. ___________________________________________ The chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell. Chromosomes become visible. 8. ___________________________________________ Sister chromatids separate from each other 9. ___________________________________________ 2 haploid (N) daughter cells form. 10. _________________________________________ Sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes. Nuclear envelope re-forms. 11. _________________________________________ 12. __________________________________________ 13. _________________________________________ 14. _________________________________________ 15. _________________________________________ 16. __________________________________________ Spindle fibers attach to the homologous chromosome pairs Individual chromatids move to each end of the cell The nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope beaks down. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber. crossing-over (if any) occurs