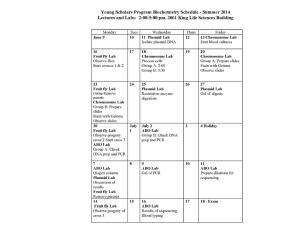
File
advertisement

NUCLEOTIDES, NUCLEIC ACID,
AND HEREDITY
Nucleotides are the building blocks (monomer)
of nucleic acids.
Nucleic acid is a polymer composed of
nucleotides
Heredity is the transfer of characteristics,
anatomical as well as biochemical, from
generation to generation.
SEJARAH PENEMUAN ASAM NUKLEAT
1879, Albrecht Kossel menemukan
asam nukleat yang tersusun
oleh suatu gugus gula, gugus
fosfat, dan gugus basa
Structure of Cell
Degradation of nucleic acid
Nucleoprotein
Nucleic acid
Protein
Nuclease
Nucleotide
Nucleotidase
Phosphate
Nucleoside
Nucleosidase
Base
Ribose
Nucleus (Inti sel)
• Setiap sel makhluk hidup mempunyai
nucleus (inti sel) dimana didalamnya
terdapat nucleoplasma
• Nucleus berperan dalam:
1. Menyimpan informasi genetik
2. Duplikasi DNA
3. Transkripsi dalam sintesis protein
Nucleic Acids (Asam nukleat)
• Dalam tubuh setiap makhluk hidup mengandung
asam nukleat.
• Merupakan makromolekul.
• Bentuknya bisa berupa DNA (deoxyribonucleic
acid) dan RNA (ribonucleic acid).
• Beberapa organisme bersel tunggal seperti virus
tubuhnya hanya terdiri dari DNA atau RNA saja.
Structure of nucleotides
Know this!
Below is the general structure of a nucleotide. The
pentose sugar, the base, and the phosphate moieties
all show variations among nucleotides.
Pyrimidine and purine
Nucleotide bases in nucleic acids are pyrimidines or purines.
Know these!
Major bases in nucleic acids
Know these!
• The bases are
abbreviated by their first
letters (A, G, C, T, U).
• The purines (A, G) occur
in both RNA and DNA
• Among the pyrimidines, C
occurs in both RNA and
DNA, but
• T occurs in DNA, and
• U occurs in RNA
GULA RIBOSA
• Gula pada asam
nukleat adalah ribosa.
• Ribosa (b-D-furanosa)
adalah gula pentosa
(jumlah karbon 5).
• Perhatikan penomoran.
• Dalam penulisan diberi
tanda prime(') untuk
membedakan
penomoran pada basa
nitrogen
5
4
1
3
2
PERHATIKAN
• Ikatan gula ribosa dengan basa nitrogen (pada atom karbon
nomor 1).
• Ikatan gula ribosa dengan gugus fosfat (pada atom karbon
nomor 5).
• Gugus hidroksil pada atom karbon nomor 2
Structure of nucleotides
Nucleotides have three characteristic components:
A phosphate group
A nitrogenous base
(pyrimidines or purine)
A pentose sugar
Structure of nucleosides
Remove the phosphate group, and you have a nucleoside.
H
Nucleotide nomenclature
Phosphodiester linkages in the covalent backbone of DNA and RNA
Some adenosine monophosphates
The major deoxyribonucleotides
The major ribonucleotides
Schematic representation of the nucleotide sequences of nucleic acids
Nucleoside, nucleotides and nucleic acids
p h o s p h a te
su g a r
p h o s p h a te
p h o s p h a te
su g a r
base
base
su g a r
base
su g a r
base
p h o sp h a te
nucleoside
nucleotides
sugar
b a se
nucleic acids
The chemical linkage between monomer units in nucleic acids
is a phosphodiester
Ribonucleosides/RibonucleotidesTerminology
(where sugar = ribose)
Base
Nucleoside
Nucleotide
Adenine (A)
Adenosine (A)
=Adenylate
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Guanine (G)
Guanosine (G)
=Guanylate
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP)
Guanosine diphosphate (GDP)
Guanosine triphosphate (GTP)
Cytosine (C)
Cytidine (C)
= Cytidylate
Cytidine monophosphate (CMP)
Cytidine diphosphate (CDP)
Cytidine triphosphate (CTP)
Uracil (U)
Uridine (U)
=Uridylate
Uridine monophosphate (UMP)
Uridine diphosphate (UDP)
Uridine triphosphate (UTP)
Thymine (T)
Thymidine (T)
=Thymidylate
Thymidine monophosphate (TMP)
Thymidine diphosphate (TDP)
Thymidine triphosphate (TTP)
DeoxyNucleosides/DeoxyNucleotidesTerminology
where sugar = deoxyribose
Base
Nucleoside
Nucleotide
Adenine (A)
Deoxyadenosine (A) Deoxyadenosine monophosphate (dAMP)
=Deoxyadenylate
Deoxyadenosine diphosphate (dADP)
Deoxyadenosine triphophate (dATP)
Guanine (G)
Deoxyguanosine (G) Deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP)
=Deoxyguanylate
Deoxyguanosine diphosphate (dGDP)
Deoxyguanosine triphophate (dGTP)
Cytosine (C)
Deoxycytidine (C)
=Deoxycytydylate
Deoxycytidine monophosphate (dCMP)
Deoxycytidine diphosphate (dCDP)
Deoxycytidine triphophate (dCTP)
Uracil (U)
Deoxyuridine (U)
=Deoxyurydylate
Deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP)
Deoxyuridine diphosphate (dUDP)
Deoxyuridine triphophate (dUTP)
Thymine (T)
Deoxythymidine (T) Deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP)
=Deoxythymidylate Deoxythymidine diphosphate (dTDP)
Deoxythymidine triphophate (dTTP)