Blood and Blood Spatter
advertisement

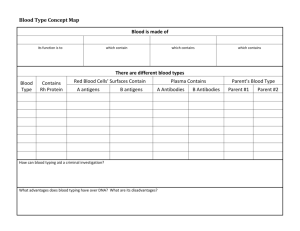
Blood and Blood Spatter Blood • 3 Types of Cells – Red Blood Cells – White Blood Cells – Platelets • All contained in plasma that contains proteins: – – – – Antibodies Hormones Clotting factors Nutrients (amino acids, minerals, etc.) Blood Cells • Red Blood Cells – Hemoglobin in the cell is iron-containing protein that transport oxygen to the tissues of the body • White Blood Cells – Fights diseases and foreign invaders • Platelets – Aid in blood clotting and are involved in repairing damaged blood vessels Antibodies • B-lymphocytes (special white blood cells) secrete antibodies – Helps white blood cells identify foreign proteins • Y-shaped proten molecule that binds to the shape of an antigen. – The binding site of the antibody is located on the tip of the Y and the antibody recognizes a foreign substance as an invader and attaches to it. DNA PROFILING • Dr. Alec Jeffreys used white blood cells as a source of DNA to produce the first DNA Profile • DNA profiling or DNA fingerprinting is widely accepted in programs such as The Innocence Project to help free inmates who have been falsely convicted of crimes. Blood Splatters • Passive Fall – Blood falls directly to floor at 90-degree angle produces circular drops • Arterial spurts – Typically found on walls or ceilings causes by the pumping action of the heart • Splashes – Shaped like exclamation points – Can help locate the position of the victim at time of attack Blood Splatters • Smears – Left by bleeding victims depositing blood as they touch something • Trails – Left my bleeding victims trying to move – Droplets can appear as round, smeared, or spurts • Pools – Form around victim who is bleeding heavily Directionality of Blood • The shape of an individual blood drop provides clues to the direction of where the blood originated. – Circular drop: blood fell straight down – Elongated: possible to determine direction the blood was traveling as it struck the surface – Blood strikes the surface • Cohesion: force between 2 similar substances • Adhesion: force between 2 unlike surfaces (ex- blood and wall) • Surface tension: elastic characteristic along the outer edge of liquid caused by attraction of like molecules