File
advertisement

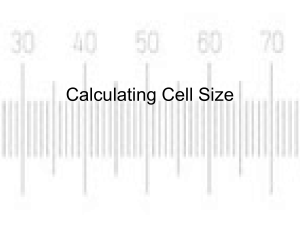
What are some characteristics that all living things have? All living things are made of cells, grow, reproduce, respond to environments, require nutrition, maintain homeostasis, perform metabolic reactions Mr. Van Roekel 11-4-14 2.1.1 Outline the cell theory: 2.1.2 Discuss Evidence for the cell theory 2.1.3 State that Unicellular organisms carry out all the functions of life. 2.1.4 Compare the relative sizes of molecules, cell membrane thickness, viruses, bacteria, organelles, and cells using appropriate units 2.1.5 Calculate linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in known magnifications 2.1.6 Explain the importance of surface area to volume ratio as a factor limiting cell size 2.1.7 State that multicellular organisms show emergent properties 2.1.8 Explain that cells in multicellular organisms differentiate to carry out specialized functions by expressing some of their genes but not others 2.1.9 State that Stem cells retain the capacity to divide and have the ability to differentiate along different pathways 2.1.10 Outline one Therapeutic uses of stem cells Theory made up of three main points All living things are made of one or more cells ◦ To date, no living entity has been found that has not been made of cells Two Types of organisms ◦ Multicellular Organisms – made up of many cells and have specialized cells to carry out specific functions ◦ Unicellular Organisms – single-celled organisms and can carry out al functions of life independently Cells are the smallest unit of life ◦ Cells carry out functions of life on their own or by various functions of organelles ◦ Parts of the cell cannot survive on their own. All Cells come from pre-existing cells ◦ All cells descend from common ancestor ◦ Cells multiply by division Mitosis & Meiosis performed by multicellular organisms to produce daughter cells Binary Fission and budding performed by bacteria cells 2.1.1 Outline the cell theory All Living Things are made of cells ◦ Robert Hooke- first observed cork cells using homemade microscope. Coined the term “cells” ◦ Antonie van Leeuwenhoek- first to observe living cells, described them as ‘animalcules’ All cells come from preexisting cells ◦ Louis Pasteur- Disproved theory of spontaneous generation. Two containers, one open to environment, one closed. Growth only occurred in container open to environment. All cells come from pre-existing cells ◦ Robert Remak- discovered/observed cell division while studying chick embryos. Cells are the smallest unit of life ◦ Many cells carry out the functions of life (nutrition, growth, reproduction, etc…) ◦ Unicellular organisms do these on own ◦ Multicellular organisms have specialized cells to carry out all functions of life Discuss at least three scientists and how they contributed to the cell theory. Discuss four exceptions to the cell theory. Robert Hooke – First to discover cells by looking at cork Antonie van Leeuwenhoek- first to observe living cells, described them as ‘animalcules’ Robert Remak- discovered/observed cell division while studying chick embryos. Louis Pasteur- Disproved theory of spontaneous generation. Fungal Hyphae- extremely large and multinucleated. Have a continuous cytoplasm (acellular) Muscle Cells – very long and multinucleated Unicellular Organisms (Amoeba) ◦ Atypical cells (not like normal cells) – larger than most single celled organisms but still carries out functions of life ◦ Can one cell be “made of many cells” Viruses ◦ Can only reproduce using a host cell, do not perform all functions of life. Is it living? Functions of life: ◦ Respiration/Metabolism – all chemical reactions in an organism ◦ Nutrition – providing a source energy to organisms ◦ Response to environment – based on internal or external stimulation and is essential to survival ◦ Growth and Development – may be limited but is evident in one way or another ◦ Homeostasis – maintaining a constant internal environment ◦ Reproduction – passing genetic material to offspring Unicellular organisms perform these functions on their own Multicellular organisms have specialized cells to carry out these functions, but as a whole, perform all functions of life Plant Cell Animal Cell Nucleus Bacteria Mitochondria 100 µm 10-100 µm 3-6 µm 1-5 µm 3 µm Virus Ribosome Membrane Thickness Molecules 100 nm 20 nm 10 nm 1 nm 2.1.4 Compare the relative sizes of molecules, cell membrane thckness, viruses, bacteria, organelles, and cells using the appropriate SI unit. Some units that I use & know Unit abbr. Metric equivalent kilometer km 1,000m 1 x 103m meter m 1m 1m centimeter cm 0.01m 1 x 10-2m 0.001m 1 x 10-3m millimeter mm micrometer nanometer write this correctly μm 0.000 001m nm 0.000 000 001m 1x 10-6m 1 x 10-9m To Convert ÷ 1,000 X 1,000 X 1,000 X 1,000 μm = micrometers We usually use this in discussion of cells. There are 1,000μm in one mm. 2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in images of known magnification 2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in images of known magnification 2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in images of known magnification 2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in images of known magnification 2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in images of known magnification 2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in images of known magnification