codominance
advertisement

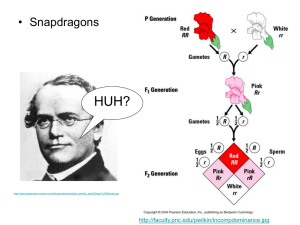
Codominance and Multiple Alleles Most genetic examples that we look at involve alleles that are dominant and recessive. Some genes do not work this way and their alleles share dominance of the characteristic. We call this Codominance. Snapdragon plants are one example of an organism with codominant genes. They can produce red flowers or white flowers in the homozygous condition. When the two homozygous plants cross pollinate the resulting offspring produce pink flowers. The characteristics of the two alleles have blended. Gametes CR CR CW CRCW CRCW CW CRCW CRCW Multiple Alleles This is where a gene has three or more alleles instead of the usual two. A good example of this is human blood groups, where there are three possible alleles: • IA • IB • IO The alleles IA and IB are codominant The allele IO is recessive to the other two. Genotype Blood group I AI A A I AI O A IBIB B IBIO B I AI B AB I OI O O If two parents have the blood types AB and O, what are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring? If parents with heterozygous type A and heterozygous type B blood have children, what are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? Questions 1. A rooster with grey feathers is mated with a hen with grey feathers. When their offspring are examined, there are 15 chicks with grey feathers, 6 with black, and 8 with white. a) What is the simplest explanation for the inheritance of these colours in chickens? b) What offspring would you predict from the mating of a grey rooster and a black hen? 2. Mrs Brown and Mrs White had babies in the hospital at the same time. Mrs Brown took home a baby girl and Mrs White a baby boy. However Mrs White was sure the doctor told her she had a girl, so she made enquiries at the hospital. Blood tests showed that: • Mr Brown was type O and Mrs Brown was type AB • Mr and Mrs White were both type B • Baby boy was type A and baby girl type O Was Mrs White right?