End of Course Exam Review
Objective: Review key terms and topics in biology
that students often find confusing.
1. Validity refers to whether or not an experiment was effectively
designed to answer the research question.
Robert wanted to find out if playing music helps plants grow taller. He
set up two groups of plants as shown below:
Cardboard box
music
player
window
Group A
Group B
Is this a valid experiment? Explain why or why not.
• No.
• Group A and B plants not getting the same amount of light.
2. Reliability refers to how to much confidence you can have that the
results of an experiment are accurate.
Alicia wanted to find out if playing music helps plants grow taller. She
set up two plants as shown below:
Light bulb
music
player
Cardboard box
Group A
Group B
What should Alicia do to make sure the results of her experiment are
reliable?
Repeat experiment or use more plants.
2. Reliability refers to how to much confidence you can have that the
results of an experiment are accurate.
Alicia wanted to find out if playing music helps plants grow taller. He
set up two plants as shown below:
Light bulb
music
player
Cardboard box
Group A
Group B
What should Alicia do to make sure the results of his experiment are
reliable?
Repeat experiment or use more plants.
3. Manipulated variable refers to the one thing that’s changed in an
experiment.
Jose wanted to find out if playing music helps plants grow taller. He set
up two groups of plants as shown below:
Light bulb
music
player
Cardboard box
Group A
What is the manipulated variable in this experiment?
• Playing of music
Group B
4. Responding variable refers to the thing that’s measured to see how
it responds to the manipulated variable.
Jose wanted to find out if playing music helps plants grow taller. He set
up two groups of plants as shown below:
Light bulb
music
player
Cardboard box
Group A
Group B
What is the responding variable in this experiment?
• Height of plants
5. Controlled variables refer to all the things that are kept the same
between experimental groups to make sure that it’s a fair test, to make
sure the experiment is valid.
What should be the controlled variables in this experiment?
Light bulb
music
player
Cardboard box
Group A
Group B
• All same kind of plants.
• Same amount of light, same amount of water, same amount of
soil.
6. What is photosynthesis and why is it important to life on Earth?
• Way plants use light to make food (sugar).
• Plants at beginning of almost all food chains.
Hydrothermal vent
7. Identify the inputs and outputs of photosynthesis using
words and/or chemical formulas
carbon dioxide + water + light
Sugar (glucose) + oxygen
Where does photosynthesis take
place in plant cells?
______________________________
In the chloroplasts
8. In photosynthesis, where do the carbon atoms in glucose
come from?
• From carbon dioxide.
• Carbon dioxide molecules are taken apart, and atoms
rearranged to form glucose and oxygen.
CO2 + H2O + energy
Carbon
dioxide
water
light
C6H12O6 + O2
Glucose
(sugar)
oxygen
9. What is cellular respiration and why is it important to plants and
animals?
• Way living things break down sugar to get energy
• All living things get energy from sugar.
Describe the roles of photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and
burning of fossil fuels in the cycling of carbon in nature.
a. photosynthesis – Plants take in carbon dioxide from air
b. respiration – Animals breathe out carbon dioxide
c. decomposition – Carbon goes into ground when organisms die
d. Burning fossil fuels– Puts carbon dioxide into air.
10. Identify the inputs and outputs of cellular respiration
using words and/or chemical formulas.
Sugar (glucose) + oxygen
Where does cellular respiration take place in
cells? _______________________
In the mitochondria
carbon dioxide + water + energy
(ATP)
Cell respiration produces energy by
adding a 3rd phosphate to ADP,
converting it to ___________
ATP
Life builds from the bottom up. Give examples of how large complex
molecules are made up of smaller, simpler ones…
• Starch molecules made up of sugars
• Protein made up of amino acids
• DNA made up of nucleotide bases (A,G,C,T)
Glucose and ATP
• Both forms of energy, both needed by cells.
• Glucose has more energy, but less usable form.
• ATP has less energy, but more usable form.
Glucose like $100 bill
--
ATP like $1 bills
Do plants do cellular respiration?
Yes!
Plants
need to
break
down
sugar for
energy
too!
Questions?
Video: Photosynthesis & Cell Respiration
http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-simple-but-fascinating-storyof-photosynthesis-and-food-amanda-ooten#watch
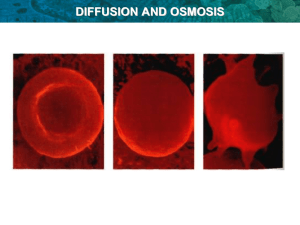
11. What’s the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
• Diffusion = movement
of molecules from
area of high
concentration to low.
Red food coloring diffuses through a glass of water
• Osmosis = diffusion of
water across a
membrane.
Water moves by osmosis from left to right
12. How does osmosis affect movement of water in and out of cells?
Water tends to move in or out of cells by osmosis in such a
way as to reach equilibrium (equal concentrations inside
and outside)
Salt water
Cells in salt water
tend to become
dehydrated as water
moves out of cells.
Pure water
Cells in pure water
tend to become
swollen as water
moves into cells.
Equilibrium = Everything in _________
balance
Equilibrium = Everything in balance
What happens if there are too many frogs….?
Equilibrium = Everything in balance
What happens if there are too many grasshoppers….?
Equilibrium = Everything in balance
Maintaining water balance
Sea water
Fresh water
Pure water
Before salt water
Low saltwater
High salt water
After salt water
Which jar contains pure water? Salt water? Corn syrup?
A
corn syrup
More water
diffused out of
egg
B
C
pure water
More water
diffused into egg
salt water
Water diffused in
and out of egg
equally.
13. What’s the difference between active and passive transport in cells?
• Passive requires no energy from cells, happens by itself. Ex:
_______________________________
diffusion, osmosis.
• Active requires energy from cells. Ex: using ATP energy to
move materials from area of low concentration to high.
What’s the difference between
osmosis and diffusion?
active and passive transport?
Diffusion or Osmosis?
osmosis
diffusion
passive transport.
1. Rolling ball downhill is like _________
2. Rolling ball uphill is like ____________transport.
Concentration gradient
Low concentration
High concentration
Cell membrane
passive transport.
1. Rolling ball downhill is like _________
2. Rolling ball uphill is like ____________transport.
Concentration gradient
High concentration
Low concentration
Cell membrane
passive transport.
1. Rolling ball downhill is like _________
active
2. Rolling ball uphill is like ____________transport.
Concentration gradient
Low concentration
High concentration
Cell membrane
passive transport.
1. Rolling ball downhill is like _________
active
2. Rolling ball uphill is like ____________transport.
Concentration gradient
Low concentration
High concentration
Cell membrane
Animations and Quiz: (diffusion, active vs. passive transport)
http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/diffusion.html
Videos
Diffusion & Osmosis
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OXCKjhE1xco
Active & Passive Transport
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kfy92hdaAH0
Questions?
Check for Understanding
Of what’s been covered so far….
– Put a ✓ by the things you understand well.
– Circle the number of items you don’t understand well.
On scratch paper:
• Your name
• Tell me what topics/words you don’t understand well.
• Any questions you have about anything.
14. Explain how DNA, chromosomes, genes, ribosomes, and proteins
are related to each other.
•
•
•
•
DNA = molecule that holds code for making proteins. “Blueprint for life.”
Chromosomes = bundles of DNA.
Gene = section of DNA that holds code for a making particular protein.
Ribosome = part of cell that helps assemble protein from gene code.
Ribosomes join amino acids together to make protein molecules….
Video: DNA
http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-twisting-tale-ofdna-judith-hauck#watch
15. How many sets of chromosomes does a typical animal cell have?
• 2 sets of
chromosomes,
one from each
parent
46
How many chromosomes does each human body cell have? _______
23
How many homologous pairs? __________
16. What kind of cells are made in mitosis? How do daughter cells
compare with the parent cells?
• Body cells.
• Daughter cells same as parent cell.
Parent cell
Mitosis = “My TOES-ees”. How
you make more toe cells, body
cells.
Daughter cells
17. What kind of cells are made in meiosis? How do daughter cells
compare with parent cells?
• Reproductive cells (sperm and egg).
• Daughter cells different from
parent cells (half as many
chromosomes)
Mei-O-sis =
Parent cell
The way we
make EGG and
sperm cells. All
offspring look
DIFFERENT.
Daughter cells
Videos: Mitosis & Meiosis
Short (2 minutes)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ba9LXKH2ztU
Long (7 minutes)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=toWK0fIyFlY
18. Why does sexual reproduction result in more genetic variation in
offspring than asexual reproduction?
• Sexual = each offspring gets different combination of
genes from 2 parents.
• Asexual = each offspring gets same genes from 1
parent. Same as cloning.
19. What is the difference between a dominant allele and a recessive one?
How many recessive alleles does an organism have to have in order to show
that trait?
• Dominant allele is stronger form of a trait, recessive weaker.
Dominant overpowers recessive.
• Need 2 recessive alleles to show the trait.
20. A homozygous blue eyed man marries a heterozygous
brown-eyed woman. What is the probability that their first
child will have blue eyes? Use a Punnett square to explain
your answer. (B = brown eyes, b = blue eyes)
b
b
B
Bb
Bb
b
bb
bb
50% probability blue eyes (bb)
50% probability brown eyes (Bb)
21. In mice, black fur (B) is dominant over brown (b) and short tails (S) are dominant over long
(s). If a mouse heterozygous both for black fur and short tail is crossed with a mouse
homozygous both for black fur and long tail, what is the probability that the first offspring will
have black fur and long tails?
BbSs x BBss
Bs
BS
Bs
BBSs
BBss
F.O.I.L.
(First-Outside-Inside-Last)
bS
BbSs
bs
Bbss
50% chance of black fur, long tail
Check for Understanding
Of what’s been covered so far….
– Put a ✓ by the things you understand well.
– Circle the number of items you don’t understand well.
On scratch paper:
• Your name
• Tell me what topics/words you don’t understand well.
• Any questions you have about anything.
Punnett Square Practice
1.
2.
http://www.biologycorner.com/bio2/genetics/notes_dihybrid.html
Punnett Square Problems worksheet (below)
What is evolution?
• How life changes over time, the way new species of living things
come from previously existing ones.
22. How does sexual reproduction contribute to evolution
by natural selection?
• Sexual reproduction = more variations (differences) in
offspring.
• More variations = more chance of some offspring being
better adapted for survival.
23. What are mutations?
• Changes in DNA. Caused by…
– Mistakes made in copying DNA for new cells, or
– Exposure to chemicals, radiation from environment.
24. How can mutations affect evolution of a species by
natural selection?
• Mutations = another way we get more variations (differences ) in
offspring.
• More variation = more chances some may be better adapted for
survival than others.
How did mutations
in finch beaks and
tortoise necks affect
evolution of these
animals in the
Galapagos islands?
25. What’s the difference between inherited and
acquired characteristics? Give an example of each.
• Inherited characteristics passed from parents to
offspring by DNA. Ex: hair color, eye color.
• Acquired characteristics are not. Ex: getting big
muscles from exercising, losing leg in accident.
26. How does evolution by natural selection explain why
giraffes have long necks?
• Long ago, giraffe ancestors had shorter necks.
• Giraffes born with longer necks better able to survive, so reproduced
and passed trait to offspring. Short neck giraffes didn’t survive and
died out.
• Misconception: Giraffes used to have short necks. They made their
necks get longer by stretching, passed trait to offspring.
Video: Evolution & Natural Selection
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Me_041nrRZk
27. Constraints = Things that limit how much you can do in an experiment. Suppose you
wanted to find out how many bald eagles in live in Washington state. Describe two constraints,
other than cost, that scientists could encounter while trying to solve this problem. In your
description be sure to:
- Identify two constraints other than cost.
- Describe how each constraint is a limitation on the solution .
• Eagles always moving around. Hard to count if they don’t
stay in one place.
• Big area to cover. Hard to find them in forests, mountains,
etc.
When eradicating invasive species threatens endangered
species recovery
San Francisco Bay bird threatened both by removal and existence of salt marsh cordgrass
Efforts to eradicate invasive species
increasingly occur side by side with programs
focused on recovery of endangered ones. But
what should resource managers do when the
eradication of an invasive species threatens an
endangered species?
The scientists combined biological and
economic data for Spartina and the Clapper
Rail to develop a modeling framework to
balance conflicting management goals,
including endangered species recovery and
invasive species removal, given budgetary
constraints.
28. Nitrogen makes up 78% of atmosphere, and living things need it to
make proteins. But atmospheric nitrogen has to be changed into a
different forms for living things to use it for making proteins. How do
plants and animals get nitrogen in a form they can use?
N2
• N in air taken in by bacteria
in soil, changed to form
plants can take in through
roots.
• Animals get nitrogen from
eating plants, other animals
Peanuts are high in protein because the
roots of the peanut plant contain bacteria
that can “fix” nitrogen for making protein.
NO2
NO3
Which
Naturescape tree
is able to “fix”
nitrogen?
Red Alder
Use the space below to draw a simplified diagram of the nitrogen
cycle. Be sure to identify and explain the following: nitrogen fixation,
decomposition, excretion, uptake by producers, reuse by consumers,
and denitrification.
N2 in Atmosphere
Reuse by consumers (eating)
Uptake by producers
Nitrogen fixation
(bacteria)
Denitrification
(bacteria)
Decomposition,
Excretion (dying and
defecating)
29. How is energy transformed and transferred in the ecosystem shown?
• Light energy transformed to chemical energy (sugar) during
photosynthesis by plants. Transform = change form
• Chemical energy transferred when animals eat plants or other
animals. Transfer = same form, moving from one thing to another.
How are renewable resources different from non-renewable ones? Give
examples of each.
• Renewable ones are unlimited in supply, non-renewable ones
are limited.
• Renewable: solar power, wind power, trees.
• Non-renewable: fossil fuels (coal, oil, gas)
What is sustainable development and why is it important? Give an
example.
Way of using natural resources so they don’t run out.
More solar power,
less fossil fuels.
When cutting forests, leave enough for
animals.
What are invasive species and how do they disturb the equilibrium
(balance) of an ecosystem?
• Animals/plants that came
from somewhere else.
• They tend to take over,
crowd out native species.
This throws food webs out
of balance.
What would happen to the food web if
all the flowers were crowded out by
blackberry bushes?
X
X
XX X X
X
X
X
30. Unintended consequences = things that happen that were not intended,
usually not good. Describe two unintended consequences that could result
from adding plants to your garden that are new to the Pacific NW, and
explain how the unintended consequences could affect other plants and
animals here.
• Might escape from your
garden . Could end up
crowding out other
plants.
• Could be poisonous to
animals. This would kill
them, disrupt food web.
What has been an unintended consequence of people using
antibacterial soaps and house cleaners?
By overusing them, we are leaving the naturally resistant
ones to survive and reproduce.
If a doctor prescribes antibiotics when you get sick, why is it
important for you to take all the pills, even if you get better halfway
through?
If you don’t take them all, you’ll leave behind
the ones that are already resistant to the
antibiotic. They’ll reproduce, meaning the
antibiotic won’t work next time.
Check for Understanding
Of what’s been covered so far….
– Put a ✓ by the things you understand well.
– Circle the number of items you don’t understand well.
On scratch paper:
• Your name
• Tell me what topics/words you don’t understand well.
• Any questions you have about anything.
That’s it!
3 Test Taking Tips:
1. Skip hard ones, come back to them later
2. READ & FOLLOW DIRECTIONS!
3. Check answers when done. Did you include everything
asked for in answers?
More EOC Review stuff on class website….
Still Unclear….?
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Punnett Squares (dihybrid cross)
Osmosis & diffusion
Active & passive transport
Cell respiration & photosynthesis
DNA, chromosomes, genes, & proteins
Meiosis & mitosis
Energy transformation and transferral
Constraints
Unintended consequences
Nitrogen cycle