An Egg-speriment PPT
advertisement

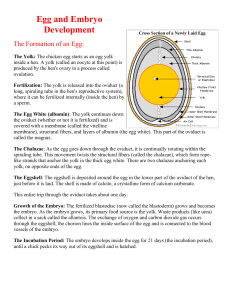
An Egg-speriment Back ground information and experimental design Why do astronauts wear space suits? • Space suits serve as an effective boundary between the external environment of space and the internal environment within the space suit. Without this boundary the astronauts would die. What is homeostasis? • The body’s ability to maintain its internal environmental conditions despite changes in the external environment. How does the human body act as a container? • The human body is a large and complicated container that is made up of many smaller containers called cells. • Different cells have different functions. How big are cells? • Most cells are so small that they require a microscope to see them. There are exceptions. A chicken egg is a single cell. It is protected by a hard shell surrounded by several soft membranes. Anatomy of a chicken cell The Yolk • Although the egg is a cell the yolk is not the nucleus. The nucleus of an egg is located inside the yolk and is barely visible. The Shell • Bumpy and grainy texture • 17,000 pores in a egg shell • Egg shell is made of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) • Semi permeable- air and moisture can pass through • Has a coating that keeps out bacteria and dust Inner and outer membranes • Located between the shell and the egg white • Provide defense against bacteria • Strong- made of keratin (protein in human hair) Air Cell • A air space that forms after the contents of the egg cools after being laid. • Usually at the large end of the egg • Grows as the egg gets older. Albumin • Egg white • Comes from the Latin Albus meaning “white” • Contains 4 alternating layers of thick and thin albumin, made up approximately 40 different proteins. Chalazae • Opaque ropes of egg white • Hold the yolk near the center of the egg • Most visible when the egg is the freshest Vitelline Membrane • The clear casing that encloses the yolk Quantitative observations • Observations that involve results that are measureable with standard scales • Examples- Mass (g), temperature (°C), volume (cm3), time (s) Qualitative • Involve descriptions and results that are measureable with non-standard scales • Examples- hot or cold, color- red or pink Controlled Experiment • An experiment in which all but one variable is controlled. Summary • Write a summary for your CN. • Example Summary: • The human body is able to maintain a constant internal environment despite changing external conditions. Cells are like individual compartments. By studying cells we can record how they react to changing external conditions. DO NOW: 9/23/14 Take down the following notes • Solution- a uniform mixture of two or more substances. • Solute- the dissolved substance in a solution • Solvent- the substance that does the dissolving. • Isotonic solution- concentration of solutes inside and outside the cell are equal • Hypertonic solution- the concentration of solutes outside the cell are greater than on the inside • Hypotonic solution- the concentration of solutes outside the cell is less than the concentration inside the cell. Experimental Design • Design a controlled experiment that tests the effect of the external environment on the internal environment of an egg. • Read the “Eggs-periment Protocol” (p.154) Procedures (Protocol) 1. Remove the shells from 3 chicken eggs by soaking the eggs in vinegar for 72 hours. 2. Carefully pat each egg dry, get the starting mass of each egg and record in a data table 3. Label each cup with the appropriate solution: – Distilled water, 50% corn syrup solution, ______? 4. In your data table write a prediction about the effect of the environment on each egg. Sample Table Table 1. EGG 1 2 3 Environment Distilled Water 50% Corn Syrup Solution ? Starting Mass (g) Prediction Final Mass (g)