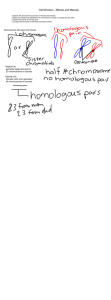Take out a piece of paper and write for two
minutes what makes you unique
Activity
Human
Cat
Shrimp
Bean
Chromosome number (haploid or diploid?
46
?
?
?
Number of pairs of homologous
chromosomes
23
?
127
?
23
19
?
?
Chromosome number (haploid or diploid?)
23
?
?
11
Number of pairs of homologous
chromosomes
0
?
?
?
Before Meiosis
After Meiosis I
Chromosome number (haploid or diploid?)
After Meiosis II
Development of Male and
Female Gametes
Gametogenesis –
formation of female
or male sex cells
Female cytoplasm
does not divide
equally after each
nuclear division – the
OOTID receives
most of cytoplasm
Sperm cells have
equal division of
cytoplasm
Sperm are streamlined for movement, Egg cells use
nutrients and organelles within cytoplasm to fuel
future divisions
Spermatocytes (Diploid) – give rise to sperm cells –
are capable of mitosis before meiosis ever begins
Males can produce 1 billion sperm a day!
Females are born with ~ 2 million primary oocytes.
Oocytes have already entered meiosis I but remain
suspended until prophase I until puberty.
Meiosis is resumed in one oocyte once a month
Cell Division and Life
Cycles
Asexual reproduction = offspring through mitosis
Bacteria and Yeast – daughter cells with the same
chromosome number as parent cell
Sexual reproduction = chromosome number changes
through meiosis (gametes – half the chromosome
number as the somatic cells) and fertilization (zygote
– two gametes joining where chromosome number is
restored to that of somatic cells)
Pollen contains male sex cells, female egg stored in flower. Gametes contain a haploid
chromosome. Diploid zygote is formed after fertilization. Undergoes mitosis to
produce seeds. Further mitosis produces mature plant called sporophyte. Specialized
cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores. Spores undergo mitosis to produce
mature multicellular gametophyte (also a haploid). Specialized cells develop into
gametes. Cycle begins again.
The gametes are haploid and single celled. Gametes fuse and form a diploid zygote.
Zygote undergoes mitosis to form multicellular diploid adult body. Specialized cells
undergo meiosis to produce gametes. Animals do not undergo mitosis to form
multicellular gametophyte. Haploid gametes unite, fertilize and cycle begins again.
Abnormal Meiosis
Nondisjunction – two homologous chromosomes fail to
separate during meiosis or mitosis. One daughter cell has too
many chromosomes and the other too few. Any cell can be
affected, but most dramatic is in sex cells during meiosis.
Polyploidy – more than two complete chromosome sets. Three
chromosome sets – tripoloidy; four chromosome sets –
tetraploidy.
Diploid egg cell fertilized by a haploid sperm = 3n cell
In humans, nondisjunction produces gametes with 22-24
chromosomes.
If gamete of 24 chromosomes, and joins with normal gamete
will have zygote with 47 chromosomes. Zygote will have three
chromosomes in place of normal pair Trisomy
If gamete of 22 chromosomes joins with normal gamete will
have zygote with 45 chromosomes. Will have only one of the
chromosomes rather than homologous pair. Monosomy
Nondisjunction Disorders
Trisomic Conditions – Down Syndrome (trisomy 21)
Monosomic Conditions – Turner Syndrome Female
with single x chromosome. both homologous pairs
moved to the same pole during meiosis I. Egg with
no X chromosome is fertilized with sperm – 45
chromosome zygote.
Nondisjunction in sperm or egg – child inherits 2 X
chromosomes and single Y. Male at birth but at
puberty begins producing high levels of female sex
hormones.
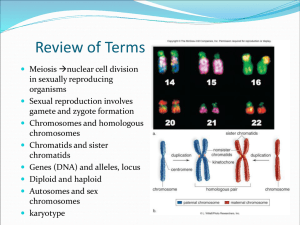
Karyotype Charts
Detecting results of abnormal meiosis.
Mix small sample of tissue with solution that
stimulates mitotic division. Another solution is
added to stop division at metaphase.