Cells: Plants and Animals
advertisement
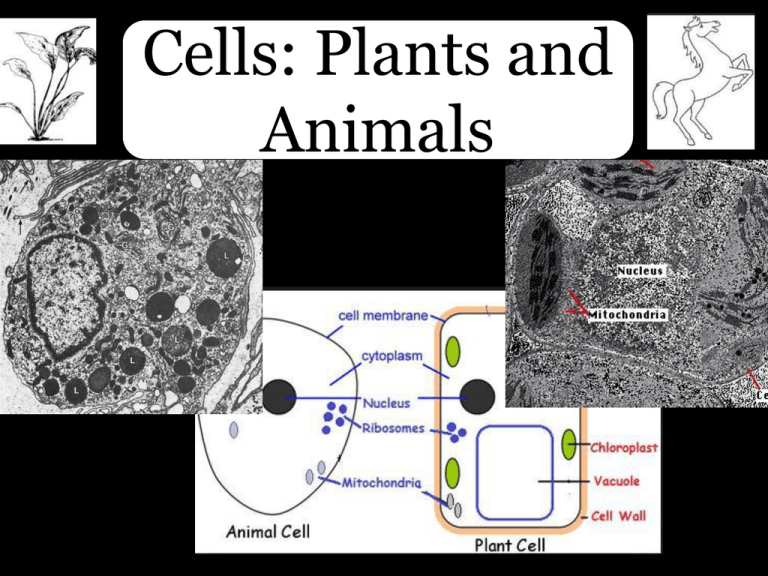
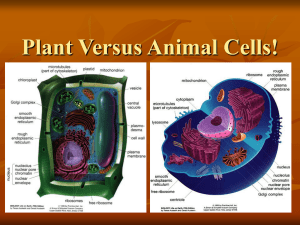
Cells: Plants and Animals Cells: Plants and Animals 1. Overview of Cells 2. Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells 3. Cells Organization within the Body 4. Tissue Overview How Cells Were Named • Cells in cork • walled boxes that are similar to tiny rooms, or cellula, occupied by monks = "cell.“ Cells in a plant Cells in an animal Cell Size Cells Contain Organelles Comparing Animal and Plant Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell • Variety of Shapes • One or more small vacuoles • Centrioles • Lysosomes • Often have cilia or flagella • Cell Membrane • Cytoplasm • ER (smooth and rough) • Ribosomes • Mitochondria • Golgi apparatus • Nucleus • Cell Wall • Rectangular • One large, central vacuole • Plastids • Chloroplasts • Rarely have cilia or flagella Comparing Animal and Plant Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell • Variety of Shapes • One or more small vacuoles • Centrioles • Lysosomes • Often have cilia or flagella Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum • Golgi Apparatus • • • • • • Cell Wall • Rectangular • One large, central vacuole • Plastids • Chloroplasts • Rarely have cilia or flagella Animal Cell Plant Cell Animal Cell • Double layer of phospholipids • controls the flow of water Animal Cells Cell Membrane Electron Microscope Image of Rickettsia felis Plant Cell Cell Membrane Electron Microscope Image of a Pollen Tube of an Orange Bush Monkey Flower Animal Cell Plant Cell • Surrounded by double membrane • Holds DNA • Involved in cell division Animal Cell Nucleus Electron Microscope Image of a White Blood Cell Animal Cell Plant Cell • Make energy for the cell • Can be different shapes • Surrounded by a double membrane Plant Cell Mitochondrion Electron Microscope Image of a Plant Cell Animal Cell Plant Cell • Different functions depending on cell type • Produces chemicals for the cell • Controls the release of ions • Collects proteins Animal Cell Endoplasmic Reticulum Electron Microscope Image of a Cartilage Cell Animal Cell Plant Cell • Surrounded with a single membrane • Packages substances to be transported Animal Cell Golgi Electron Microscope Image of a Bone Marrow Cell Comparing Animal and Plant Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell • Variety of Shapes • One or more small vacuoles • Centrioles • Lysosomes • Often have cilia or flagella Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum • Golgi Apparatus • • • • • • Cell Wall • Rectangular • One large, central vacuole • Plastids • Chloroplasts • Rarely have cilia or flagella Comparing Animal and Plant Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell • Variety of Shapes • One or more small vacuoles • Centrioles • Lysosomes • Often have cilia or flagella Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum • Golgi Apparatus • • • • • • Cell Wall • Rectangular • One large, central vacuole • Plastids • Chloroplasts • Rarely have cilia or flagella Animal Cell • Membrane bound sac • Intracellular digestion • Release of cellular waste • Generally small in animal cells Animal Cell Vacuoles Electron Microscope Image of a Pancreatic Cell Animal Cell • Part of cytoskeleton of the cell • Ring of nine groups of fused microtubules • Groups of three microtubles • Plants do not have centrioles Animal Cell Centriole Electron Microscope Image of a White Blood Cell Animal Cell • Contain enzymes necessary for intracellular digestion • In white blood cells, these lysozymes digest bacteria • Cause cell death if improperly released into cytoplasm Animal Cell Lysosome Electron Microscope Image of a Nerve Animal Cell Lysosome Electron Microscope Image of a Nerve Animal Cell Lysosome Electron Microscope Image of a Nerve • Rigid, protective cell wall • Made of polysaccharides • Provides and maintains shape of the cell • Protective barrier • Animal Cells do not have a cell wall Plant Cell Plant Cell Electron Microscope Image of a Sunflower Leaf Plant Cell • Membrane bound sac • Store nutrients and waste products • Increase cell size during growth • Generally large in plant cells Plant Cell Central Vacuole Electron Microscope Image of a Guard Cell of a New Dawn Climbing Rose Plant Cell • Contain chlorophyll, which allows the plant to make energy from sunlight • Surrounded by a double outer membrane Plant Cell Chloroplast Electron Microscope Image of a Sugar Beet Comparing Animal and Plant Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell • Variety of Shapes • One or more small vacuoles • Centrioles • Lysosomes • Often have cilia or flagella Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum • Golgi Apparatus • • • • • • Cell Wall • Rectangular • One large, central vacuole • Rarely have lysosomes • Plastids • Chloroplasts • Rarely have cilia or flagella More About Animal Cells PITUITARY CELL SERTOLI CELL LEYDIG CELL EGG NERVE CELL Cells in Perspective Cells in Perspective CELL – Smallest unit, Simplest animals consist of a single cell. CELL TISSUE ORGAN TISSUE – Groups of cells with same general function and texture (texture = tissue) e.g., muscle, nerve, epithelium, and connective tis. ORGAN – Two or more types of tissues; larger functional unit e.g., skin, kidney, intestine, blood vessels ORGAN SYSTEM - Several organs SYSTEM e.g., respiratory, digestive, reproductive systems FOUR BASIC TYPES OF TISSUES IN THE BODY -------------------------------------- Epithelium Connective tissue Muscular tissue Nervous tissue Epithelium Functions: • Cover organs, line organs, blood vessels, and secretory cells of glands Connective Tissue Function: • binds the other tissues together to form organs • include blood, cartilage, and bone CONNECTIVE TISSUE CONNECTIVE TISSUE Function: Muscle • generation of contractile force Distribution: • Smooth – involuntary movements of organs, respiratory tract, blood vessels, uterus, etc. • Cardiac – involuntary contractions of the heart • Skeletal – voluntary movements, mostly associated with the skeleton Nervous Tissue Functions: • transmission, reception, and integration of electrical impulses Characteristics: • neurons – very large excitable cells with long processes called axons and dendrites • Glial cells – the supporting cells of nervous tissue • Nerves – collections of neuronal processes bound together by connective tissue FOUR BASIC TYPES OF TISSUES IN THE BODY -------------------------------------- Epithelium Connective tissue Muscular tissue Nervous tissue Where are these basic tissues located? EPITHELIUM CONNECTIVE TISSUE MUSCULAR TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE Epithelium Where are these basic tissues located? EPITHELIUM CONNECTIVE TISSUE MUSCULAR TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE Epithelium Where are these basic tissues located? EPITHELIUM CONNECTIVE TISSUE MUSCULAR TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE Connective tissue Where are these basic tissues located? EPITHELIUM CONNECTIVE TISSUE MUSCULAR TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE Connective tissue Where are these basic tissues located? EPITHELIUM CONNECTIVE TISSUE MUSCULAR TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE Muscular tissue Where are these basic tissues located? EPITHELIUM CONNECTIVE TISSUE MUSCULAR TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE Muscular tissue Where are these basic tissues located? EPITHELIUM CONNECTIVE TISSUE MUSCULAR TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE Where are these basic tissues located? EPITHELIUM CONNECTIVE TISSUE MUSCULAR TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE • http://viewer.serenusview.com/Viewer.aspx?SlideId=d68a4e8e8932-492c-911c-0a2a968463aa Plant Cells http://viewer.serenusview.com/Viewer.aspx?SlideId=2c7d93ed-dae240bb-90fc-74253b381d4e Normal Blood Cells • http://staging.digitalscope.org/Viewer.aspx?SlideId=b0af451a-ce41463b-ac84-68cb4e2d142e Abnormal Blood Cells Shapes of Epithelial Cells • http://viewer.serenusview.com/LinkHandler.axd?LinkId=469f376 8-acb7-4ef3-aa82-2bdd18f77dc6 Intestinal Cells • http://viewer.serenusview.com/LinkHandler.axd?LinkId=5a615 a12-3e73-4b15-a6fa-910ac47caf9f Eye Cells Cells: Plants and Animals 1. Overview of Cells 2. Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells 3. Cells Organization within the Body 4. Tissue Overview