EOC PRACTICE QUESTIONS #2
Bio 3.1 - Explain how traits are
determined by the structure and function
of DNA.
DNA and RNA are both made up of
_______________which contain a
__________,___________, and a
__________________.
•
•
•
•
Nucleotides
5-Carbon Sugar
phosphate group
nitrogen base
The sugar in DNA is _________ and
in RNA is ____________.
• Deoxyribose
• Ribose
The bases in DNA are:
•
•
•
•
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
The bases in RNA:
•
•
•
•
Adenine
Uracil
Guanine
Cytosine
DNA shape is a ___________(twisted
ladder)
• double helix
RNA shape is:
• single stranded
RNA has 3 forms:
- Carries the DNA code from the nucleus to
the ribosome ______.
- Carries the amino acid from the cytoplasm
to the ribosome ______.
- Place where the amino acids are put
together to make a protein. ________.
• messenger-RNA (M-RNA)
• transfer-RNA (T-RNA)
• ribosomal-RNA (R-RNA)
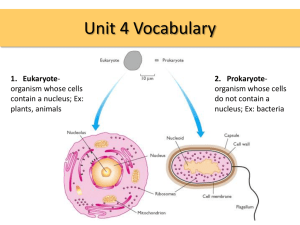
Chromosomes in the nucleus of
eukaryotic cells contain ___________and
_____________.
• nucleic acids
• protein
DNA is the genetic information in the
nucleus that codes for the production of
______________.
• proteins
DNA Replication (Copy, Synthesize,
Duplicate, Complimentary Base Pairs)
occurs in the ___________,
• nucleus
The weak bond that holds together the
complimentary base pairs in DNA are
____________________.
• hydrogen bonds
Replicated DNA contains one old strand
that serves as a template and one new
strand making it _______________.
• semiconservative
Replication must occur prior to any type
of cell division so that each daughter cell
has a __________ to run the cell.
• copy of DNA
The stage of the cell cycle that DNA is
replicated in is the _______ of _______.
• S-phase
• Interphase
The process that converts the DNA code
into messenger RNA so that it can leave
the _____is called ________.
• nucleus
• transcription
The process the converts messenger
RNA into a protein is called _________
and occurs at the _____________.
• Translation
• ribosome
Name the process, then tell where
the process takes place.
Replication
Nucleus
Transcription
Nucleus
Translation
Ribosome
A series of three nitrogen bases on
messenger RNA is called a ______.
• codon
A series of three nitrogen bases on
transfer RNA is called an _______.
• anticodon
Replicate TCC-AGT-TAG
• AGG-TCA-ATC
Transcribe TCC-AGT-TAG into
mRNA.
• AGG-UCA-AUC
Translate the mRNA into a protein - AGG-
UCA-AUC
Arginine-Serine-Isoleucine
If the anticodon on T-RNA reads UGC,
what amino acid does it code for?
• ACG
• Threonine
A random change in a DNA sequence is
called a ______________.
• mutation
Radiation, radon, asbestos, chemicals are
all ______________.
• mutagens
There are two types of mutations:
_______ and ___________.
• Point
• Frame shift
True or False - Most mutations are
harmful.
• False
Identify the following types of frame shift
mutations by labeling them as inversion,
deletion, duplication or translocation.
•
Original DNA Sequence – ABCDEF
•
ADEF
•
ABCXYZ
•
AEDCBF
•
Deletion
Translocation
Inversion
Duplication
ABBCDEF
Bio.1.2.2 - Analyze how cells grow and
reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis and
cytokinesis.
Bio.3.2.1 - Explain the role of meiosis in sexual
reproduction and genetic variation.
Cells must divide due to __________ratio
and lack of ____to tell the cell what to do.
• surface area to volume
• DNA
Cells have to divide to allow an organism
to: _____, _____ injuries, and ______.
• Grow
• Repair
• Reproduce
Part of the cell cycle where the cell
spends the majority of its life cycle
growing and synthesizing DNA is
_________.
• Interphase
The stages in mitosis are : ________
•
•
•
•
•
PMAT
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Label the diagrams below.
•
•
•
•
A. Telophase
B. Metaphase
C. Prophase
D. Anaphase
This is when the nucleus divides: ____
• Mitosis
The division of the cytoplasm is
called _____________.
• cytokinesis
In plant cells a ___________forms during
cytokinesis for the cell wall to develop. In
animal cells a ___________forms.
• cell plate
• cleavage furrow
Type of division that makes haploid
cells ____________.
• Meiosis
Type of division the makes diploid
cells ___________.
• Mitosis
Type of division that occurs in somatic
or body cells ___________.
• Mitosis
Type of division that occurs to form
gametes _________.
• Meiosis
Type of division that makes 4 daughter
cells ____________.
• Meiosis
Type of division that makes 2 daughter
cells __________.
• Mitosis
Type of division that has two
divisions ___________.
• Meiosis
Type of division that is one division
____________.
• Mitosis
Type of division that is asexual
______.
• Mitosis
Type of division that is sexual
______.
• Meiosis
Type of cell division that is does not
allow for variation _______.
• Mitosis
Type of cell division that allows for
variation _________.
• Meiosis
___________and _____________allow
for genetic variation.
• Crossing over
• fertilization
Name the processes below.
Mitosis
Meiosis
____________and __________ cause
changes in DNA
• Gene Shuffling (crossing over and
fertilization)
• mutations
Human gametes contain
__________chromosomes.
• 23 (22X or 22Y)
Human somatic cells contain_________
chromosomes.
• 46 (44XX or 44XY)
Type of cell in the human that undergoes
the most rapid mitosis is _________.
• skin
The __________ holds sister chromatids
together when DNA replicates during the
S-phase of interphase.
• centromere
Label the following types of asexual
reproduction.
Vegetative Propagation
Regeneration
•Sporulation
Binary
Fission
Chromosomes that are the same length,
centromere is in the same location, and
the same traits are called
_______________.
• homologous pairs
These pairs line up during synapsis of
prophase 1 of meiosis and gene shuffling
occurs in the process called
______________.
• crossing over
If a corn anther contains 20 chromosomes
in the cells, how many chromosomes will
the pollen cell have?
• 10
_________is the process in which the
gametes unite forming a ________.
• Fertilization
• zygote
Label the stages of human
development below
Fertilization
Blastula (stem)
Zygote
Cleavage due to Mitosis
Gastrula (differentiation)
This is a diagram of __________.
crossing over during
meiosis
Gametogenesis in a male is called
______. It occurs in the _________.
______sperm are produced.
• Spermatogenesis
• Testes
• 4
Gametogenesis in a female is called
_________. It occurs in the ________.
____________are produced.
• Oogenesis
• Ovaries
• 1 egg and 3 polar bodies
Bio.3.2.2 Predict offspring ratios based
on a variety of inheritance patterns
(including dominance, co-dominance,
incomplete dominance, multiple alleles,
and sex-linked traits).
The transmission of genes from parent to
offspring is called _________.
• heredity
A unit of hereditary information is
called a __________.
• gene
Different forms of a gene are called
___________.
• alleles
Two of the same alleles is called
_______________.
• homozygous or pure
Two different alleles is called _____.
• heterozygous or hybrid
The bossy allele that always shows itself
and masks the other alleles is
__________.
• Dominance
The quiet allele that only shows itself
when paired with itself is the _______.
• Recessive
An organisms genetic make-up (actual
genes) is its ______________.
• genotype
An organisms physical characteristics are
its _______________.
• phenotype
Results in a phenotype where the two
dominant alleles show up equally
____________.
• codominance
Results in a blended phenotype
_____.
• incomplete dominance
Cross used to determine the genotype for
a known phenotype ________.
•
test cross
Type of organism always used in a test
cross because it has a known genotype
and phenotype.
• homozygous recessive
How can two organisms have the
same phenotype yet different
genotypes?
• One is homozygous dominant and one is
heterozygous
Mendel’s principle that the alleles
separate during meiosis _______.
• Principle of Segregation
Mendel’s principle that the bossy
gene always wins
• Principle of Dominance
Mendel’s principle that the alleles
separate independently of each other
• Principle of Independent Assortment
Cross involving one trait
• monohybrid
Cross involving two traits
• dihybrid
The likelihood an event will occur is
called ______________.
• probability
Probability (is / is not) based on prior
events.
• is not
The Probability that a woman will have
three boys in a row is ________.
• ½ x ½ x ½ = 1/8
Tall is dominant over short in pea plants.
Cross two hybrid plants. What is the
genotypic ratio? What is the phenotypic
ratio?
• 1:2:1
• 3:1
Short tails (S) are dominant to long tails
(s). Brown hair (B) is dominant to White
hair (b). What is the unknown parent’s
genotype for the cross below?
• SsBb
For the cross below, how many of the
offspring will be Short tailed and Brown?
9/16
For cross below, how many of the
offspring will be Short tailed and white?
3/16
For cross below, how many of the
offspring will be Long tailed and Brown?
3/16
For cross below, how many of the
offspring will be Long tailed and White?
1/16
That makes the phenotypic ratio for
this cross ______________.
9:3:3:1
In camellias there are red flowers, white
flowers and red and white flowers. Is
this an example of incomplete or
codominance?
• Codominance
Cross a heterozygous red and white
flower with a white flower and give the
genotypic and phenotypic outcomes
• genotype 50% RR’ and 50% R’R’
• phenotype 50%Red and White and 50% White
In snapdragons there are red flowers,
white flowers and pink flowers. Is this
an example of incomplete or
codominance?
• Incomplete Dominance
Cross two heterozygous flowers and give
the genotypic and phenotypic outcomes
• Genotypic ratio 1:2:1
• phenotypic ratio 1:2:1
A dog with black fur (B) produces a litter of
puppies in which 50% of the puppies are
black and 50% are white (b). What is the
genotype of the parent ?
Bb
List the genotypes and phenotypes of blood
types
• Phenotypes
•Genotypes
•
•
•
•
•IAIA, IAi
•IBIB, IBi
•IAIB
•ii
A
B
AB
O
Is it possible for a mom with blood type A
and a dad with blood type B to have a
child with O blood? ____How?
Yes
IAi x IBi
Cross a type A mother whose mother had
O blood with a father that has AB blood.
Give the possible phenotypic outcomes.
• 50%A
• 25%B
• 25%AB
A trait that shows up only on the sex
chromosomes is considered to be
• sex-linked
Two sex-linked diseases are
• Colorblindness
• Hemophilia
The sex chromosomes of a female
are _____and a male are _____.
• XX
• XY
______inherit sex-linked traits most
often. They get them from their _____.
• Sons
• Moms
Cross a colorblind female with a
normal male. What is the
probability the offspring will be
colorblind?
• 50% of the offspring, 100% of the boys
Is it possible for a carrier female to have a
daughter that is color blind? _____ If so
how?
• Yes
• The father must be colorblind
A family tree is called a ________.
• pedigree
The symbol for a male is a _____ and
for a female is a _______.
• Square
• circle
If they have the disease the symbol
is _________.
• colored in
What are the genotypes for each of
the people on these pedigrees?
Which would represent colorblindness
or hemophilia?
Sex-linked recessive
Which would represent sickle cell or
cystic fibrosis?
Autosomal Recessive
Which would represent Huntington’s
disease or Achondroplasia?
Autosomal Dominant
The diagram below is called a _____. It is
a picture of ________. The person in the
diagram below is a Male/Female.
• Karyotype
• homologous pairs
• Female
The person has the genetic disorder
_________ , also called _________. This is
caused by the failure of chromosomes to
separate correctly which is called _____.
Down’s Syndrome
Trisomy 21
nondisjunction
Genetic disorder characterized by
abnormal shape of red blood cell that
make them unable to carry oxygen is
______. People who are heterozygous are
immune to the mosquito carrying disease
called ______________.
• sickle cell anemia
• malaria
Genetic disorder that leads to the buildup
of a thick mucus in the lungs is _____.
• cystic fibrosis
Skin color, eye color, height are
determined by many genes and are
called _________ traits. The phenotype
that shows up more frequently are
blended.
• polygenic
Which diagram represents fertilization
that will develop into a normal female
zygote?
• 1
____________determined all sequence of
all the alleles in humans.
• Human Genome Project
_________is the process of making
changes in the DNA code of organisms.
• Genetic Engineering
A circular piece of DNA found in
bacteria is called a _________.
• plasmid
The combination of genetic material from
2 or more organisms is called ________.
• recombinant DNA - rDNA
__________cut the DNA at the same
sequence on different strands of DNA.
• Restriction enzymes
_________puts the two new pieces
back together.
• DNA ligase
This technology is used to make
______and ________.
•
•
•
•
•
Insulin human
growth hormone
Bt corn
Clotting factor
Drought and insect resistant crops
Bacteria are used in genetic engineering
because they reproduce ________ (no
variation) and _______. The DNA is then
transcribed and translated producing the
__________.
• Asexually
• Rapidly
• protein
Organisms that have genes from another
organism are called ______. BT corn is
an example.
• transgenic organism
The below is a picture of ________.
recombinant DNA (r-DNA)
The diagram below is called
_______.
Gel Electrophoresis or DNA Fingerprinting
Who are the soldiers parents?
C&D
Fruits and vegetable with longer
shelf lives and cows producing
more milk are examples of
• Selective breeding or artificial selection
• Genetic Engineering
The _________ makes many copies of a
DNA sequence in a short amount of time
• polymerase chain reaction
_____________inserts normal gene
sequences through inhalers into
people with diseases like cystic
fibrosis so that correct protein
sequences may be produced.
• Gene therapy