Excretory System
advertisement

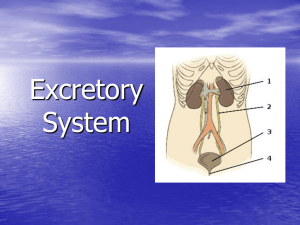
Excretory System DENNIS ANYAMELE Functions & Purpose The purpose of the excretory system is to get rid of waste in the body and help maintain homeostasis in an organism. Role in Homeostasis The excretory system helps the body maintain homeostasis, a stable internal environment. It does this by removing waste to keep the body function properly. Interaction with Other Systems The excretory system works the most with the circulatory and endocrine system. The circulatory circulates blood through the system to get rid of unneeded substances. The endocrine system monitors kidney function so that the cell will have the best internal temperature. Evolution of Excretory System The excretory system has evolved from a series of tubules in every segment of the body into the complex system that it is now. Organs Primary Peripheral Liver Bladder Skin Urethra Lungs Ureters Kidneys Liver The liver gets rid of overused red blood cells and left over amino acids from the blood and breaks down the waste Skin Sweat glands throughout the skin get rid of urea, salts, and water from the blood through sweat. Lungs Water vapor and carbon dioxide, products of cellular respiration, are excreted from the body through the lungs. Kidneys Filters throughout the kidneys, called nephrons, filter urine from the blood to be excreted. Ureters, Bladder, & Urethra The ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra work together to get rid of waste by urine. Conclusion The excretory system keeps the body running by getting rid of waste that would not make the body function properly. Citation Page Qld science teachers. (2011, November 22). Retrieved from http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/junior-science/biology/excretory-system Activity 8-2. Human Excretory System. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.columbia.edu/~mvh7/STEP/Regents Bio/The endocrine system/human excretory system.pdf Cliff Notes. (2012). Cliff Notes. Retrieved from http://www.cliffsnotes.com/study_guide/Human-Excretory-System.topicArticleId8741,articleId-8714.html Lubey. (n.d.). roderunner.com. Retrieved from http://home.roadrunner.com/~lubehawk/BioHELP!/hexcrsys.htm Farabee, M. J. (2010, May 18). Excretory System. Retrieved from http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookEXCRET.html Radar studios, A. (2011). Animal Systems. Retrieved from http://www.biology4kids.com/files/systems_excretory.html