Mutagenesis Roundtable Discussion
advertisement
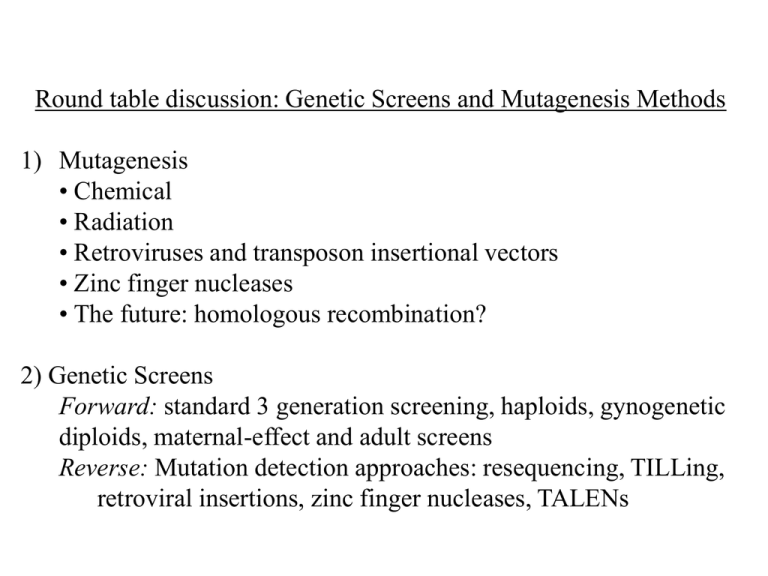
Round table discussion: Genetic Screens and Mutagenesis Methods 1) Mutagenesis • Chemical • Radiation • Retroviruses and transposon insertional vectors • Zinc finger nucleases • The future: homologous recombination? 2) Genetic Screens Forward: standard 3 generation screening, haploids, gynogenetic diploids, maternal-effect and adult screens Reverse: Mutation detection approaches: resequencing, TILLing, retroviral insertions, zinc finger nucleases, TALENs Mutagens g-rays • Deletions (usually large) & translocations (often not mendelian) • Mutation rate: 1/200 F1 individuals • Utility: null phenotype, removing adjacent duplicate genes, non-complementation screen. ENU (ethylnitrosourea) • spermatogonial treatment yields point mutations ---Mutation rate: 1/1,000 F1 individuals ---Utility: nulls and hypomorphs, unbiased wrt genes mutated • sperm treatment yields points and deletions Mutation rate: 1/200 Insertional mutagenesis • retroviral (MLV-VSV) insertion into or close to gene (N. Hopkins) • Mutation rate: 1/10,000 F1 individuals (some hotspot genes?) • Transposable element insertions (Tol 2)—gene traps • Rapid cloning! Relative Attributes of Genetic Systems Yeast Forward ++ Drosophila ++ C. elegans ++ zebrafish ++ +/(difficult, expensive) (phenotype-based) ++ Reverse (gene-based) mouse homologous recombination * Not really genetics + P-elements RNAi* homologous recomb. + RNAi* Mutation Detection + Morpholinos* Mutation Detection ZFN, TALENs ++ homologous recombination Pros Standard 3 generation screen Haploids Gynogenetic diploids All stages and genomic regions accessible Mendelian ratios Natural breeding is the only “technique” Requires only 1 generation All genomic regions accessible Mendelian ratios Requires only 1 generation Diploids screened: all stages accessible Cons Requires two generations Labor-intensive More tanks required Useful only at early stages Background effects may obscure some phenotypes Biased against telomeric regions Non-Mendelian ratios EP procedure reduces throughput Background of EP effects Zebrafish Zygotic Mutant Screen--Natural Crosses G0 F1 */+ F2 +/+ 50% */+ 50% +/+ F3 Screen F3 embryos morphologically at 1 dpf, 2 dpf, 5 dpf. 2/3 of all mutants comprise 3 general phenotypic classes Widespread cell death Heart edema/poor circulation Widespread cell death starting in CNS Wild type General retardation in development Wild type What types of genes might be mutated? General “housekeeping” genes. What are they? Zebrafish Zygotic Mutant Screen--Natural Crosses G0 F1 */+ F2 +/+ 50% */+ 50% +/+ F3 Screen F3 embryos morphologically at 1 dpf, 2 dpf, 5 dpf. Zebrafish Spermatogenesis Spermatogonial stem cell ENU induces mutations at all stages of spermatogenesis. Clones of mutations can occur, so keep track of F1s from each Founder male. Leal et al., 2009; Schulz et al., 2009 F1 F2 Early pressure (diploid) F1 F2 Gynogenetic diploid Block 2nd polar body formation with ‘Early Pressure’ (EP) Reverse Genetic Approaches in Zebrafish 1) ANTISENSE (MORPHOLINOS) 2) MUTATION DETECTION • TILLING: i) whole genome (Illumina): “Zebrafish Mutation Project” (Stemple): http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Projects/D_rerio/zmp/ ii) Gene-by-gene: “Zebrafish TILLING Consortium” (Moens, Solnica-Krezel): https://webapps.fhcrc.org/science/tilling/ • Retroviral mutagenesis (Burgess, Lin) Wang et al. (2007) Efficient genome-wide mutagenesis of zebrafish genes by retroviral insertions. PNAS 104: 12428 (e.g. sfrp1a) 3) TARGETED MUTAGENESIS • Zinc-finger nucleases Sander et al. (2011) selection-free Zn-finger nuclease engineering by context-dependent assembly (CoDA) • TALENs Zebrafish Zygotic Mutant Screen--Natural Crosses G0 F1 */+ F2 +/+ 50% */+ 50% +/+ F3 Screen F3 embryos morphologically at 1 dpf, 2 dpf, 5 dpf. Zebrafish TILLING pipeline (Targeted Induced Local Lesions in Genomes) Mutation detection (Cel1 or Illumina) library fertility over time 60% percent fertility 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 2001 (n=11) 2002 (n=5) 2003 (n=8) 2004 (n=4) 2005 (n=13) 2006 (n=20) 2007 (n=24) 2008 (n=22) 2009 (n=19) 2010 (n8) year N=135