*** 1 - Institute of Statistical Science, Academia Sinica

Some stories about evolution
Wen-Ping Hsieh wphsieh@stat.nthu.edu.tw
Institute of Statistics
National Tsing Hua University
Sep. 6, 2012
1
Outline
• Introduction to genetics
• Genetic polymorphisms
• Y-chromosome Adam and Mitochondria Eve
• Human genome diversity
2
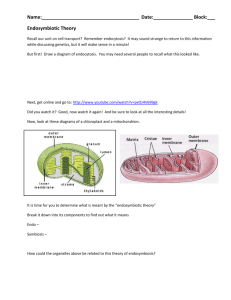
A Quick Introduction to Genetics
• DNA->RNA->Protein
• Recombination
• Mutation
• Polymorphism
3
Source: Wikipedia
4
http://www.accessexcellence.org/RC/VL/GG/central.php
5
Recombination Rate
• There are only a few crossover events occurred to each human chromosome in each meiosis.
• Recombination rate is higher between two close loci.
• Recombination rate is not consistent across chromosomes.
6
DNA Polymorphisms
• Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
• Microsatellites or Short Tandem Repeats (STR)
• Insertion and deletion
7
Fossil Evidence of Human Evolution
8
Study of Blood Groups
• Blood type ABO
• Different allele frequency across populations
Region
Europe
British
Italian
Basques
East Asian
African
Indigenous
American
Indigenous
Australian
23
20
18
1.7
A
27
25
20
22
2
19
13
0.3
8
7
B
8
2
75
61
69
98
O
65
67
73
76
9
Classification of Populations
• With polymorphisms of ABO, RH and MN blood types, scientists can easily distinguish populations of the five continents. (The study of William Boyd)
• When we count in more features, almost all populations can be distinguished. That is, people live in Taipei can be genetically different from people in Taichung if we consider enough numbers of genetic features.
10
適者生存 or 幸者生存
• Sickle Cell Anemia and Malaria defense
– Natural selection
• O blood type of native American
– Founder's effect
– Natural selection: Syphilis epidemics
• Neutral genes
11
Forces of Evolution
• Mutation
• Selection
• Random drift
• Migration
12
Genetic Distances
• How different are two individuals?
– Difference between parents and children
– Difference between grandparents and grandchildren
– Difference between any two unrelated persons.
• How different are two populations?
13
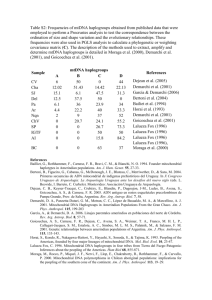
Genetic Distance among Five
Continents
• The genetic distance was calculated from 100 genes for 15 Groups (three groups in each continent).
大洋洲 美洲 歐洲
大洋洲
美洲
歐洲
亞洲
非洲
24.7
22.6
16.6
20.6
14.6
13.5
10.0
9.5
8.7
9.7
14
Phylogeny Tree
亞洲 美洲 歐洲 大洋洲 非洲
15
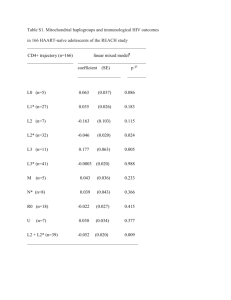
Y chromosome and Mitochondria
• Y chromosome can be traced to back to one man in Africa. That specific male is called the Scientific
Adam .
• Both men and women carry mitochondria but only Moms pass it along. Hence, all our mitochondria can be traced to one single woman in Africa and she is called the Scientific Eve .
• Both appeared at around 144,000 years ago.
• Haplogroups
16
Recent Viewpoint
Meet the Denisovans, indigenous Australia's Siberian kin Source: The Australian
17
18
How to Construct Phylogeny Tree
• Distance-based
– Neighbor-joinning
– UPGMA
• Maximum parsimony
19
Evolutionary History of Human
• DNA consists more information than fossils.
• The rules of DNA change is a lot more simpler than the metrics measured from fossils.
20
21
European Haplogroups of mtDNA
West Britain and Scandinavia http://freepages.genealogy.rootsweb.ancestry.com/~jswdna/haplogroupn.gif
22
European Haplogroups of mtDNA
Central and Eastern Europe, France, England
23
European Haplogroups of mtDNA
All around Europe
24
European Haplogroups of mtDNA
Northern Scandinavia, Saami
25
European Haplogroups of mtDNA
Eastern Baltic Sea, Ireland and the west of Britain
26
European Haplogroups of mtDNA
Ötzi the Iceman, Northern Italy, Around the Mediterranean
32% of people with Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry
27
European Haplogroups of mtDNA
Mediterranean, Greece, Italy/Sardinia and Spain
Ireland, England-Wales, Scotland
28
The Genographic Project
29
Interactive Trail for the
Journey of Mankind http://www.bradshawfoundation.com/journey/
30
Migration of Austronesian ( 南島語系 )
Source: Wiki
31
Inference with Y chromosome
32
Other Side Stories
• Y-chromosomal Aaron
– Haplogroup J-P58 consist of more than 50% of
Kohanim. It infers the most recent common ancestor living around 3200( ± 1100) years ago.
– Haplogroup J-M410 consist of around 14% of
Kohanim. It infers the most recent common ancestor living around 4200( ± 1300) years ago.
• mtDNA and Y chromosome in Venezuela
33
Conclusion
• 統計是遺傳研究不可或缺的一部份
• 遺傳則是統計研究裡面充滿想像與驚奇的
旅程
34
References
• Geni, Popoli e Lingue ( 追蹤亞當夏娃 ) by Luigi
Luca Cavalli-Sforza (2003)
• The journey of man: a genetic odyssey.
Spencer Wells. (2002)
• The seven daughters of Eve ( 夏娃的七個女兒 ).
Bryan Sykes. (2001)
• National Geographic: The human family tree http://topdocumentaryfilms.com/humanfamily-tree/
35