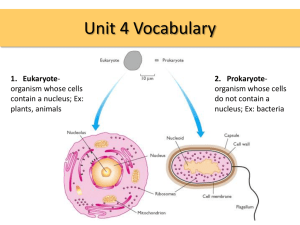
Introduction to the
Case of the Mysterious Snake
To preserve the animations, please be sure to work through
the slide show before editing; movements will not appear on
the slide itself – only during a slide show
Notes about what to say are included on the slide notes
area
Professor Chiszar’s Big Surprise
snakes
Include a nice photo of a timber rattlesnake
I had a photo of Prof. Chiszar in
his lab, but the url is no longer
available – I suggest adding a
photo of someone handling
snakes in a lab setting
Timber rattlesnake
Crotalus horridus
For a nice photo, see:
http://animals.timduru.org/dirlist/snake/TimberRattlesnake_01-OnSand.jpg
http://animals.timduru.org/dirlist/snake/TimberRattlesnake_01-OnSand.jpg
Timber rattlesnake: Crotalus horridus
For a nice video see
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EMaBH7EKYMU The newborn snake pops
out at about 2:30 on the video
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EMaBH7EKYMU
Timber rattlesnake: Crotalus horridus
For an interesting video see:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y7B8L47jP
D0
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y7B8L47jPD0
Professor Chiszar’s big surprise
For an nice photo see:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/adaptations/Ov
oviviparity
http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/adaptations/Ovoviviparity
One more surprise!
It’s a boy!
What would you like to ask Prof.
Chiszar about this baby snake?
Where do babies come from?
• Ultimately: from cells
• How do cells reproduce? Mitosis
A Primer on Basic Features of Mitosis
& Meiosis
To preserve the animations, please be
sure to work through the slide show
before editing
mitosis
• Metaphase: homologous chromosomes
independently line up
• Produces two genetically identical nuclei (two
genetically identical daughter cells after cell
division)
nucleus
nucleus
cell
nucleus
nucleus
nucleus
nucleus
Original
nucleus
Daughter
nucleus
Daughter
nucleus
Could the baby snake be produced by
mitosis?
Well, where do baby snakes usually come
from?
For a nice photo of fertilization, see
http://www.webmd.com/baby/ss/slideshowconception
http://www.webmd.com/baby/ss/slideshow-conception
meiosis
• DNA replicates once, but cell divides twice
– First meiosis: duplicated, homologous chromosomes pair up at
metaphase so each cell gets one set of duplicated chromosomes
– Second meiosis: duplicated chromosomes line up independently
at metaphase so each cell gets one sister chromatid (i.e. all cells
are haploid and have only one copy of each chromosome)
• Produces gametes with one set of chromosomes
– Four gametes (sperm) or one big gamete (egg) & three tiny cells
called polar bodies
nucleus
nucleus
cell
nucleus
nucleus
nucleus
nucleus
nucleus
nucleus
nucleus
Mitosis
Cell division
2X
Meiosis
Cell division
Cell division
Cell division
Cell division
meiosis
sex chromosomes
X
Y
XY, male
X
Y
X X
Y Y
X X
Y Y
X X
Y Y
X
Y
X
X
Y
Y
Genetic Sex
Determination
In Mammals
Mitosis
X
X
Y
Y
X
X
X
Y
Cell division
X
XY
Meiosis
X
Y
Cell division
X
Y
Cell division
X
X
X
Cell division
Cell division
2X
XX
XY
X
X
Y
Y
X
X
X
X
Genetic Sex
Determination
In Birds,Reptiles
Mitosis
Z
Z
W
W
Z
Z
Z
W
Cell division
Z
ZW
Meiosis
Z
W
Cell division
Z
W
Z
Cell division
Z
Z
Cell division
Cell division
2X
ZZ
ZW
Z
Z
W
W
Z
Z
Z
Z
Parthenogenesis in Vertebrates
• Production of offspring from unfertilized eggs
Some Variations in Vertebrate Reproduction
Homologs
Parthenogenesis
Gynogenesis
Ab
M1
(P1
(P3
aB
M2
P2)
P4)
Haplotype
Haplotype
M1 M2
M1 M2
Defective
Meiosis
Defective
meiosis
Diploid egg
Diploid
egg
M1 M2
Hybridogenesis
Diploid
egg
M1 P1
P1 P2
Fertilization
M1
M2
P1 or P2
M1 M2
Paternal
genome
eliminated
Defective
meiosis
Haploid egg
(paternal genome
eliminated)
Diploid
egg
P3 P4
Fertilization
M1
M1
P3 or
P4
Development
Development
Development
M1 M2
M1 M2
M1 P3
or M1 P4
P3 or P4
Parthenogenesis in Vertebrates
Where might meiosis “go wrong”
so that a diploid egg cell is
produced?
Mitosis
A
AA, Bb
Genotype of
Diploid Parent
Cell
B
A
B
A
A
B
b
Meiosis
A
A
b
B
Cell division
b
b
A
A
Cell division
Cell division
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
b
b
b
b
B
B
Cell division
Cell division
2X
AA, Bb
A B
A B
A b
A b
A b
A b
A B
A B
Bonus slides – showing
chromosomes with alleles
mitosis
with alleles
A
A
b
AA, Bb
B
A A
A A
b b
B B
A A
A A
b b
B B
AA, Bb
A
A
A A
B b
A
A
AA, Bb
AA, Bb
b
b
B
B
meiosis
with alleles
A
A
B
AA, Bb
b
A
A
b
B
A A
A A
b b
B B
A A A A
b b B B
A A
A A
AA, Bb
b b
A, b
B B
A, b
A, B
A, B
A A
A A
AA, Bb
B B
A, B
b b
A, B
A, b
A, b
Mitosis
A
AA, Bb
Genotype of
Diploid Parent
Cell
B
A
B
A
A
B
b
Meiosis
A
A
b
B
Cell division
b
b
A
A
Cell division
Cell division
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
b
b
b
b
B
B
Cell division
Cell division
2X
AA, Bb
A B
A B
A b
A b
A b
A b
A B
A B