Genetics 2 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

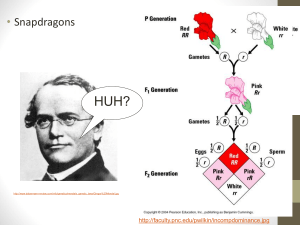
Genetics 2 • Genetics 1 Review • Segregation • Genotype and Phenotype • Incomplete dominance and codominance Genetics 1 Review In the previous lecture, you learned about Gregor Mendel and his study of pea plants. What is a Punnet Square and what does it help us predict? What are alleles? What does it mean to have a dominant and a recessive allele? How is it possible for two tall pea plants to have a short pea plant offspring? What does homozygous and heterozygous mean? Segregation Alleles are different forms of a gene. For example, the gene for height in pea plants has two alleles, (T) and (t). (T) is the allele for Tall height and (t) is the allele for short height. Gregor Mendel wanted to understand why two heterozygous tall (Tt) pea plants could produce a short (tt) offspring. He said that these alleles must segregate, or separate during reproduction. Segregation and Gametes Segregation is the separation of alleles during sexual reproduction. When plants and animals reproduce, their cells separate so that their offspring get half of the genetic material from each parent. That is, half of your cells are from your mom and half are from your dad. Gametes are sex cells (Like sperm and egg cells) During sexual reproduction, each parent produces a gamete that has half of its genetic material. Phenotype and Genotype Two vocabulary words that you should know are phenotype and genotype. Genotype refers to the genetic make-up of an organism. For example, a heterozygous pea plant (Tt) has a genotype that has both the tall (T) and short (t) alleles for height. Phenotype refers to the physical characteristics of an organism. For example, even though the heterozygous (Tt) pea plant carries the short gene, it will still be tall, because the tall allele (T) is dominant. The phenotype is tall. Incomplete Dominance and Codominance As we learned already, there are dominant and recessive alleles for various traits. However, sometimes alleles are not completely dominant over others. For example, the alleles for red and white flowers show incomplete dominance. Incomplete dominance: when one allele is not completely dominant over another. Incomplete dominance and Codominance The alleles for red and white flowers are: Red (R) and White (r). When a flower is homozygous Red, its alleles are ___ ___ . When a flower is homozygous White, its alleles are ___ ___ . When a flower is heterozygous, its alleles are ___ ___. Incomplete Dominance RR=Red Rr= Pink rr=White Incomplete Dominance What happens if you cross two heterozygous pink flowers (Rr x Rr) ?? What are the phenotypes of the offspring of the two pink flowers? Codominance Codominance: both alleles contribute to the phenotype. In other words, both colors show up evenly. They do not mix like in incomplete dominance. Example of codominance: A brown bird and a black bird are crossed and their offspring have some brown feathers and some black feathers. Do you understand the difference between Codominance and Incomplete Dominance?