Let*s Review
advertisement

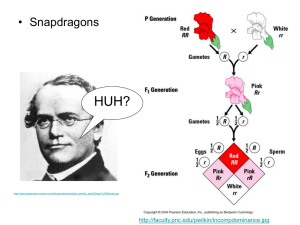
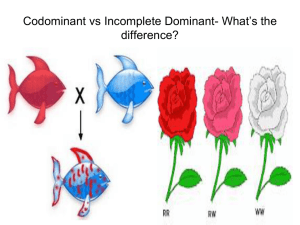
Beyond Dominant & Recessive Alleles Incomplete Dominance & Codominance S Learning Goals S 1. Describe incomplete dominance. Describe codominance. S 2. Compare and contrast incomplete dominance and codominance. Give 2 similarities and 1 difference. S 3. Explain how letters are chosen when doing punnett square problems for incomplete dominant and codominant traits S 4. Explain what multiple alleles are and give an example S 5. Describe what a polygenic trait is and give an example. Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles S Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, and many traits are controlled by multiple alleles or multiple genes. Incomplete Dominance S Incomplete dominance - when one allele is not completely dominant over another. S Heterozygous genotype = BLEND S Since one allele is not completely dominant over the other allele, we use two different capital letters to represent the alleles S Example: A cross between red (RR) and white (WW) snapdragons produces pink flowers (RW). Homozygous Heterozygous Homozygous RR RW WW (Red) (Pink) (White) Codominance S Codominance - both alleles contribute to the phenotype. S Heterozygous genotype = both traits appear S Since one allele is not completely dominant over the other allele, and both traits appear together, we use two different capital letters to represent the alleles S Example: A cross between black (BB) and white (WW) chickens produces chickens speckled with black and white feathers (BW). Multiple Alleles S Multiple alleles -genes that are controlled by more than two alleles. S An individual can’t have more than two alleles (Remember you get one copy from each parent). However, more than two possible alleles can exist in a population. •Example: A human’s blood type is determined by a single gene that has three different alleles. Polygenic Traits S Polygenic traits -traits controlled by two or more genes. S Skin color in humans is a polygenic trait controlled by more than four different genes. Learning Goals S 1. Describe incomplete dominance. Describe Codominance. S 2. Compare and contrast incomplete dominance and codominance. Give 2 similarities and 1 differences S 3. Explain how letters are chosen when doing punnett square problems for incomplete dominant and codominant traits S 4. Explain what multiple alleles are and give an example S 5. Describe what a polygenic trait is and give an example. Whiteboard Practice S Step 1: Incomplete Dominance or Codominance?????? S Step 2: You will be given the 3 phenotypes, Write the corresponding genotypes. S 2 alleles (1 from mom, 1 from dad) S Use the 1st letter for each trait S Both letters are capitol S Step 3: Set up and fill-in a punnett square. Calculate percent probability for ALL 3 TRAITS!!! Let’s do the st 1 one together S Birds can be blue, white, or white with blue- tipped feathers S 1. Incomplete Dominance or Codominance? S 2. Genotypes: bluewhite – blue-tipped – 3. Show a cross between a white and blue-tipped bird Practice Identifying S A cat can be black, tan, or tabby (black & tan) S 1. Incomplete Dominance or Codominance? S 2. Genotypes: blacktan – tabby – 3. Show a cross between a heterozygous tabby and tan cat Practice Identifying S A Who can have curly hair, spiked hair, or wavy S 1. Incomplete Dominance or Codominance? S 2. Genotypes: curlyspiked – wavy- 3. Show a cross between a curly and wavy Who Practice Identifying S A sneech can be tall, short, or medium S 1. Incomplete Dominance or Codominance? S 2. Genotypes: tallshort – medium – 3. Show a cross between two heterozygous sneeches Practice Identifying S A horse can be black, white, or roan (black & white) S 1. Incomplete Dominance or Codominance? S 2. Genotypes: black – white – roan - 3. Show a cross between a heterozygous roan and black horse Practice Identifying S Flowers can be white, pink, or red S 1. Incomplete Dominance or Codominance? S 2. Genotypes: whitepink – red- 3. Show a cross between a white and red flower