slides - Yin Lab @ NIU
advertisement

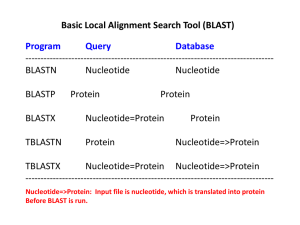
Run BLAST in command line mode Yanbin Yin Fall 2014 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK52640/ 1 Why you do need to run BLAST in command line terminal? - NCBI’s server does not have a database that you want to search - Millions of users are using NCBI BLAST server too - Your query set has more than one sequence or even a genome - The BLAST output could be processed and used as input for other Linux softwares 2 For doing blast search 1. Determine what is your query and database, and what is the command 2. Format your database 3. Run the blast command (what E-value cutoff, what output format) 4. View the result 5. Parse the result (hit IDs, hit sequences, alignment, etc.) There are two versions of BLAST -blast2 (legacy blast) -blast+ (this is what you installed in your home/tools/) https://www.biostars.org/p/9480/ http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?CMD=Web&PAGE_TYPE=BlastDocs&DOC_TYPE=Download 3 BLAST2 (legacy blast) blastall - | less -p # specify blastp, blastn, blastx, tblastn, tblastx More commands in blast package Query Protein DNA Database Protein DNA formatdb (format database) megablast (faster version of blastn) rpsblast (protein seq vs. CDD PSSMs) impala (PSSM vs protein seq) bl2seq (two sequence blast) blastclust (given a fasta seq file, cluster them based on sequence similarity) blastpgp (psi-blast, iterative distant homolog search) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1763/pdf/ch4.pdf 4 blastall options -p -d -i -e -m -o -F -v -b -a program name database file name (text fasta sequence file) query file name e-value cutoff (show hits less than the cutoff) output format output file name (you can also use >) filter low-complexity regions in query number of one-line description to be shown number of alignment to be shown number of processers to be used 5 New version blast+, e.g. blastp At your home ls -l tools/ncbi-blast-2.2.30+/bin/ 22 executable files (commands) blastp blastn tblastn blastx tblastx blastp -help | less -query query file name -db database file name -out output file name -evalue e-value cutoff -outfmt output format -num_descriptions http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1763/ -num_alignments pdf/CmdLineAppsManual.pdf 6 Exercise 1: find CesA/Csl homologous sequence in charophytic green algal genome Klebsormidium flaccidum genome was sequenced, analyzed and published in http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4052687/. We want to find out how many CesA/Csl genes this genome has. Note that the raw DNA reads are available in GenBank, but the assembled genome and predicted gene models are not Go to Methods of the above paper and find the link to the website that provides the genome and annotation data Wget the predicted protein sequence file wget -q http://www.plantmorphogenesis.bio.titech.ac.jp/~algae_genome_project/klebsormi dium/kf_download/131203_kfl_initial_genesets_v1.0_AA.fasta Make index files for the database makeblastdb -in 131203_kfl_initial_genesets_v1.0_AA.fasta -parse_seqids Check how many proteins have been predicted less 131203_kfl_initial_genesets_v1.0_AA.fasta | grep '>' | wc 7 Wget our query set wget -q http://cys.bios.niu.edu/yyin/teach/PBB/cesa-pr.fa Do the blastp search blastp -query cesa-pr.fa -db 131203_kfl_initial_genesets_v1.0_AA.fasta -out cesa-pr.fa.out -outfmt 11 Check out the output file less cesa-pr.fa.out Change the output format to a tab-delimited file blast_formatter -archive cesa-pr.fa.out -outfmt 6 | less Filter the result using E-value cutoff blast_formatter -archive cesa-pr.fa.out -outfmt 6 | awk '$11<1e-10' | less blast_formatter -archive cesa-pr.fa.out -outfmt 6 | awk '$11<1e-10' | cut -f2 | less 8 How do you extract the sequences of the blast hits? blastdbcmd Query blast Seqs DATABASE Linux cmds Hit IDs blast_formatter Hit Seqs Linux cmds Further analyses: Multiple alignment Phylogeny, etc. 9 Save the hit IDs blast_formatter -archive cesa-pr.fa.out -outfmt 6 | awk '$11<1e-10' | cut -f2 | sort -u > cesa-pr.fa.out.id Retrieve the fasta sequences of the hits blastdbcmd -db 131203_kfl_initial_genesets_v1.0_AA.fasta -entry_batch cesapr.fa.out.id | less blastdbcmd -db 131203_kfl_initial_genesets_v1.0_AA.fasta -entry_batch cesapr.fa.out.id | sed 's/>lcl|/>/' | sed 's/ .*//' | less blastdbcmd -db 131203_kfl_initial_genesets_v1.0_AA.fasta -entry_batch cesapr.fa.out.id | sed 's/>lcl|/>/' | sed 's/ .*//’ > cesa-pr.fa.out.id.fa Wget the annotation file from the Japan website wget -q http://www.plantmorphogenesis.bio.titech.ac.jp/~algae_genome_project/klebsormidiu m/kf_download/131203_gene_list.txt Check what our genes are annotated to be grep -f cesa-pr.fa.out.id 131203_gene_list.txt 10 If a program (e.g. BLAST) runs so long on a remote Linux machine that it won’t finish before you leave for home … Or if you somehow want to restart your laptop/desktop where you have a Putty session is running (Windows) or a shell terminal is running (Ubuntu) … In any case, you have to close the terminal session (or have it be automatically terminated by the server). If this happens, your program will be terminated without finishing. If you expect your program will run for a very long time, e.g. longer than 10 hours, you may put “nohup” before your command; this ensures that even if you close the terminal, the program will still run in the background until it is finished and you can log in again the next day to check the output. For example: nohup blastp -query yeast.aa -db yeast.aa -out yeast.aa.ava.out -outfmt 6 & You will get an additional file nohup.out in the working folder and this file will be empty if nothing wrong happened. 11 Exercise 2: emboss You are at your home cd tools lftp emboss.open-bio.org Inside emboss lftp site cd pub/EMBOSS get emboss-latest.tar.gz Bye to exit from lftp bye Test if emboss has been installed: water Now you are back to your home on Ser tar zxf emboss-latest.tar.gz ./configure –prefix=$HOME/tools/emboss make make install If you are the root, one command can do all the above for you sudo apt-get install emboss 12 Change sequence format seqret –help seqret -sequence /home/yyin/Unix_and_Perl_course/Data/GenBank/E.coli.genbank -outseq E.coli.genbank.fa -sformat genbank -osformat fasta Calculate sequence length infoseq –help infoseq -sequence /home/yyin/cesa-pr.fa -name –length -only More command examples: needle –help water –help fuzznuc –help pepstats -help pepinfo –help plotorf -help transeq -help prettyseq –help 13