Sequence Alignment and comparison
advertisement

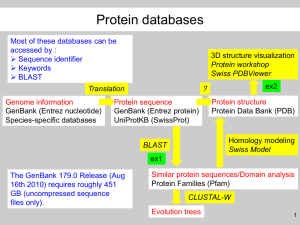
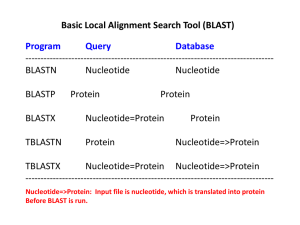
SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT AND COMPARISON BETWEEN BLAST AND BWA-MEM S C H O O L O F C O M P U T I N G AN D R E W M AX W E L L 9 / 1 1 / 2 0 1 3 OUTLINE • BLAST • BWA-MEM • Comparisons BLAST • Basic Local Alignment Search Tool • Developed by NCBI • • • • NCBI - National Center for Biotechnology Information NLM – US National Library of Medicine NIH – National Institute of Health http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ • Latest Version (executable) • 2.2.28+ • ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast+/LATEST/ BLAST • A suite of tools that work together to search for similar sequences of different protein or nucleotide DNA sequences. • Three Categories of Applications 1. Search Tools 2. BLAST Database Tools 3. Sequence Filtering Tools • BLAST Command Line User Manual • http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1763/ SEARCH APPLICATIONS • Execute a BLAST search. • blastn – Nucleotide Blast • Nucleotide database using nucleotide query. • blastp - Protein Blast • Protein database using protein query. • blastx • Protein database using translated nucleotide query. • tblastx • Translated nucleotide database using a translated nucleotide query. • tblastn • Translated nucleotide database using a protein query. SEARCH APPLICATIONS CONT. • psiblast • Position-Specific Iterated BLAST • Finds sequences significantly similar to the query in a database search and uses the resulting alignments to build a Position-Specific Score Matrix (PSSM). • rpsblast • Reverse Position-Specific BLAST • Uses a query to search a database of pre-calculated PSSMs and report significant hits in a single pass. • rpstblastn • Searches database using a translated nucleotide query. BLAST DATABASE APPLICATIONS • Create or examine BLAST databases. • makeblastdb • Creates BLAST databases. • blastdb_aliastool • Manage BLAST databases. • Search multiple databases together or search a subset of sequences within a database. • makeprofiledb • Builds an RPS-BLAST database. • blastdbcmd • Examine the contents of a BLAST database. SEQUENCE FILTERING APPLICATIONS • Segmasker • Identifies and masks low complexity regions* of protein sequences. • Dustmasker • Similar to segmasker but for nucleotide sequences. • Windowmasker • Uses a genome to identify sequences represented too often to be of interest to most users. • *Low-Complexity Regions – Regions of a sequence composed of few elements. • These will be ignored by BLAST unless explicitly told to include them in searches. • May achieve high scores that may bump more significant sequences. BLAST ALGORITHM http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK62051/bin/blastpic1.jpg E-VALUE • The number of hits to see by chance when searching the database. • This value decreases exponentially when the score is increased. • The lower the e-value is, the more significant the match is. • This also depends on the length of the query sequence. E-values will be higher with shorter sequences because there is a higher probability of a query sequence occurring in the database by chance. BITSCORE • The bitscore value is derived from the raw alignment score S. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21106/bin/glossfig1.jpg • Lambda and K are statistical parameters of the scoring system. EXAMPLE RUN FASTA FORMAT • Text-based format representing nucleotide or peptide sequences. • A “>”, followed by the sequence identifier, then an optional description. • >seq_1 Some description • GAGGGCTCATCCGGGAATCGAACCCGGGACCT CTCGCACCCTAAGCGAGAATCATACGACTAGACC AATGAGCCGTGTTCAAAGAGTGTCAAAATGTGTTTC GAGCGTCTATGTCCAAAGTGAATTGCTTGTCTTTTGA GTTTTGCGATTG SAMPLE OUTPUT BWA-MEM • Burrows-Wheeler Aligner • A software package for aligning sequences against large reference genomes. • The BWA package contains three different algorithms: BWA-backtrack, BWA-SW, and BWAMEM. • Manual Page • http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/bwa.shtml BWA-MEM • Can align 70bp to 1Mbp • MEM – Maximal Exact Matches • Local alignment HOW TO RUN • Index the reference FASTA file. • Run BWA-MEM with a query file (in FASTQ format) against the reference database. • The output is in a SAM file format. FASTQ FORMAT • Similar to a FASTA format, but with a quality score added. • @HWI-EAS397:8:1:1067:18713#CTTGTA/1 • TGGAGATGAGATTGTCGGCTTTATTACCCAGGGGC GGGGGGTTATTGTA • + • Y^]Lcda]YcffccffadafdWKd_V\``^\aa^BBBBBBBBBB BBBBB • The quality score is an integer mapping of the probability that the base is incorrect. SAM FILE • Eleven mandatory fields and a variable amount of optional fields. • The optional fields are a key-value pair of TAG:TYPE:VALUE. These store extra information. SAM REQUIRED FIELDS SAM OPTIONAL FIELDS BWA-MEM ALGORITHM • Seeds alignments with maximal exact matches • Then, uses affine-gap Smith-Waterman algorithm. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smith%E2%80%93Waterman_algorithm BWA-MEM OPTIONS • t – Number of threads • T – Don’t output alignment with score lower than INT. • a – Output all found alignments for single-end or unpaired paired-end reads. • (In output, ‘*’ are considered zero.) EXAMPLE RUN SAMPLE OUTPUT REFERENCES • NCBI Help Manual http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK3831/ • Bwa - http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/ • FASTA - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FASTA_format • FASTQ - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FASTQ_format • Li, H, et al. (2009). The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Vol. 25 no 16, Bioinformatics Applications Note.