4 Genetic engineering
advertisement

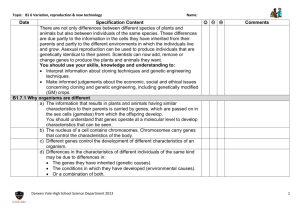
Genetic Engineering TITLE: Genetic Engineering Objectives • What is genetic engineering? – grade C-A* • How are genes transferred from one organism to another? – grade C-A* • What are the issues involved in genetic engineering? – grade C-A* Outcomes: • Complete a learning summary fill in the gaps exercise; • Label a diagram to show how human insulin can be produced using genetic engineering; • Look at modelled exam questions and complete your own based on the model KEY WORDS: Summary – see worksheet • In genetic engineering, genes from the chromosomes of humans and other organisms can be ‘cut out’ using enzymes and transferred to cells of other organisms. • Genes can also be transferred to the cells of animals, plants or microorganisms at an early stage in their development so that they develop with desired characteristics. • New genes can be transferred to crop plants • Crops that have had their genes modified in this way are called genetically modified crops (GM crops) • Examples of genetically modified crops include ones that are resistant to insect attack or to herbicides • Genetically modified crops generally show increased yields. Genetically modified organisms ‘GMOs’ • Concerns about GM crops include the effect on populations of wild flowers and insects, and uncertainty about the effects of eating GM crops on human health. Benefits… • Crops grow more rapidly and produce more – there are more people in the world to feed; • Pest and disease resistance can be given to crops to increase yields • Crops can be given frost / drought resistance • Production of medicines that reduce the risk of rejection and side effects – human insulin Maybe we will be able to genetically engineer humans to replace defective genes that cause genetic diseases. Cattle and methane Exam style question • Scientists are investigating how to reduce methane emissions from cattle. Most of this methane is emitted by the cows belching. • Scientists have found that less methane is belched if the cows eat high-sugar rye grass. • This rye grass has been produced by genetic engineering. (i) Suggest how the high-sugar rye grass might have been produced by genetic engineering. Model answer • remove gene using enzymes • from plant with high sugar production • insert gene into rye grass cells using enzymes • (ii) Some people might object to the growing of genetically-engineered, highsugar rye grass for feeding cattle. • Give two reasons why. Model answer • concern about effect on (health) of cow • concern about effects on human (health) as humans eat cow products (dairy / meat) • concern about food chain effects or effects on ecosystem • effect on gene pool • ignore not natural or cost • ignore ethical / religious arguments • if no other marks awarded ‘we don’t know the long term effects’ = 1 mark TITLE: Genetic Engineering Objectives • What is genetic engineering? – grade C-A* • How are genes transferred from one organism to another? – grade C-A* • What are the issues involved in genetic engineering? – grade C-A* Outcomes: • Complete a learning summary fill in the gaps exercise; • Label a diagram to show how human insulin can be produced using genetic engineering; • Look at modelled exam questions and complete your own based on the model KEY WORDS: