NovoNordisk - University of Washington Biostatistics
advertisement

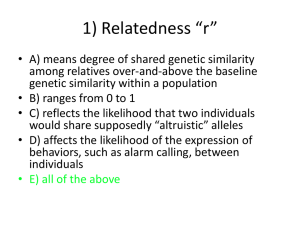
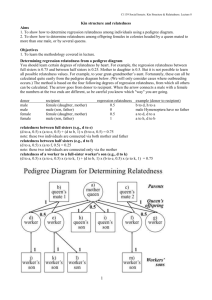
Genetic Analysis Center Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington Bruce Weir Ken Rice Tim Thornton Sharon Browning Brian Browning Katie Kerr Adam Szpiro Cathy Laurie David Levine Cecelia Laurie Sarah Nelson Stephanie Gogarten Adrienne Stilp Caitlin McHugh Matt Conomos Quenna Wong Jean Morrison Inae Hur Deepti Jain Tin Louie Figure 4 All autosomal SNPs with missing rate < 5% used to calculate PCs SNP set A Identity By Descent • 34 sample pairs with KC > 1/32 • 10 PO from HapMap • 21 expected Dups • 1 unrelated (bottom right) • 2 unexpected Dups Deconvoluting relatedness, population structure and admixture 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Estimate relatedness using KING-robust (robust to population structure, but not to admixture or departures from HWE) Partition the sample into a mutually unrelated set and the remaining (relatives of the unrelated set) Perform standard PCA on the set of unrelated individuals Project PC values for the set of related individuals Re-estimate relatedness using REAP-PC (uses PCs to provide unbiased kinship coefficients in the presence of population structure, admixture and HWE departures) Repeat steps 2-5 to obtain final sets of PCs and kinship coefficients – to adjust for relatedness and ancestry in association tests Matt Conomos and Tim Thornton 36 GAC Support for HCHS/SOL Genetic Studies 1. 2. 3. 4. Logistical support for working groups QA/QC and imputation of genetic data Estimate relatedness and ancestry variables Participate in development of paper proposals and analysis plans by working groups 5. Perform genetic analyses and distribute primary results to working groups 6. Participate in interpretation of results and manuscript preparation, which will be led by working group members 7. Statistical methodology development Outline of Genotypic Data QA/QC Process Genotyping batch effects (missing call rate, intensity, and allele frequency) Sample quality (missing call rate, allelic imbalance, heterozygosity) Sample identity (gender mismatches, unexpected dups, unobserved dups, Metabochip mismatches) – resolved 64 of 170 samples with issues Chromosomal anomalies (filter those causing genotyping errors) Relatedness, admixture and population structure SNP quality (missing call rate, Hardy-Weinberg, duplicate discordance, Mendelian errors) Preliminary Association tests (QQ, Manhattan and cluster plots; expected hits) Imputation to 1000 Genomes 52