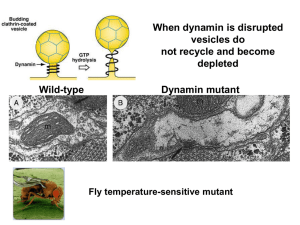
A general account of chemical basis of signalling.
advertisement

Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Neurotransmitters Kuls oo m Bibi Kulsoom Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Nervous System Kuls oo m http://archive.ck12.org/ck12/images?id=334457 Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Neuron Kuls oo m http://springvisualculture1b.blogspot.com/2010/04/neuron-psychologist.html Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Neurotransmitter A chemical substance that is • Synthesized in a neuron. • Stored in presynaptic nerve terminal. Synthesis of neurotransmitter Axon of a neuron • Released into synaptic cleft. • Act upon the postsynaptic neuron, Stored neurotransmitter muscle or organ. Presynaptic membrane Kuls oo m Axon terminal Postsynaptic membrane Synaptic cleft Postsynaptic membrane receptors Effect specific to target tissue Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Classification of Neurotransmitters Type of Substance Examples Ester Acetylcholine Glycine Amino acids Gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) Glutamate Aspartate Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Kuls oo m Catecholamines Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) Dopamine Amines Serotonin Indolamines Histamine Taurine Peptides Endorphins, enkephalins, substance P, cholecystokinin Others ATP, NO, CO Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Functional Classification Function Examples Glutamate Excitatory (leads to depolarization ) Aspartate Serotonin Histamine ATP, CO Glycine Kuls oo m Inhibitory (leads to hyperpolarization ) Excitatory & Inhibitory (leads to depolarization and hyperpolarization depending on type of receptor ) Gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) Taurine Acetylcholine Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Dopamine Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) NO Endorphins, enkephalins, substance P, cholecystokinin Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Acetylcholine • Synthesized from acetyl CoA and choline. • Stored in presynaptic terminal • Released into synaptic cleft • Act upon the postsynaptic receptors Acetyl CoA + Choline • Receptors are two types 1. Muscarinic, Kuls oo m Acetylcholine esterase 2.Nicotinic • Acetylcholine esterase hydrolyzes acetylcholine. 1.Muscarinic 2.Nicotinic Effect specific to target tissue Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Types of Cholinergic Receptors Muscarinic Acetylcholine Kuls oo m http://www.nature.com/npp/journal/v37/n1/images/npp2011199f2.jpg Nicotinic Acetylcholine Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Types of Cholinergic Receptors Receptor Type Natural Stimulators Location of receptors Mechanism of action Muscarinic 1.Ach 2.Muscarine • CNS (M1-M5) • M1, M3 & M5 • Secretory glands e.g., Salivary, activation of stomach & Sweat glands (M1) phospholipase C • Cardiac tissue (M2) IP3 & DAG generation • Smooth muscles (M3) increased calcium • Parasympathetic system • M2 & M4 inhibition of adenylate cyclase decreased cAMP Nicotinic CNS Neuromuscular junction Autonomic ganglia Adrenal medulla Kuls oo m 1.Ach 2.Nicotine Activation of nicotinic receptors opening of Na+ and K+ channels depolarization Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Distribution of Cholinergic Receptors Peripheral Nervous System CNS ACh Nic ACh ACh Muscarinic Parasympathetic Nictinic: Adrenal medulla Kuls oo m ACh Nic NE ACh Nic ACh Muscarinic: Sweat glands ACh Nicotinic: Skeletal muscles Adrenergic: Heart and blood vessels Sympathetic Somatic Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Myasthenia Gravis Kuls oo m http://jama.ama-assn.org/content/vol293/issue15/images/medium/jpg0420f1.jpg Kuls oo m Kuls oo m kulsoom Catecholamines Epinephrine Catecholamines are derivatives of tyrosine & (Adrenaline) contain a catechol (dihydroxybenzene) ring. The difference between epinephrine and Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) norepinephrine: one additional methyl group in Kuls oo m structure of epinephrine. 2 The difference between norepinephrine and dopamine: one additional hydroxyl group in the structure of norepinephrine. Dopamine H 2 12 http://website.lineone.net/~dave.cushman/epipen.html Kuls oo m Kuls oo m kulsoom Sympathetic System Sympathetic Nervous System: Thoracolumber Preganglionic nerve fibers Postganglionic nerve fibers ACh Noradrenaline Target tissue Ganglion Kuls oo m Blood Adrenal Medulla: Vasodilation Skeletal muscle Adrenaline Thoracic ACh Noradrenaline Adrenal Medulla Digestive system Vasoconstriction Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Synthesis of Adrenaline and Noradrenaline Adrenal Medulla Synthesis of Adrenaline & Noradrenaline Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Tyrosine Hydroxylase Kuls oo m Synthesis of Adrenaline & Noradrenaline Sympathetic Nerve DOPA decarboxylase Dopamine Hydroxylase Phenylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase Effect specific to target tissue Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Mechanism of Action Kuls oo m 15 http://www.sp.uconn.edu/~bi107vc/images/anim/SigtranRA.gif Kuls oo m Kuls oo m kulsoom Adrenergic Receptor Alpha Beta kulsoom Alpha 1 Alpha 2 Beta 1 Beta 2 Beta 3 Kuls oo m Adrenergic receptors are seven-pass transmembrane proteins. 16 Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Mechanism of Action • These are called G protein-coupled Gα receptors (GPCRs). β β • The three subunits are: Gα, Gβ, Gγ Kuls oo m • Gα carries the binding site for the Giα Gsα Gqα nucleotide and is different in different types of G proteins Gs, Gi and Gq. • Gβ and Gγ are same in all types of G proteins. 17 http://withfriendship.com/images/c/14666/Adrenergic-receptor-wallpaper.gif Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Distribution of Adrenergic Receptor Receptor type 1 Tissue location Arterioles (coronary, visceral, cutaneous), veins, internal sphincters, Iris dilator muscle. 2 Presynaptic membrane, pancreas, veins, adipose tissue, GIT sphincters, salivary glands. Kuls oo m 1 Heart (SA node, atrial muscle, AV node, ventricles), kidney(JG apparatus), Adipose tissue. 2 Arterioles(muscular), veins, bronchi (muscles), liver, pancreas, uterus , Iris constrictor muscle. 3 Adipose tissue, urinary bladder. Kuls oo m Kuls oo m kulsoom = Adrenaline & Noradrenaline 1 2 Gq Gi Gs Phospholipace C Adenylate cyclase Adenylate cyclase PIP2 DAG IP3 Kuls oo m 2+ Decreased Ca Increased Ca2+ Smooth muscle Contraction Decreased cAMP Inhibition of neurotransmitter release from neuron Smooth muscle Contraction Increased cAMP • Glycogen breakdown • Smooth muscle relaxes • Cardiac muscle contracts Effector cell = inhibits = leading to 19 Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Effect of Autonomic NS on Heart Sympathetic Nerves Parasympathetic Nerves (Vagus) NE ACh 2 1 M2 & Norepinephrine Kuls oo m ↑ heart rate ↑ conduction velocity + Cardiomyocyte ↑contractility ↑ rate of myocyte relaxation _ http://www.cvphysiology.com/Blood%20Pressure/BP010.htm http://bioserv.fiu.edu/~walterm/fund_sp2004/heart/f12-20_baroreceptor_and_c.jpg Kulsoom animated from http://www.cvphysiology.com/Blood%20Pressure/BP010.htm Kuls oo m Kuls oo m kulsoom Distribution of Adrenergic Receptor E = Epinephrine Kuls oo m At low epinephrine concentrations, the beta-2 At high epinephrine concentrations, the alpha-1 adrenergic adrenergic receptors will be occupied because receptors will be occupied too. Because there are more these receptors have a higher affinity for alpha-1 receptors the predominant effect at high epinephrine epinephrine. concentration is vascular smooth muscle contraction. 21 Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Dopamine Dopamine Precursor Phenylalanine Site of synthesis CNS, heart, pulmonary artery, kidney. Receptor D1-D5 (G-protein coupled) Effect Excitatory (D1), Inhibitory (D2). Involved in movement, cognition, Kuls oo m pleasure, and motivation Disease Decreased levels leads to Parkinson’s Disease and high levels are observed in schizophrenia. http://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Dopamine_chemical_structure.png Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Glycine Kuls oo m Glycine Precursor Serine Site of synthesis CNS Receptor Glycine-A & B, NMDA Effect Excitatory: motor function NMDA=N-methyl-D-aspartate http://o.quizlet.com/i/I8RJX-RlIpAe58vmHdpL0w_m.jpg Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Aspartic Acid L-Aspartate Kuls oo m Aspartate Precursor Oxaloacetate Site of synthesis CNS Receptor NMDA receptors Effect Excitatory: Learning and memory. NMDA=N-methyl-D-aspartate http://0.tqn.com/d/chemistry/1/7/V/V/1/L-aspartic_acid.png Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Glutamate Glutamate Kuls oo m Glutamate Precursor -ketoglutarate Site of synthesis CNS Receptor AMPA, NMDA, kainate, metabotropic Effect Excitatory: include cognition, memory and learning. AMPA = amino-methyl propanoic acid Kuls oo m Kuls oo m -aminobutyric acid (GABA) CO2 Synthesis: Glutamate decarboxylase Glutamate -aminobutyric acid (GABA) Kuls oo m GABA Precursor Glutamate Site of synthesis CNS Receptor GABA-A & B Effect Inhibitory: include cognition, memory and learning. Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Serotonin Synthesis: Tryptophan Hydroxylation & decarboxylation Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) Serotonin Kuls oo m Precursor Tryptophan Site of synthesis Intestinal mucosal cells, CNS Receptor 5HTA-F Effect Excitatory: include pain perception, regulation of sleep, appetite, temperature, blood pressure, cognitive functions & mood. Disease Decreased levels leads to some types of depression. http://www.wormatlas.org/neurotransmitterstable.htm Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Histamine Histidine Histamine Histamine Kuls oo m Precursor Histidine Site of synthesis CNS, basophils, mast cell Receptor H1-H4 Effect Excitatory:, sleep regulation, smooth muscle constriction, (acid secretion by stomach & immune system). Disease Low levels in CSF in Schizophrenia. http://web.campbell.edu/faculty/nemecz/323_lect/Nitrogen_metabolism/images/histamine.jpg Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Neuropeptides There are around 200 neuropeptides identified. Neuropeptides Kuls oo m Precursor Amino acids form large peptide which are cleaved to form short peptides. Examples -Endorphins, Met- enkephalins, Somatostatin, Substance P, CCK etc. Site of synthesis CNS, ANS, GIT (mainly) Receptor G- protein coupled seven helical transmembrane proteins Effect Excitatory & inhibitory: hunger, thirst, pleasure, pain, learning & memory. Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Miscellaneous Neurotransmitters • ATP: – Is found in both the CNS and PNS – Produces excitatory or inhibitory responses depending on receptor type. – Induces Ca2+ wave propagation in astrocytes – Provokes pain sensation Kuls oo m • Nitric oxide (NO) : – Activates the intracellular receptor guanylyl cyclase – involved in learning and memory. • Carbon monoxide (CO): – a main regulator of cGMP in the brain Kuls oo m Kuls oo m Kuls oo m http://myyatradiary.blogspot.com/2011/08/treks-beyond-badrinath-swargarohini.html