ES-cell specific enhanceosomes
advertisement

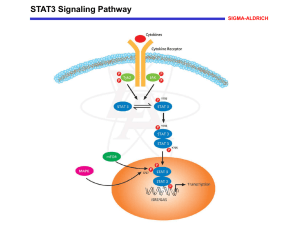
June 13, 2008 Cited by 705 Authors First author • Xi Chen Corresponding authors • Chia Lin WEI, Ph.D. • Huck-Hui Ng , Ph.D. • Group Leader • Executive Director • Genome Institute of Singapore • National University of Singapore • Genome Institute of Singapore They focus on stem cell biology and are addressing two questions: 1) What makes a stem cell a stem cell? 2) How to make a non-stem cell a stem cell? Background Embryonic Stem(ES) Cell • Pluripotency (differentiate into almost all lineages) • Self-renewing ability • Revolutionized biological research through the creation of genetically altered animals. • Human ES cell (promising) Pluripotency Self-renewal Main Purpose How is the ES cell pluripotency maintained? Maintenance of Pluripotency • • • Extrinsic: the LIF and BMP signaling pathways play a central role in the maintenance of a pluripotential stem cell phenotype. 1. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) The binding of LIF to its receptor activates STAT3 through phosphorylation • • 2. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs) The binding of BMP4 to its receptors triggers the phosphorylation of Smad1 and activates the expression of members of the Id(inhibitor of differentiation) gene family • Intrinsic: factors such as transcription factors (TFs) are also essential for specifying the undifferentiated state of ES cells. – Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc, Klf4, Nanog, Esrrb, Zfx Main Design Gain insights into the transcriptional regulatory networks in ESC Because Transcription factors (TFs) and their specific interaction with targets are crucial for specifying gene expression programs Objects • 13 transcription factors: Nanog, Oct4, STAT3, Smad1, Sox2, Zfx, c-Myc, n-Myc, Klf4, Esrrb, Tcfcp2I1, E2f1, CTCF • 2 transcription regulators: p300, Suz12 Methods • ChIP-seq Outline • ES-cell specific enhanceosomes Mapping of Binding Sites of 13 TFs by Using ChIP-seq Motif Analyses of TFBSs A Subset of Multiple Transcription-Factor-Binding Loci Nanog-Oct4-Sox2 cluster function as ES-Cell enhanceosomes p300 Is Recruited to the Nanog-Oct4-Sox2 Cluster • ES-cell Regulatory Network Combinatorial Binding of TFs is correlated with ES-CellSpecific Expression Regulatory Network Defining ES-Cell Specific Expression Mapping of Binding Sites of 13 TFs by Using ChIP-seq ChIP-seq Determine the threshold through Monte Carlo simulations Remove peaks that were also found in the negative control library Use ChIP-qPCR to further refine the threshold used Valid Motif Analyses of TFBSs Matrices predicted by the de novo motif-discovery algorithm Weeder A Subset of Multiple Transcription-Factor-Binding Loci MTL: Multiple Transcription-Factor-Binding Loci • Plot of the number of TFs bound per co-bound locus. The distribution of randomly occurring co-bound loci is obtained by simulation A Subset of Multiple Transcription-Factor-Binding Loci Distribution of clusters with different numbers of co-bound TFs. (Promoter regions are defined ass sequences 2500 bp upstream and 500 bp downstream of TSS) MTL Associated with Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, Smad1, and STAT3 as ES-Cell Enhanceosomes 32.9% 43.4% 87.4% 56.8% The convergence of the two key signaling pathways (via Smad1 and STAT3) with the core circuitry defined by Nanog, Oct4, and Sox2 MTL Associated with Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, Smad1, and STAT3 as ES-Cell Enhanceosomes The binding sites of Nanog group are likely ES-cell specific enhancers MTL Associated with Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, Smad1, and STAT3 as ES-Cell Enhanceosomes The binding of Smad1 and STAT3 depend on Oct4, but otherwise is not p300 Is Recruited to the Nanog-Oct4-Sox2 Cluster the occurrence of p300 in different MTL types • p300 was found to co-occur with the Nanog-Oct4-Sox2 cluster • Most p300-binding sites are associated with 3–6 other TFs • The composition of most p300containing clusters include Nanog, Oct4, or Sox2 p300 Is Recruited to the Nanog-Oct4-Sox2 Cluster ChIP-qPRC of p300 Binding of p300 to the genomic sites depends on Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog motif from p300-enriched sequences resembles the sox-oct element Outline • ES-cell specific enhanceosomes Mapping of Binding Sites of 13 TFs by Using ChIP-seq Motif Analyses of TFBSs A Subset of Multiple Transcription-Factor-Binding Loci Nanog-Oct4-Sox2 cluster function as ES-Cell enhanceosomes p300 Is Recruited to the Nanog-Oct4-Sox2 Cluster • ES-cell Regulatory Network Combinatorial Binding of TFs is correlated with ES-CellSpecific Expression Regulatory Network Defining ES-Cell Specific Expression Combinatorial Binding of Transcription Factors Is Associated with ESCell-Specific Expression Class I genes are enriched in binding sites for Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, Smad1 Class II genes are bound heavily by c-Myc and n-Myc Combinatorial Binding of Transcription Factors Is Associated with ESCell-Specific Expression the expression level of classI, class II and III are higher than genes in class IV and class V 60% of genes upregulated in ES cells are from class I and class II Combinatorial binding patterns of TFs have predictive power for EScell-specific expression Regulatory Network Defining ES-Cell Specific Expression • Aim: – Construct a network that specifies ES-cells • Dataset: – 2 public undifferentiated v.s differentiated gene expression datasets. – Chip-Seq results generated by this study Regulatory Network Defining ES-Cell Specific Expression Workflow (1) Gene • Two tables TSS – Genes ranked by their expression fold change – Genes ranked by their binding score to a TF K= 10 kb K= K+ 10 kb Expression-ranked genes list Big Binding-ranked genes list Yes No Chip-Seq peaks in TSS ± k ? Yes K <= 1Mb ? No Fold-Change Score = 0 Score = # Tags associated with called peak Small +k -k TSS Regulatory Network Defining ES-Cell Specific Expression Workflow (2) Note: A responder analysis is one in which each subject is classified as either a ‘responder’ or a ‘non-responder’. Expression-ranked genes list Binding-ranked genes list for a TF Responder Analysis TF Gene ESC regulatory network Summary • TFs are wired to the ES-cell genome in two major ways. – Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, Smad1, STAT3 – c-Myc, n-Myc, Zfx, E2f1 • Highly dense binding loci involving these factors have characteristic features of enhanceosomes • The coactivator p300 is predominantly recruited to dense binding loci involving proteins found in the first cluster • Constructed a transcriptional regulartory network model that integrates the two key signaling pathways with the intrinsic factors in ES cells. Discussion (1) -- comparison Chen et al • • The authors did a concurrent survey of the location of multiple TF in a single cell type. Shares some similarities to the work of Kim et al. Chen et al Kim et al Organism Mouse Mouse TF 13 TF+ 2 TR 9 TF Platform Chip-Seq promoter DNA microarrays Anti-body Target endogenous proteins Target biotin-tagged proteins Network constructio n Chip-Seq + Gene expression Chip-Seq + PPI Number of networks 1 3 Kim et al STAT3, Smad1, Oct4, Sox2, Zfx, Klf4,c-Myc, n-Myc, Nanog Esrrb, Tcfcp2l1, E2f1,CTCF Dax1, Rex1, Zpf281 , Nac1 Discussion (2) -- enhancersome Enhanceosome : is a nucleoprotein complex composed of distinct sets of TFs bound directly or indirectly to enhancer DNA • The study showed that the Nanong-Oct4-Sox2 cluster exhibits features of enhencesome: – The binding sites are densely clustered within relatively compact genomic segments. – These regions act as enhancer when placed downstream of the luciferase reporter. – Associated with active region marks (H3K4me3). – P300 (enhancer marker) is recruited to the Nanog-Oct4-Sox2 cluster. Daniel,P. et al, Cell, 2007 Thanos,D. and Maniatis,T., Cell, 1995 Discussion (3) -- weakness • To further confirm the enhancersome's function genome wide and the relationship between the different TFs - STARR-seq - biochemical verification • The network might involve more regulatory factors. Acknowledgements Pro Ren Group members: Zehua Liu, Jingyi Wu, Mohamed Nadhir Djekidel All the audience