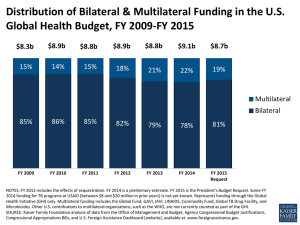
Presentation
advertisement

Responsibility To Rebuild (R2Rb) David Suntha- BA (Hons), MA, LLM (Merit) Paper Outline R2Rb = binding responsibility on states to rebuild/build states. = multilateral state practice has normalised the R2Rb within international relations Clearest examples: Reconstruction postWWII Europe and Asia Part I English School/Liberal Realism - the international system = beyond a global ‘state of nature’ “- sustained formal structure as an anarchical society of sovereign states governed by international law and other mechanisms and communicating among themselves through the institution of diplomacy. Part 1 Cont… IR = social activity with its own set of norms, rules and institutions, whether they be procedural, prudential, moral, and legal. ES - School prizes international ‘order’ and a lack of radical or large-scale change as the norm of IR. Part 1 cont… Post-CW, ES dominates IR through the UN and humanitarianism interventionism. ES utilised to advance Liberal Peace Theory “create a state defined by rule of law, markets, and democracy” Part II “if you break it, you own it” – Colin Powell paraphrasing Geneva Conventions. R2Rb = Norm of IR, built up from States Practice through multilateral institutionsWorld Bank, International Monetary Fund and United Nations. Older than R2P- Sykes-Picot agreement of 1917; League of Nations Mandate System, Post WW II Europe & Asia reconstruction. Part II cont… An Agenda for Peace cemented R2Rb as binding obligation on states= reverted to ‘mandate’ system established in UN Charter Eg- Bosni, Kosovo, Timor Leste, State led R2Rb continues as state led initiatives: - Russia in Abkhazia, South Ossetia & Crimea Part II cont… Liberal realist concerns= intro unstable elements into the international community: -e.g - Kosovan Diaspora and criminal enterprise: Organ smuggling. [1] International Monetary Fund. 2013. Op Cit Part II cont… UNSMIL: arguably rapidly expanded binding nature of R2Rb - reaffirmed Libyan ownership though emphasized mandate similar to Kosovo and Timor Leste. United Nations. 2011. Resolution 2009 (2011). Adopted by the Security Council at its 6620th meeting, on 16 September 2011. Available at: http://daccess-ddsny.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N11/502/44/PDF/N1150244.pdf?OpenElement (Accessed: 17/04/2012) Conclusion Legally a tentative argument can be made for R2Rb Politically and practically R2Rb remains controversial and limited due to incurred costs for states.