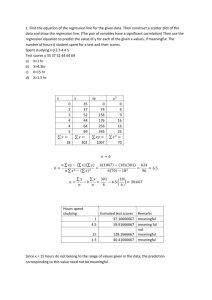
Plant Physiology, 5e

Experiment published by Jan Baptisa van Helmont in 1648:
"...I took an earthenware vessel, placed in it 200 pounds of soil dried in an oven, soaked this with rainwater, and planted in it a willow branch weighing 5 pounds. At the end of five years, the tree grown from it weighed 169 pounds and about 3 ounces. Now, the earthenware vessel was always moistened (when necessary) only with rainwater or distilled water, and it was large enough and embedded in the ground, and, lest dust flying be mixed with the soil, an iron plate coated with tin and pierced by many holes covered the rim of the vessel. I did not compute the weight of the fallen leaves of the four autumns. Finally, I dried the soil in the vessel again, and the same 200 pounds were found, less about 2 ounces. Therefore 169 pounds of wood, bark, and root had arisen from water only."
Most of the weight of the tree came from carbon dioxide and water
6 CO
2
+ 6H
2
O + Light Energy --> C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
Figure 7.1 Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave
Figure 7.2 Electromagnetic spectrum
elodea leaf X 400
Figure 7.4 Schematic diagram of a spectrophotometer
Figure 7.8 Action spectrum compared with an absorption spectrum
Figure 7.15 Transmission electron micrograph of a chloroplast from pea ( Pisum sativum )
Figure 7.16 Schematic picture of the overall organization of the membranes in the chloroplast
Figure 7.6 Molecular structure of some photosynthetic pigments (A)
Figure 7.5 Light absorption and emission by chlorophyll
Figure 7.22 Transfer of electrons and protons in the thylakoid membrane
Figure 7.18 Four major protein complexes of the thylakoid membrane (B)
Figure 7.10 Basic concept of energy transfer during photosynthesis
Figure 7.21 Detailed Z scheme for O
2
-evolving photosynthetic organisms
Figure 7.30 Chemical structure and mechanism of action of two important herbicides
Figure 7.11 Relationship of oxygen production to flash energy
Figure 7.34 Regulation of photon capture and the protection and repair of photodamage
Figure 7.13 Enhancement effect
Figure 7.18 Four major protein complexes of the thylakoid membrane (A)
Figure 7.19 Funneling of excitation from the antenna system toward the reaction center
Figure 7.20 Structure of the trimeric complex; (B) From within the membrane
Figure 7.23 Orbital occupation diagram for ground and excited states of reaction center chlorophyll
Figure 7.26 Structure and reactions of plastoquinones that operate in photosystem II
Figure 7.31 Summary of the experiment carried out by Jagendorf and co-workers
Figure 7.32 Subunit composition (A) and compiled crystal structure (B) of chloroplast F
1
F o synthase
ATP
Figure 7.33 Similarities of photosynthetic and respiratory electron flow in bacteria (A)
Figure 7.35 Chemical structure of violaxanthin, antheraxanthin, and zeaxanthin