Document
advertisement

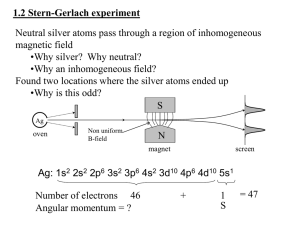
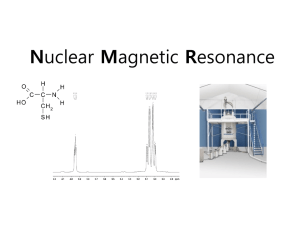
Lecture VI Many - electron atoms dr hab. Ewa Popko S-states probability P-states probability The Zeeman effect The Zeeman effect is the splitting of atomic energy and the associated spectrum lines when the atoms are placed in a magnetic field. This effect confirms experimentally the quantization of angular momentum. potential energy The potential energy of an object in a magnetic field depends on the magnetic moment of the object and the magnetic field at its location U B S N S N magnetic moment of a current loop The magnetic moment of a wire loop carrying current depends loop. a and the area a A of the current Iin the loop on the 1 2 3 4 Ib nˆ B Ib nˆ B 0 0 IA B 2 2 IA The Zeeman effect The orbiting electron is equivalent to a current loop 2 with radius r and area r . e The average current I is the average charge per unit time T for one revolution, given by T=2r/v. e ev 2 e e iA A r me vr L T 2r 2me 2m e The Zeeman effect Suppose B is directed towards z-axis. The interaction energy of the atom magnetic moment with the field is: U z B where z is the z-component of the vector . On the other hand: e z Lz 2m and Lz=ml with m l 0,1,2,3..... . Thus e U z B ml B ml B B 2m B Bohr magneton Zeeman effect The values of ml range from –l to +l in steps of one, an energy level with a particlular value of the orbital quantum number l contains (2l+1) diffrent orbital states. Without a magnetic field these states all have the same energy; that is they are degenerate. The magnetic field removes this degeneracy. In the presence of a magnetic field thy are split into (2l+1) distinct energy levels: U ml B B with ml 0,1,2,... Adjacent levels differ in energy by U (e / 2m)B B B μB e eV 5.79 105 2me T The Zeeman effect Energy diagram for hydrogen, showing the splitting of energy levels resulting from the interaction of the magnetic moment of the electron’s orbital motion with an external magnetic field. The Zeeman effect Splitting of the energy levels of a d state caused by an applied magnetic field, assuming only an orbital magnetic moment. Selection rules The photon carries one unit ( ) of angular momentum. Therefore the allowed transitions: l must change by 1 and ml must change by 0 or 1 Solid lines – allowed transitions; dashed forbidden Nine solid lines give only three energies: Ei-Ef ; Ei-Ef +BB; Ei-Ef -BB The Zeeman effect Conclusions: spectrum lines corresponding to transitions from one set of levels to another set are correspondingly split and appear as a series of three closely spaced spectrum lines replacing a single line. Anomalous Zeeman effect Spin angular momentum and magnetic moment Electron posseses spin angular momentum Ls. With this momentum magnetic momentum is connected: e s Ls me e s ge Ls 2me where ge is the gyromagnetic ratio For free electron ge=2 Spin angular Własny momentmomentum pędu - spin and magnetic moment Allowed values of the spin angular momentum are quantized : Ls s( s 1) 3 Ls 2 The z – component of the spin angular momentum: spin quantum number s = ½ Lsz ms 1 2 ms 1 2 The z- component of the spin magnetic moment sz e e Lsz me me 1 2 e sz B 2me Ls ms 1 2 1 ms 2 sz Electron in a magnetic field E E0 sz B ms 1 2 ms 1 2 To label completely the state of the electron in a hydrogen atom, 4 quantum numbers are need: name label magnitude Principal quantum number Orbital quantum number magnetic quantum number Spin quantum number n 1, 2, 3, ... l 0, 1, 2, ... n-1 ml ms od –l do +l ± 1/2 Many – electron atoms and the exclusion principle Central field approximation: - Electron is moving in the total electric field due to the nucleus and averaged – out cloud of all the other electrons. - There is a corresponding spherically symmetric potential – energy function U( r). Solving the Schrodinger equation the same 4 quantum numbers are obtained. However wave functions are different. Energy levels depend on both n and l. • In the ground state of a complex atom the electrons cannot all be in the lowest energy state. Pauli’s exclusion principle states that no two electrons can occupy the same quantum – mechanical state. That is, no two electrons in an atom can have the same values of all four quantum numbers (n, l, ml and ms ) Shells and orbitals n 1 shell K l orbital 0 s 2 L 0 s L 1 p M M M N N N N 0 1 2 0 1 2 3 s p d s p 3 4 d f Nmax - maximum number of electrons occupying given orbital Nmax 2 2 6 2 6 10 2 6 10 14 Shells K, L, M n 1 2 l 0 0 ml 0 0 3 1 -1 0 0 1 0 1 -1 0 2 1 -2 -1 0 1 2 ms N 2 8 18 N : number of allowed states state with ms = +1/2 state with ms = -1/2 Hund’s rule - electrons occupying given shell initially set up their spins paralelly carbon oxygen 1s22s22p2 1s22s22p4 The periodic table of elements Atoms of helium, lithium and sodium n =3, l = 0 3s n =2, l = 1 n =2, l = 1 2p n =2, l = 0 n =2, l = 0 n =2, l = 0 2s n =1, l = 0 n =1, l = 0 n =1, l = 0 1s Helium (Z = 2) Lithium(Z = 3) Sodium (Z= 11) Electron configuration – the occupying of orbitals 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p6 7s2 6d10 5f14 K : 1s 2 3 p 6 4 s1 Ca : 3 p 6 4s 2 Sc : 3d 1 4 s 2 Ti : 3d 2 4 s 2 V: 3d 3 4 s 2 Cr : 3d 5 4 s1 Mn: 3d 5 4 s 2 Cu : 3d 10 4 s1 Total angular momentum - J J L LS J j j 1 Possible two magnitudes of j : J z m j , j l s or j l-s m j j, j 1,, j 1, j Example: l = 1, s = ½ j 1 12 3 2 lub j 1 12 1 2 m j 23 , 12 , 12 , 23 lub m j 12 , 12 j = 3/2 j = 1/2 TheStern-Gerlach experiment Diamagnetics .Diamagnetics Shells totally filled with electrons. Total magnetic moment equals zero. (In a filled orbital, the vectors for both the orbital angular momentum and the spin angular momentun point in all posible directions and thus cancel). • Noble gas - He, Ne, Ar….. • diatomic molecule gas - H2, N2….. • solid states of ionic bonds - NaCl(Na+, Cl-)… • solid states of covalent bonds - C(diamond), Si, Ge….. • most organic materials Paramagnetics . Paramagnetics Shells partially filled with electrons Total magnetic moment different from zero. ef g J ( J 1) B The component of the magnetic moment directed towards external magnetic field ef ,H g M J B Fine and hyperfine structure Line splittings resulting from magnetic inetractions are called fine structure. The nucleus of the atom has also magnetic dipole moment that interacts with total magnetic moment of electrons. These effects are called hyperfine structure. NMR ( nuclear magnetic resonance) Like electrons, protons also posses magnetic moment due to orbital angular momentum and spin ( they are also spin-1/2 particles) angular momentum. Spin flip experiment: Protons, the nuclei of hydrogen atoms in the tissue under study, normally have random spin orientations. In the presence of a strong magnetic field, they become aligned with a component paralell to the field. A brief radio signal flips the spins; as their components reorient paralell to the field, they emit signals that are picked up by sensitive detectors. The differing magnetic environment in various regions permits reconstruction of an image showing the types of tissue present. An electromagnet used for MRI imaging Wilhelm Roentgen 1895 Roentgen lamp Roentgen 1895; X -ray: 10-12m – 10-9m me v 2 hc eVAC h max 2 min X-ray continuum spectra me v 2 hc eVAC h max 2 min min hc eV AC X-ray spectra and Moseley law min hc eV AC The continous –spectrum radiation is nearly independent of the target material. Sharp peaks (characteristic spectra) depend on the accelerating voltage and the target element. Frequencies of the peaks as a function of the element’s atomic number Z: f (2.48 10 Hz)(Z 1) 15 Moseley law 2 X-ray spectra and Moseley law - explanation Characteristic x-ray radiation is emitted in transitions involving the inner shells of a complex atom. Let us assume, that due to electric field one of the two K – electrons is knocked out of the K shell. The vacancy can be filled by another electron falling in from the outer shells. Ka is the transition from n=2 to n=1. As the electron drops down it is attracted by Z protons in the nucleus screened by the one remaining electron in the K shell. The energy before (Ei) an after (Ef) transition: Ei (Z 1) (13.6eV ) / 2 2 2 E f ( Z 1) 2 (13.6eV ) E K ( Z 1) 2 (10.2eV ) a E 15 2 f (2.47 10 Hz)( Z 1) h X-ray diffraction pattern X-ray diffraction pattern X Diffraction maxima: 2d sin m