Composite fermion groundstate of Rashba spin
advertisement

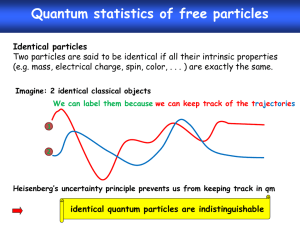
Composite Fermion Groundstate of Rashba Spin-Orbit Bosons Alex Kamenev Fine Theoretical Physics Institute, School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Minnesota Tigran Sedrakyan Leonid Glazman ArXiv1208.6266 Chernogolovka QD2012 Motivation Four-level ring coupling scheme in 87Rb involving hyperfine states |F,mF> Ramancoupled by a total of five lasers marked σ1, σ2, σ3, π1, and π2 Spin-orbit coupling constant Rashba spin-orbit-coupling Rotation + two discrete time-reversal parity symmetries Bose-Einstein condensates of Rashba bosons Interaction Hamiltonian: H int density operators 1 2 2 2 d r g ( n n ) g ( n n ) 0 2 2m TRSB g2 0 1 ikr 1 k ~ e i arg(k ) 2 e Spin-density wave g2 0 k ~ 1 cos(kr) i sin( kr ) 2 Chunji Wang, Chao Gao, Chao-Ming Jian, and Hui Zhai, PRL 105, 160403 (2010) Chemical Potential: density However, let us look at Rashba fermions: Spin-orbit coupling constant k0 2kF k0 mv Estimate chemical potential: (2k0 ) (2kF ) ~ 4 2n Near the band bottom, the density of states diverges as ( E) ~ 1 / E k F2 EF ~ n2 2m As in 1D! Reminder: spinless 1D model mean-field bosons spinless fermions k 0 exact bosons Lieb - Liniger 1963 n 0 n k Tonks-Girardeau limit g1D Can one Fermionize Rashba Bosons? Yes, but… 1. Particles have spin 2. The system is 2D not 1D Fermions with spin do interact Eint g (1 cos ) g k0 2kF Hartree Fock 2kF Variational Fermi surface Ekin n k k0 2 F 2 Eint gn 2 minimizing w.r.t. 1/ 4 n 2 gk0 Ekin g 3/ 2 Eint n n k0 Berg, Rudner, and Kivelson, (2012) 2 Self-consistent Hartree-Fock for Rashba fermions Berg, Rudner, and Kivelson, (2012) nematic state Elliptic Fermi surface at small density: (k x k0 ) 2m 2m y 2 H HF nematic fermions k y2 k02 my m m gn g 3/ 2 n gn k0 mean-field bosons Fermionization in 2D? Chern-Simons! bosonic wave function Chern-Simons phase fermionic wave function (plus/minus) One flux quantum per particle Broken parity P Higher spin components are uniquely determined by the projection on the lower Rashba brunch Fermionic wave function is Slater determinant, minimizing kinetic and interaction energy Chern-Simons magnetic Field mean-field approximation Particles with the cyclotron mass: in a uniform magnetic field: Integer Quantum Hall State Particles with the cyclotron mass: in a uniform magnetic field: Landau levels: One flux quanta per particle, thus n=1 filling factor: IQHE Gapped bulk and chiral edge mode: interacting topological insulator Phase Diagram chemical potential Bose Condensate broken R and T Spin-Density Wave broken R broken R, T and P Composite Fermions spin anisotropic interaction Phase Separation total energy per volume Bose condensate composite fermions phase separation Rashba Bosons in a Harmonic Trap condensate composite fermions high density Bose condensate in the middle and low density composite fermions in the periphery Conclusions At low density Rashba bosons exhibit Composite Fermion groundstate CF state breaks R, T and P symmetries CF state is gaped in the bulk, but supports gapless edge mode, realizing interacting topological insulator CF equation of state: There is an interval of densities where CF coexists with the Bose condensate In a trap the low-density CF fraction is pushed to the edges of the trap Lattice Model In a vicinity of K and K’ points in the Brillouin zone: