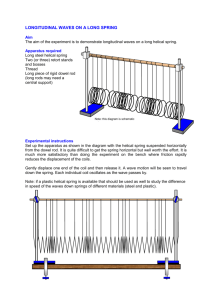
Part I: Magnetic field induced quasi
advertisement

SYNTHETIC HELICAL LIQUID IN A QUANTUM WIRE George I. Japaridze Ilia state University and Andronikashvili Institute of Physics SYNTHETIC HELICAL LIQUID IN A QUANTUM WIRE What is a helical liquid (HL)? Unconventional State of matter with spin-momentum locking p p S S SYNTHETIC HELICAL LIQUID IN A QUANTUM WIRE What is a helical liquid (HL)? Unconventional State of matter with spin-momentum locking Helical modes: where do they occur? topological insulators Pankratov, Pakhomov & Volkov, SSC 61, 93 (1987) Hasan and (edges): Kane, RMP 82, 3045 (2010) quasi-­­1d Super Cond superconductors: Pot t er and Lee, PRL 105, 227003 (2010) Semiconducing Streda and Seba, PRL 90, 256601 (2003) nanowires: -magnetic Braunecker, Japaridze, Klinovaja, DL, PRB 82, 045127 (2010) field carbon nanotubes: Klinovaja, Schmidt, Braunecker, DL, PRL 106 156809 (2011), and PRB 84, 085452 (2011) Insulators with Strong Spin-Orbit Interaction:Spin-Hall Effect: Edge states L. Fu, C. L. Kane and E. J. Mele PRL 98, 106803 (2007). J. E. Moore and L. Balents, PRB 75, 121306(R) (2007). S.-C. Zhang, Nature Physics 1, 6 (2008). Majorana Fermions in 1d Alicea, PRB 81, 125318 (2010) Oreg, Refael, and von Oppen, PRL 105, 177002 (2010) Lutchyn, Sau, and Das Sarma, PRL 105, 077001 (2010) Kitaev, Phys.-­Usp. 44, 313 (2001) Alicea, Oreg, Refael, v.Oppen, Fisher, Nature Phys.7,412 (2011) Gangadharaiah, Braunecker, Simon, DL, PRL 107, 036801 (2011) Semiconducting Nanowires Various materials: ZnO, InAs, InP, GaAs, AlAs, Ge, Si, SiGe, GaN, GaP, CdS, … Operate both in the conduction band (CB) and valence band (VB) ELECTRONS Charge: similar Spin: very different HOLES Particularly characteristic for semiconductors Holes turn out to be advantageous in many aspects! Ge/Si Core/Shell Nanowires Xiang et al., Nature (2006); Hu et al., Nat. Nano (2007); Hu et al., preprint (2011) Ex Nanowire grown along [110] Large Ge/Si valence band offset of ~ 0.5 eV, narrow interfaces → replace with hard wall at core radius Rc ≡ R Lauhon et al., Nature (2002), Lu et al., PNAS USA (2005) v E Lorenz transformation H •c v=0 E • The 1D lattice Hamiltonian: Hl a t = − t , (c†n ,σ cn +1,σ + h.c.) n ,σ + +αR (c† , f , [ † − c c n ,↑ n +1,↓ n ,↓ cn +1,↑ ) + h.c.] n U ρn , ↑ ρn ,↓ + V ρn ρn +1 + JS n · S n +1 ... n V. Gritsev, G. Japaridze, M. Pletyukhov, and D. Baeriswyl , Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 137207 (2005). S. Gangadharaiah, J. Sun, and O. A. Starykh, Phys. Rev. B 78, 054436 (2008). Part I: Magnetic field induced quasi-helical liquid state in a disordered 1D electron system with strong spin-orbit interaction Anders Ström, Bernd Braunecker and G.J. PRB 87, 075151 (2013). Helical mode: spin coupled to momentum Rashba spin-orbit field along z-axis H R px z 04. pptx e.g. InAs nanowire λSO ~ 100 nm, Fasth et al., PRL 98, 266801 (2007) Helical Hole States Kloeffel, Trif, DL, arXiv:1107.4870 E-field along x: Rc = 5.0 nm Rs = 6.5 nm strong Rashba SOI (~ 1-10 meV) Ex = 6 V/µm No RSOI! Helical Hole States Kloeffel, Trif, DL, arXiv:1107.4870 E-field along x: Ex = 6 V/µm strong Rashba SOI (~ 1-10 meV) Bx opens a gap 0.8 T:~ 0.25 meV 0.3 T: ~ 0.10 meV Rc = 5.0 nm Rs = 6.5 nm Helical States from Rotating Zeeman Field Braunecker, Japaridze, Klinovaja, Loss, PRB 82, 045127 (2010) 2kF local spin basis transformation: spin-dependent shift in k-space 2kF 2kF Effect of Interaction : strong renormalization of Zeeman gap! see also, Stoudenmire, Alicea, Starykh, Fisher, PRB 84, 014503 (2011) Band structures Spins look antiparallell for opposite velocities. Helical? Corrupted by the magnetic field HS! Let’s calculate the spin overlaps! Band structures Spin Overlaps Limits: Band structures Spin Overlaps Detail for aa overlap. 0.3 meV (ca 1 T) yields overlap squared of about 0.01. Disorder: Anderson Localization in 1D !! (absent in the Helical Liquid State!!) Overlaps: Limits: Disorder RG Scaling equations! For full Luttinger liquid with spin: For spinless or helical Luttinger liquid: Above gap Below gap Disorder Localisation length Can have loc. from ab disorder, if gap is smaller than ca 6ehjhjhjee5 eV, almost 1 K. Below the gap, we only need to consider disordered aa backscattering. 01.pptx Part II: SYNTHETIC HELICAL LIQUID IN A QUANTUM WIRE Mariana Malard, Henrik Johannesson and GJ PRB 89, 201403(R) (2014). Band picture insulating phase branch 2 (k ) _ _ + + F k F q0 k F q0 k F q0 Q 2(k F q0 ) k k F q0 Band picture conducting helicalbranch electron 2 liquid (k ) p _ S _ + p S + F k F q0 k F q0 k F q0 Q 2(k F q0 ) k F q0 k Our proposal HL in a quantum wire using electrical fields only and standard nanoscale semiconductor technology! modulation of the spin-orbit Rashba interaction top nanogates quantum wire Semiconduc tor heterostructu re + spin-orbit Dresselhaus + e-e interactions The MODEL hopping and chemical potential + uniform Rashba and Dresselhaus interactions + modulated Rashba interaction + e-e interaction Effective theory sine-Gordon potential relevant for K<½ gap helical Dirac hamiltonian branch-mixing potential For future success in building of GermanGeorgian Science Bridge Thank you for your attention!