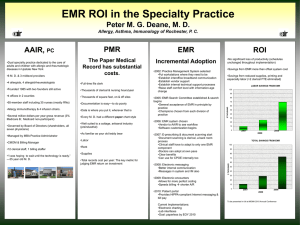
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)
advertisement

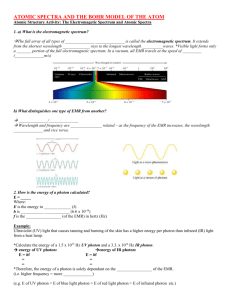
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) •Electromagnetic radiation is does not need a medium to travel through, this is what really makes it special. •EMR displays wave properties and is made up of two alternating fields, and electric field and a magnetic field •Applet •This can be a little difficult because EMR acts as a wave, but has no medium, only changing fields which transfer energy Electromagnetic Spectrum • The electromagnetic spectrum describes all of the different types of light • EMR spectrum • There are many trends found on the EMR Spectrum including f, λ, and energy The visible spectrum Radio Spectrum The speed of light • The speed of light is thought to be the universal speed limit, 3 X 108 m/s or 186,000 miles/second in a vacuum • Light travels slower in other mediums • It has its own constant c • E=mc2 • One of the early experiments to determine the speed of light was the Michelson-Morely experiment Absorption of light • As you may know, when an atom is excited, its electrons jump to an “excited state” when they relax, they give of light. • You can excite an atom by heating it, or having it absorb an electron • When it drops back to ground state, it gives off a “photon of light” Microwave Cooking • You can also do the reverse, you can make something hot by bombarding it with light • Certain bond lengths absorb certain types of EMR • Microwave cooking applet Light absorption Duality of light • Light behaves as a wave but it also behaves as a particle or “photon” • A photon can be thought of as a packet of energy, or a particle of light • Light acts like a wave or a particle depending on the experiment you are doing • This is confusing stuff, and at this level we have to just accept it Polarization of light • The plane of natural light spins as it propagates • When it reflects off of a horizontal surface, the plane tends to have vibrate in one direction • You can use Polaroid lenses to filter out glare Snell’s law is refraction • When light travels through the interface from a less dense medium to a more dense medium it bends toward the normal • When light travels through the interface from a more dense to a less dense medium it bends away from the normal • The normal, is a line drawn perpendicular to the boundry between the two materials Snell’s law Bow fishing Why its hard to shoot a fish! Lenses Critical angle • The critical angle is when the light no longer passes through a material and bounces off Mirrors • Mirrors reflect light • The angle of incidence always equals the angle of reflection Convex mirror Concave mirror Rods see black and white, cones see color Color • White light contains all of the colors of the visible EMR spectrum • In other words, white is the absence of color • Black is the absence of light • Newton’s color wheel How we see something • In order for us to see something that’s yellow a couple things must happen – The object must be illuminated by light that contains yellow light – The light must be reflected/scattered by the object and some light must end up on our retina – The color yellow must be the only one reflected – So for an object to be yellow, it must absorb all other colors except yellow that are shinning on it Additive/subtractive colors • When you add two or more different colors in a source of light, our brain interprets it as being a completely different color • Applet colored light and filters • Applet additive light • Pigments added to something like white paint don’t add colors, they subtract colors