Derivation of the Nernst Equation:
advertisement

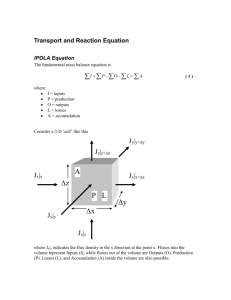
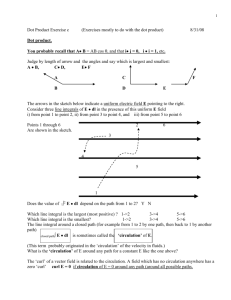
Derivation of the Nernst Equation: [𝑪]𝒓 𝒍𝒏 =(𝑽𝒍 [𝑪]𝒍 −𝑽𝒓 ) Why else do we care? What else? Other health conditions besides atrial fibrillation may result from problems with membrane potential: 1)Cystic fibrosis—poor chloride movement across the membranes 2)Epilepsy may be due to poorly working voltage gated channels Intuitive picture for Flux We start with diffusive flux: Concentration per volume=mol/cm^3* 1/cm Putting them together: 𝜕𝑉 Electric Drift: 𝐽𝐷𝑟𝑖𝑓𝑡= − 𝜇𝑧[𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 𝑐𝑚2 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑠 𝑐𝑚4 𝑐𝑚2 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑉 𝑉𝑠 𝑐𝑚3 𝑐𝑚 Combining the Drift and the Diffusion: 𝜕[𝐶] 𝐽𝐷𝑟𝑖𝑓𝑡 + 𝐽𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓= -D 𝜕𝑥 - 𝜕𝑉 𝜇𝑧[𝐶] : 𝜕𝑥 Getting everything in terms of mobility: Replace D with the Boltzmann constant : D= 𝑘𝑇𝑞 𝜇 𝑘𝑇 𝜕[𝐶] 𝐽𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙= - 𝜇 𝑞 𝜕𝑥 - 𝜕𝑉 𝜇𝑧[𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 More on the Boltzmann constant from Wikipedia: The Boltzmann constant (k or kB) is a physical constant relating energy at the individual particle level with temperature. It is the gas constant R divided by the Avogadro constant NA. k=R/ NA (See thermally agitated molecule) Looking more like it: 𝑅𝑇 𝜕[𝐶] 𝐽𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙= - 𝜇 𝐹 𝜕𝑥 - Replace 𝜕𝑉 𝜇𝑧[𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 R is the ideal gas constant and F is the Faraday constant 𝑘𝑇 𝜇 𝑞 with 𝑅𝑇 𝜇 𝐹 More on the Faraday constant from Wikipedia: (one mole of electrons) In physics and chemistry, the Faraday constant (named after Michael Faraday) is the magnitude of electric charge per mole of electrons.[1] It has the currently accepted value F = 96,485.3365(21) C/mol.[2] The constant F has a simple relation to two other physical constants: where: F=eNA e ≈ 1.6021766×10−-19 C;[3] NA ≈ 6.022141×1023 mol−1.[4] NA is the Avogadro constant (the ratio of the number of particles 'N' to the amount of substance 'n' - a unit mole), and e is the elementary charge or the magnitude of the charge of an electron. One Mole of Particles: Multiply both sides by F and z: F*z*(𝐽𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 )=F*z* (- 𝑅𝑇 𝜕[𝐶] 𝜇 𝐹 𝜕𝑥 - 𝜕𝑉 𝜇𝑧[𝐶] ) 𝜕𝑥 Cross out F in the diffusive flux; add the factor z in the drift expression Current Flux: 𝐼𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑓𝑙𝑢𝑥 = 𝐶𝑜𝑢𝑙.∗ 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑐𝑚2 𝑠 𝜕[𝐶] 𝜇𝑧𝑅𝑇 𝜕𝑥 - 𝜇𝐹𝑧 2 𝜕𝑉 [𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 Set equation=0 to get Nernst equation (no current) 0=- 𝜕[𝐶] 𝜇𝑧𝑅𝑇 𝜕𝑥 - 𝜇𝐹𝑧 2 𝜕𝑉 [𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 Factor out - 𝜇𝑧 0= - 𝜕[𝐶] 𝜇𝑧(𝑅𝑇 𝜕𝑥 +𝐹𝑧 𝜕𝑉 [𝐶] ) 𝜕𝑥 (We see that -𝜇𝑧 is a solution, so we can get rid of it.) Now we have the variables we want: 0=𝑅𝑇 𝜕[𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 + 𝐹𝑧 [𝐶] 𝜕𝑉 𝜕𝑥 Move the diffusive flux term over to the LHS 𝜕[𝐶] -𝑅𝑇 𝜕𝑥 𝜕𝑉 =𝐹𝑧[𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 Divide by -RT/Fz: 𝜕[𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 𝐹𝑧 𝜕𝑉 =− [𝐶] 𝑅𝑇 𝜕𝑥 Separation of Variables: 𝜕[𝐶] 𝜕𝑥 𝐹𝑧 𝜕𝑉 =− [𝐶] 𝑅𝑇 𝜕𝑥 Becomes 𝜕[𝐶] [𝐶]𝜕𝑥 𝐹𝑧 𝜕𝑉 =− 𝑅𝑇 𝜕𝑥 𝜕[𝐶] 𝐹𝑧 =− [𝐶] 𝑅𝑇 𝜕𝑉 Integration: Goldman-Hodgkin A little applet • http://www.nernstgoldman.physiology.arizon a.edu/#download