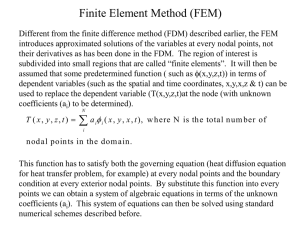
有限元法
advertisement

Theory of Elasticity
弹性力学
Chapter 8
Two-Dimensional Solution
平面问题的直角坐标求解
Content(内容)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Introduction(概述)
Mathematical Preliminaries (数学基础)
Stress and Equilibrium(应力与平衡)
Displacements and Strains (位移与应变)
Material Behavior- Linear Elastic Solids(弹性应力应变关系)
Formulation and Solution Strategies(弹性力学问题求解)
Two-Dimensional Formulation (平面问题基本理论)
Two-Dimensional Solution (平面问题的直角坐标求解)
Two-Dimensional Solution (平面问题的极坐标求解)
Three-Dimensional Problems(三维空间问题)
Bending of Thin Plates (薄板弯曲)
Plastic deformation – Introduction(塑性力学基础)
Introduction to Finite Element Mechod(有限元方法介绍)
Chapter 13
Page
1
Introduction to Finite Element Mechod
(有限元方法介绍)
• 13.1 Numerical Methods (数值方法)
• 13.2 Basics of the Finite Element Method (有限元
法基础)
• 13.3 Approximating Functions for TwoDimensional Linear Triangular Elements (二维线
性三角形单元的近似函数)
• 13.4 Virtual Work Formulation for Plane Elasticity
(平面弹性虚功方程)
• 13.5 A Simple Example (简单例子)
• 13.6 FEM Code Application (有限元序程的应用)
Chapter
13
Page
2
13.1 Numerical Methods
(数值方法)
Three numerical methods (三种数值方法)
Finite dfifference method (FDM) (有限差分法)
Finite element method (FEM) (有限元法)
Boundary element method (BEM) (边界元法)
Chapter
13
Page
3
13.1 Numerical Methods
(数值方法)
History of FEM (有限元发展历史)
•In 1943,Courant proposed a approximative
method in his mathematic paper which was
similar to FEM
(1943年Courant在他的应用数学论文中首先提出了
一个与有限单元法类似的近似方法。)
•In 1960,Clough proposed Finite Element Method
(FEM)
( 1960年,Clough提出了有限元法)
Clough
Chapter
13
Page
4
13.2 Basics of the Final Element Method
(有限元法基础)
Element and Node (单元和节点)
node (节点)
element(单元)
FEM discretizes the domain under study by dividing the region
into subdomains called elements.
(有限元方法将研究区域离散成许多子域,这些子域叫单元)
Chapter
13
Page
5
13.2 Basics of the Final Element Method
(有限元法基础)
Typical basic steps (典型基本步骤)
1. Discretize the body into a finite number of element
subdomains (离散)
2. Develop approximate solution over each element in terms
of nodal values (写出单元刚度矩阵)
3. Based on system connectivity, assemble elements and
apply all continuity and boundary conditions to develop an
algebraic system of equations among nodal values (形成总体
刚度矩阵并引入连续条件和边界条件)
4. Solve assembled system for nodal values; post process
solution to determine additional variables of interest if
necessary (求解节点值和后处理)
Chapter
13
Page
6
13.3 Approximating Functions for TwoDimensional Linear Triangular Elements
(二维线性三角形单元的近似函数)
Displacement interpolation functions (位移插值函数)
we wish to investigate procedures necessary to develop a linear
approximation of a scalar variable u(x,y) over an element.(需要选
定一个位移模式,来表示单元中的位移函数)
Assume a linear approximation: (假设为线性的)
u(x, y) c1 c2 x c3 y
For every node
u(x1 , y1 ) c1 c2 x1 c3 y1
u(x 2 , y 2 ) c1 c2 x 2 c3 y 2
u(x 3 , y3 ) c1 c2 x 3 c3 y3
Chapter
13
Page
7
13.3 Approximating Functions for TwoDimensional Linear Triangular Elements
(二维线性三角形单元的近似函数)
Displacement interpolation functions (位移插值函数)
the constants ci can be expressed
in terms of the nodal values ui (常
数ci可用节点的值ui表示)
c1
1
1u1 2u2 3u3
2 Ae
1
1u1 2u2 3u3
c2
2 Ae
Where :
1
1u1 2u2 3u3
c3
2 Ae
Chapter
13
Page
i x j y k xk y j
i y j yk
i xk x j
8
13.3 Approximating Functions for TwoDimensional Linear Triangular Elements
(二维线性三角形单元的近似函数)
So we obtain :
1
u ( x, y )
[1u1 2u2 3u3
2 Ae
1u1 2u2 3u3 x
3
1u1 2u2 3u3 y] ui i ( x, y )
i 1
Where Ψi are the interpolation functions for the triangular
element given by : (Ψi是三角单元插值函数)
1
i i x i y
i ( x, y)
2 Ae
Chapter
13
Page
Lagrange interpolation
functions (拉格朗日插值函数)
9
13.3 Approximating Functions for TwoDimensional Linear Triangular Elements
(二维线性三角形单元的近似函数)
1
i i x i y
i ( x, y)
2 Ae
It is noted that the form of the interpolation functions
depends on the initial approximation assumption and on the
shape of the element. (插值函数的形式取决于初始近似假设和
单元形状)
Chapter
13
Page
10
13.3 Approximating Functions for TwoDimensional Linear Triangular Elements
(二维线性三角形单元的近似函数)
description of element displacement filed (单元位移场
的表达)
u1
v
1
u 1 0 2 0 3 0 u2
v 0 1 0 2 0 3 v2
u 3
v3
i ( x, y)
Where:
Chapter
13
1
i i x i y
2 Ae
Page
11
13.3 Approximating Functions for TwoDimensional Linear Triangular Elements
(二维线性三角形单元的近似函数)
description of element strain filed (单元应变场的表达)
x x
( x, y ) y 0
z
x
0
u ( x, y )
[ ]u [ ][ ] [ B ][]
y v( x, y )
y
Where:
1
x
[ B] 0
1
y
Chapter
13
0
1
y
1
x
2
x
0
2
y
0
2
y
2
x
3
x
0
3
y
Page
0
1
3
1
0
y 2 Ae
1
3
x
12
2
0
3
1 0
1 2
2
2
0
0
3
0
3
3
13.3 Approximating Functions for TwoDimensional Linear Triangular Elements
(二维线性三角形单元的近似函数)
description of element stress filed (单元应力场的表达)
[C]{ } [C][B]{}
Where:
C11
[C ] C12
0
C12
C22
0
Chapter
0
0
C66
13
E
…plane stress
2
1
C11 C22 E (1 )
(1 )(1 2 ) …plane strain
E
…plane stress
2
1
C12
E
…plane strain
(1 )(1 2 )
C66
E
2(1 )
Page
13
…plane stress and plane
strain
13.4 Virtual Work Formulation for Plane
Elasticity (平面弹性虚功方程)
Virtual work formulation (虚功原理)
Ve
ij ij dV Ti nui dS Fiui dV
Se
Ve
Which can be written in compact form: (简洁写之)
{}T ([K ]{} {F} {Q}) 0 [ K ] he [ B]T [C ][B]dxdy Stiffness matrix
e
[ K ]{} {F} {Q}
Chapter
13
Fx
{F } he [ ]T dxdy Body force
e
vector
Fy
T
T x
{Q} he [ ] ds
Loading vector
e
T
y
Page
14
13.5 A Simple Example (简单例子)
Example:
例题:write the stiffness matrix of the element show in
figure. (求如图所示的单元在该坐标系下的刚度矩阵)
It is obviously :
xi a, x j 0, xm 0
yi 0, y j a, ym 0
Chapter
13
Page
15
13.5 A Simple Example (简单例子)
xj
ai
xm
yj
,
ym
1 yj
bi
,
1 ym
1 xj
ci
,
1 xm
(i, j, m)
bi a, b j 0, bm a
1
xi
1
A 1 xj
2
1 xm
Chapter
13
ci 0, c j a, cm a
yi
yj 。
a2
A
2
ym
Page
16
13.5 A Simple Example (简单例子)
k ii
k k ji
k
mi
k ij
k jj
k mj
1
1
b
b
c
c
b
c
c
b
k im
r s
r s
r s
r s
Et
k
2
2
,
rs
2
k jm
4(1 )A c b 1 b c c c 1 b b
r s
r s
r s
r s
2
2
k mm
r i, j, m; s i, j, m
1
0
0
Et
k
2(1 2 )
1
Chapter
13
1
2
1
2
0
1
2
1
2
对
1
2
0
1
2
1
2
Page
1
1
17
称
3
2
1
2
。
3
2
13.6 FEM Code Application
(有限元程序的应用)
Ansys application (Ansys 的应用)
Example 1:
Circular and circle Holes in a Plate Under Uniform Tension (中心
有孔的矩形板受拉)
FEM Mesh and load condition
Distribution of x-stress
(网格划分和载荷条件)
(X 向应分布)
Chapter
13
Page
18
13.6 FEM Code Application
(有限元程序的应用)
Example 2:
Circular Disk Under Diametrical Compression (受压圆盘)
FEM Mesh and load condition
Distribution of x-stress
(网格划分和载荷条件)
(X 向应分布)
Chapter
13
Page
19
13.6 FEM Code Application
(有限元程序的应用)
Abaqus application (Abaqus 的应用)
Example 1:
Circular and ellipse Holes in a Plate Under Uniform Tension (中
心有椭圆孔的矩形板左端固定,右端受拉)
FEM Mesh and load condition
Distribution of x-stress
(网格划分和载荷条件)
(X 向应分布)
Chapter
13
Page
20
Vocabulary(词汇)
Finite dfifference method (FDM)
有限差分法
Finite element method (FEM)
有限元法
Boundary element method (BEM)
边界元法
Triangular Elements
三角单元
Virtual Work
虚功
Node
节点
interpolation functions
插值函数
Ansys,Abaqus
有限元分析软件
Chapter
13
Page
21