longshore sediment transport
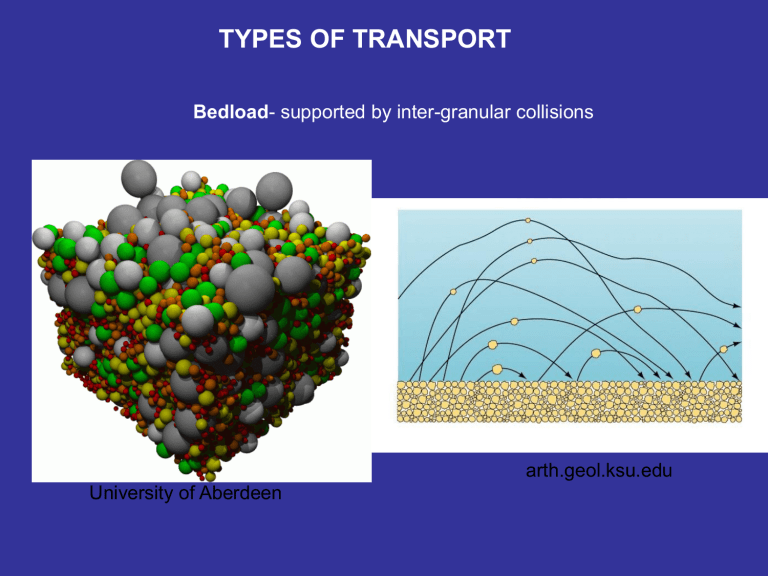
TYPES OF TRANSPORT
Bedload - supported by inter-granular collisions
University of Aberdeen arth.geol.ksu.edu
Univ twente
TYPES OF TRANSPORT
Suspended load - supported by turbulent fluctuations
LITTORAL TRANSPORT
Transport along the coast.
Can occur in both directions depending on wave climate
NET: sum of positive and negative drifts
GROSS: sum of positive and negative drift magnitudes .
How to measure???
No “miracle” longshore sediment transport meter exists!
LITTORAL TRANSPORT MEASURING TECHNIQUES
1) Current meters and optical or acoustic basckscatter sensors.
Product of 2 is estimate of instantaneous transport.
Difficulty, hard to image both signals over water column depth.
Bedload problematic, bubbles deteriorate signal.
FOBS
LITTORAL TRANSPORT MEASURING TECHNIQUES
2) Streamer traps or other trapping mechanism
Integrated transport only
Can get time dependent info
LSTF at ERDC
Komar, 1998
Sediment traps
LITTORAL TRANSPORT MEASURING TECHNIQUES
3) Amount of required dredge material
Dredge hole http://bio.sbcc.net/tur/img/aircc.jpg
LITTORAL TRANSPORT MEASURING TECHNIQUES
4) Tracer study: Use dyed or irradiated grains.
Geiger counter
LITTORAL TRANSPORT MEASURING TECHNIQUES
5) Continuity equation along with measured bathymetry differences
LITTORAL TRANSPORT CALCULATIONS
All essentially reduce to a form of the wave power
P
EC g sin
b b
Q
CP
With units of volume per time
C is NOT dimensionless
Better:
I
KP
KEC g sin
b b
With units of immersed weight per time
K IS dimensionless
LITTORAL TRANSPORT CALCULATIONS
The coefficient, K, is normally given as about 0.77 if Hrms is used.
Note the scatter and log-log scale
Slope gives K
LITTORAL TRANSPORT APPLICATIONS
Preceding based on breaker information which we rarely have.
If we make some assumptions like straight and parallel contours, negligble energy losses from offshore and small incidence angles at breaking, we can use Energy conservation, Snell’s Law and shoaling to relate equation to offshore parameters only.
Q
8 (
KH s
2
.
4
1 )( 1 g
0 .
6
T p )
0 .
2
2
1 .
4 cos
1 .
2
0 .
2
0 .
4 cos
0 .
2
b
S is ration of sediment to water density. If we assume breaker angle small than the cosine term in the denominator goes to one.
Still looks ugly
LITTORAL TRANSPORT APPLICATIONS
Littoral Drift Rose (LDR) can be used to shore variations in transport due to variations in shoreline orientation.
Drift roses are constructed using available data and longshore sediment transport equation.
D&D
LITTORAL TRANSPORT APPLICATIONS
LDR predicts accentuation of erosive feature
LDR predicts smoothing of erosive feature











