Basic Networking
advertisement

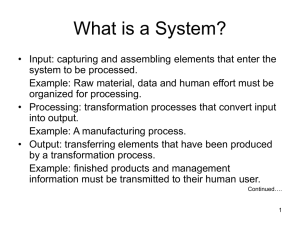
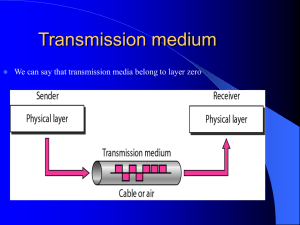
Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition Chapter 3 Checkup True or False 1. Transmission methods using fiber-optic cables achieve faster throughput than those using copper or wireless connections. 2. Seven bits form a byte. 3. A pulse of positive voltage represents a 0. 4. In frequency modulation, the frequency of the carrier signal is modified by the application of the data signal. 5. An access point is a device that accepts wireless signals from multiple nodes and retransmits them to the rest of the network. True or False 1. Transmission methods using fiber-optic cables achieve faster throughput than those using copper or wireless connections. 2. Seven bits form a byte. 3. A pulse of positive voltage represents a 0. 4. In frequency modulation, the frequency of the carrier signal is modified by the application of the data signal. 5. An access point is a device that accepts wireless signals from multiple nodes and retransmits them to the rest of the network. Multiple Choice 1. The distance between corresponding points on a wave’s cycle is called its ____. a. Phase c. amplitude b. Amplitude d. wavelength 2. The loss of a signal’s strength as it travels away from its source is known as ____. a. Impedance c. regeneration b. attenuation d. diffraction 3. _____ cable consists of color-coded pairs of insulated copper wires, each with a diameter of 0. 4 to 0. 8 mm. a. Coaxial c. Ethernet b. Twisted-pair d. Fiber-optic 4. ____ cable consists of twisted wire pairs that are not only individually insulated, but also surrounded by a shielding made of a metallic substance such as foil. a. Fiber-optic c. Shielded twisted-pair b. Ethernet d. Coaxial 5. ____ is a measure of the highest frequency of signal a multimode fiber can support over a specific distance and is measured in MHz-km. a. Broadband c. Latency b. Modal bandwidth d. Plenum Multiple Choice 6. The hardware that makes up the enterprise-wide cabling system is known as the ____. a. cable plant c. sheath b. plenum d. thinnet 7. An antenna’s ____ describes the relative strength over a three dimensional area of all the electromagnetic energy the antenna sends or receives. a. plenum c. radiation pattern b. frequency d. ferrule 8. In ____, a transmitter concentrates the signal energy at a single frequency or in a very small range of frequencies. a. structured cabling c. Webcasting b. narrowband d. broadband 9. ____ signals are transmitted by frequencies in the 300- GHz to 300,000-GHz range, which is just above the top of the wireless spectrum as it is defined by the FCC. a. Attenuation c. Infrared b. Braiding d. Broadcast 10. ____ signals are composed of pulses of precise, positive voltages and zero voltages. a. Analog c. Narrowband b. Digital d. Optical Multiple Choice 1. The distance between corresponding points on a wave’s cycle is called its ____. a. Phase c. amplitude b. Amplitude d. wavelength 2. The loss of a signal’s strength as it travels away from its source is known as ____. a. Impedance c. regeneration b. attenuation d. diffraction 3. _____ cable consists of color-coded pairs of insulated copper wires, each with a diameter of 0. 4 to 0. 8 mm. a. Coaxial c. Ethernet b. Twisted-pair d. Fiber-optic 4. ____ cable consists of twisted wire pairs that are not only individually insulated, but also surrounded by a shielding made of a metallic substance such as foil. a. Fiber-optic c. Shielded twisted-pair b. Ethernet d. Coaxial 5. ____ is a measure of the highest frequency of signal a multimode fiber can support over a specific distance and is measured in MHz-km. a. Broadband c. Latency b. Modal bandwidth d. Plenum Multiple Choice 6. The hardware that makes up the enterprise-wide cabling system is known as the ____. a. cable plant c. sheath b. plenum d. thinnet 7. An antenna’s ____ describes the relative strength over a three dimensional area of all the electromagnetic energy the antenna sends or receives. a. plenum c. radiation pattern b. frequency d. ferrule 8. In ____, a transmitter concentrates the signal energy at a single frequency or in a very small range of frequencies. a. structured cabling c. Webcasting b. narrowband d. broadband 9. ____ signals are transmitted by frequencies in the 300- GHz to 300,000-GHz range, which is just above the top of the wireless spectrum as it is defined by the FCC. a. Attenuation c. Infrared b. Braiding d. Broadcast 10. ____ signals are composed of pulses of precise, positive voltages and zero voltages. a. Analog c. Narrowband b. Digital d. Optical