lecture8-Intro to Video
advertisement

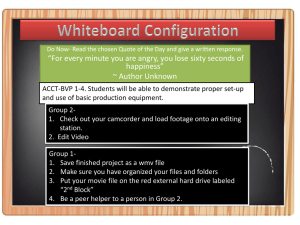
Introduction to Multimedia Lecture #9 Intro to Video Instructors: Mohamed MAGANGA Today’s Agenda 3 Topics Left •Video (pt.2) •Sound (1) •Review (1) 1. 2. 3. Announcements Warm Up Today’s Lecture Lect 9: Intro to Video “A good film is when the price of the dinner, the theatre admission and the babysitter were worth it.” Alfred Hitchcock Major Assignment - 10% Marking Criteria: 1. Technical: file organization, file names (lower case) 2. Color creativity 3. Website Design: content, layout, style, links 4. Video – Word Overlay, transitions, music, style 5. Animation: creativeness and how it was incorporated in the website EVERYTHING MUST BE WORKING TEST IT ALL 3 Warm Up Questions Which of the following terms means: “seeing two or three of the previous frames in order to predict where to put the next frame” a) Tweening b) Onion Skin c) Morphing Tweening: Process of ___________________________ to give the appearance that the first image evolves smoothly into the second image. Onion Skin: Creating animated cartoons and editing movies to see ____________________ Morphing: Process of blending together _______________ into a series of images 4 Warm up Questions: 1. Question: How many frames per second should we have when building an animation for display on a computer? 2. Question: A. B. C. D. 3. Which type of animation uses frames: Cel Based Path Based Both Neither Question: If an animation is 40 frames long and the fps is 5, how long will the animation take to play? Today’s Agenda Video – Part 1 What is Video Capturing Video Firewire vs USB Editing Video How TV Works Review 6 What is Video? Video uses the power of Motion and Sound A sequence of still images or frames that create the illusion of movement when played in succession. Movies Display at ______ fps Computer Displayed Video Display at ________ fps for smoothness 2 Types of Video: Analog: Smooth ___________ waves ex. Conventional TV Digital: Each frame is a _____________, stored as 0s and 1s Digital Video Digital Video is composed of a series of bitmap graphics, each one called a ____________. Characteristics: • Bits store color and brightness data for each video frame. • Retains image quality no matter how many times it is copied. • Easily manipulated on a pc because stored in digital format “Digital Technology is the same revolution as adding sound to pictures and the same revolution as adding color to pictures. Nothing more and nothing less.” - George Lucas, film maker of STAR Wars What kinds of Digital Videos? Classified by its platform or application (how it will be delivered) 1. Desktop video (DTV) • 2. Web-based video • 3. Incorporated in Web pages and accessed with a browser DVD-video • 4. Videos constructed and displayed using a personal computer A DVD format used for commercial DVDs that contain feature-length films. PDA video • Small-format video designed to be viewed on a PDA or cell phone screen How much planning goes into making a movie before the first scene is ever shot? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FvQV21hkMjI&feat ure=related (we will just watch the first 2 minutes) 10 Creating Digital Video 11 Ready to Make a Video – Assumption: you took the footage Let’s take a closer look! Capture Video •Download video from camcorder to computer 12 Edit Digital Video (using Computer, Digital Video software ex. Adobe Premiere, Avid) Edit it Add all kinds of cool titles Filters, transitions Superimpose clips Synchronize audio with video Authoring software: create menus and interactivity Output Video •Output to different file formats •Back out to tape, the Web, CD, DVD Capturing the Video with Camcorders If we use an: Analog Camcorder,: • Electronic impulses are recorded Must convert it to digital BEFORE we can put it on our computer to edit. To convert analog video to digital video we need a ___________ • • Digital Video Camcorder: • • Information is sent as _____________ Thus no need to convert! Capturing Video – Download video from camcorder to computer To use video in a multimedia application, it must be in digital form (0s and 1s) So how do you get a camcorder video into digitized form? Analog Video camera Video card Connecting Leads: 14 Digital camera Firewire or USB cable Software: Capturing, Editing, Outputting Digital Video Camcorders Most Digital Video Camcorders (DV Camcorders), do a little bit of compression right inside the camera. common DV compression used by today’s camcorders: DV25 is the most DV25 Format Specs: Pixel Dimension is 720 X 480 (note this is 3:2 ratio) Frame Aspect Ratio either 4:3 or 16:9 Data Rate: 25 mega bits per second (that’s why it is DV25) Frame Rate: 29.97 fps Colour Sampling: YUV 4:1:1 Colour Compression In The Camera For still images RGB is commonly used For video the model is YUV (YIQ) or YCbCr (for MPEG compression) Y luminanace (brightness) UV (CbCr) chrominance (color/hue) Question: Black and White TV only used the _____ signal (fill in the blank with Y, U or V) Answer: ______________________ Question: Which one will the human eye detect changes in more easily? How does this help us with compression? Answer:________________ Color Sampling Method for Video -compression technique You may see that the compression used 4:1:1 4:2:0 4:4:4 What does this mean? Assume we have 4 pixels Color Sampling: Refers to technique in digital video –compression technique BACKGROUND: in Video we do not store record all color in an image • Color Sampling allows Averages out pixels to cut down on bandwidth (faster transfer rates) • Eye senstivity: • Rods – light vs. dark, black vs. white -- not color • Cones – see color • We can detect brightness better than color (more rods) Color Sampling Method for Video http://dvxuser.com/articles/colorspace / You may see that the compression used 4:1:1 Color Sampling Method, What does this mean? Assume we have 4 pixels Red, Orange, Blue, Purple red + blue = Purple • 4:1:1 • Blocks of 4 pixels averaged out • 4 x 1 block Result: So all four pixels get forced to become purple (shades of brightness) Blocks of 4 pixels averaged out •4:2:0 •Blocks of 4 pixels averaged out •2x2 grid block Color Sampling Method for Video http://dvxuser.com/a rticles/colorspace Color Sampling Method Amount of Y (luminance) Amount of U (color or hue) Amount of V (color or hue) Amount of Compression 4:4:4 4 samples 4 samples 4 samples None 12 samples for each group of 4 pixels 4:2:2 4 samples 2 samples 2 samples Reduced from 12 samples to 8, 33% reduction in storage 4:2:0 4 samples 2 samples of either U or V, one 12 to 6, 50% scan line of U, then one scan reduction in / Used in Digital Betacam format HDV, MPEG-1, DVD, MPEG-2, Connection Types: Video •S video (better quality) •Yellow RCA Audio Firewire connection Sony Hi-8 20 TRV-80 To get the video off of your camera onto a computer you must use either: USB cables Firewire Video Capture Card Plugs directly • Converts video from ANALOG TO DIGITAL 21 Firewire (4 pin) USB Capturing Video –Video Capture Device Download video from camcorder to computer Firewire ( ________, _________) A means by which information could be sent from the camcorder directly to the computer A high-speed digital serial _________that allows the output of the camera to be fed directly into a computer in digitized form Digital Video footage requires 13GB of storage per hour of video. All major manufacturers agreed to use a common digital tape format and a method -- Firewire (universal standard) •4-pin to 4-pin plugs •4-pin to 6-pin plugs 22 •6-pin to 6-pin plugs Summarizing Analog vs Digital 1983 1994 ANALOG (Older Technology ) DIGITAL (Newer Technology) • Records electrical signals/pulses directly onto a medium (like a tape) with a magnetic encoding. • Disadv: Picture loses quality Video capture card needed to convert video from analog to digital for your computer 23 • Records a binary code (string of 1s and 0s) compressed on magnetic tape or other media • Adv: No image degradation Plug your video camera directly into your computer via a Firewire (aka i.Link) or USB connection. These are digital connections and allow you to "dump" footage straight from the camera to hard drive. Solid State Media Card - Memory Sticks A little history on TVs Digital video often adheres to standards for TV broadcasting – 2 standards NTSC Standard: Regular Analog TV broadcasting began in the United States in 1939 and carried through to today Frame rate was originally 30fps but when color was introduced, needed to go down to _______ fps to accommodate for colour information. PAL Standard: Britain, Europe and other countries Frame rate is set for _________ fps A little history on TVs Experiments with High Definition TV began in the late 40s and 50s but it wasn’t adopted by a single station till 1996. Before 1996 ALL TV was broadcast using _________________(see next slide) The original ANALOG video choices made about TV display (frames per second, frame size, etc..) affect the standards that were picked for DIGITAL video and applied today! How did the original TV display work? Our eyes see phosphor dots on the screen. An electron beam (gun) activates the dots. The gun scans through the dots horizontally A complete scan is when the gun starts at the top left and scans several times horizontally till it gets to the bottom right The scan only draws every OTHER line (1,3, 5, …479) then starts back at the top and draws the even lines (2,4,…480). Thus two passes Each pass is called a field The process is called Interlaced display This way it can cheat the eye, while the phosphor dots are disappearing, it is drawing the line underneath. How did the original TV display work? Increasing the frame rate in the old days required a lot more bandwidth, so they “cheated” and used interlacing to trick the eye Interlacing effect (old TVs) Line 1,3,5,7, Line 2,4,6,8.. Progressive effect ( not interlaced) (now used by Flat Screens because of the panel) Line 1,2,3,4,5,6,7.. http://www.crutchfield.com/Learn/learningcenter/home/understanding-resolution.html NTSC Standards NTSC Standard DV Frame: For NTSC 720 X 480 pixels For Pal 720 X 576 pixels Pixels are distorted (not square) because 720:480 is actually 3:2 ratio High Definition for NTSC: 1440 X 1080 1280 X 720 Frame Aspect Ratio is 16:9 1440:1080 ratio is 1.333 (pixels are not square) 1280:720 ratio is 16:9 (pixel are square ) Frame aspect ratio is the ratio of width to height of the image frame. 4:3 Frame aspect ratio 16:9 Frame aspect ratio How do we see images on a CRT Display TV vs Flat Screen 29 http://www.crutchfield.com/Lea rn/learningcenter/home/underst anding-resolution.html Older TVs 480 Scan Lines New Plasma, Flat Screen 720 or 1080 lines progressive not interlaced OLDER TECHNOLOGY -Screen resolution __________ -Electron gun beam activates the dots http://www.crutchfield.com/learn/learningcenter/home/tv_flatpanel.html?page=2 http://www.crutchfield.com/S-EMMmc3InSom/learn/learningcenter/home/tv_flatpanel.html http://www.crutchfield.com/Learn/learningcenter/home/understanding-resolution.html?page=2 PLASMA or LCD Screen resoluiton sof _________ _________ Flat grid of pixels How do we see images on a Don’t need to know Flat Panel TV more detail for the exam Most flat-panel TVs are progressive displays • Illuminating a fixed grid of tiny pixels. • Every pixel has three sub-pixels: (RGB) • Color and brightness information controlled at the sub-pixel level • Uses progressive display Screen resolutions of 1080p (progressive) 1080i (interlacing) Capturing Video – Download video from camcorder to computer Resolution Comparison Format Lines of Resolution (measurement of image quality) VHS, VHS-C 240 lines 8mm 240 lines Hi 8mm 400 lines Most older TVs (standard, SDTV) 480 lines DV 8mm, Mini DV 480 lines High Definition (HD) TV 720 lines Or 1080 lines 32 Digital Advantage: higher resolution (# of horizontal lines) Depending on features of individual unit, you may be able to achieve: Newer TVs http://www.crutchfield.com/Lea rn/learningcenter/home/underst anding-resolution.html Question: On a newer HD TV, what does the circled area mean? Firewire vs. USB It used to take A LONG time to move video from your camcorder to your computer (Hours and Hours) Firewire Firewire initiated by Apple and the IEEE in the late 80s. It is a high speed data transfer technology. Transmitted originally at 400Mbps Apple wanted to charge 1 dollar for every machine that was going to use it, this caused most PC manufacturers to decide against it, in favour of USB 1.1. USB USB 1.1. could transmit at 12Mbps Used for mice, keyboards, printers, _____________ USB 2.0 came along, backward compatible, transmitted at 480Mbps (could beat with Firewire400 and do video) Currently, we have Firewire 800, transmits at 800 Mbps, at some point in the future, they expect new 34Firewire will transmit at 3.2 Gbps! Apple IPODS no longer have firewire ports Capturing Video Download video from camcorder to computer Benefits of Digital • No Loss of Quality – Digital Videotape can be copied almost indefinitly. Important consideration in Postproduction sessions that require numerous generations of video effects. • No need of analog-to-digital conversion Digital material can be directly uploaded to digital editing systems • Reduces or eliminates problems such as dropouts due to error-correction circuitry associated with digital electronics • Archival (long-term) storage. Digital videotapes are better suited for longer periods • Quality of digital recordings is significantly better than analog recordings 35 Capturing Video Download video from camcorder to computer Controlling the Transfer Process • Video Capture software: Doesn’t matter if you are using an analog or digital camera Software Should have Features: • Start and stop the transfer • Select a file format for storing your video footage • Specify file name for each video clip • Video capture software is supplied with video editing software and with video capture devices 36 TIP: Videos are easier to edit if you divide them into several files, each containing a one or two minute video clip. In Lab – MovieMaker Learning to edit your video Capture Video Edit Digital Video (using video capture card) from camcorder to computer (using Computer, Digital Video software ex. Adobe Premiere, Avid) Edit it Add all kinds of cool titles Filters, transitions and FX Superimpose clips Synchronize audio with video Output in different file formats 37 Output Video (back out to tape, the Web, CD, DVD) In Lab – MovieMaker Movie on Adobe Premier Let’s Review When would you use Firewire? Which of the following is a benefit of using a digital video recorder? 38 If you have a digital camcorder If you have an analog camcorder No loss of data Can edit digital footage on a computer, you can NOT edit analog footage on a computer. You don’t need a video capture card All of the above are benefits of going digital.