1. White LED : Application
advertisement

PHOSPHOR CONVERTED
WHITE LED
1/219
Contents
1. White LED
2. Phosphor Converted White LED
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED application
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
5. Phosphor Mounting
A. Fabrication
B. LED Efficiency
C. Epi Growth
D. Extraction Efficiency
E. Junction
F. LED Basics
G. LED Business
H. LED Applications
2/219
1. White LED : Introduction
LED
형광체
G
B
(A)
multi chip
(single color LED)
R
(1)
R, G, B LED
(B)
single chip
(multi color LED)
(A)
(2)
B LED + Phosphor
UV LED + Phosphor
Advantage (vs. CCFL)
* Increased Color Gamut
* Mechanical Stability
* Fast switching Time
B
Y
B
R/G
UV
R/G/B
(B)
(3)
Y Ph
백색
G
B
R
R, G Ph
3/219
1. White LED : Characteristics
LCD BLU
(1-A)
LED
형광체
color gamut
color stability
chip degradation
G
B
2G/1B/1R
excellent
(~100%)
good
R
백색
(1-B)
G
B
R
excellent
(~100%)
(2-A)
(2-B)
good
B
Y
good
(~70%)
very good
B
R/G
very good
(~90%)
very good
UV
R/G/B
(3)
excellent ?
(~100%)
excellent
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
* Adv: adjustable white point
sequential color potential
Dis : complexity in control circuit
large mixing & compensation area
efficiency of green LED
(e.g.) Lumileds (LCD TV, monitor)
* Adv: adjustable white point
sequential color potential
small mixing & compensation area
Dis : complexity in control circuit
complexity in chip design
efficiency of green LED
(e.g.) Osram opto., Nichia (LCD monitor)
* Adv : simple control circuit
small mixing compensation area
Dis : fixed white point
no sequential color potential
(e.g.)
2-A : small sized BLU, flash lamp
2-B : CRI for lighting, BLU for LCD TV ?
3 : development of near UV LED
4/219
1. White LED : Application (Backlight)
LCD Backlight – Lumileds
5/219
1. White LED : Application (Backlight)
LCD Backlight – Lumileds
6/219
1. White LED : Application (Backlight)
LCD Backlight – presented at 2004 FPD (Japan) by HannStar (Taiwan)
Using R, G, B LED
Using White LED
What kind of white LED?
7/219
1. White LED : Application (Backlight)
Mixing & Compensation Area
Osram Opto, Nichia
G
B
R
Lumileds
G
B
R
8/219
2. Phosphor Converted White LED : Need for Phosphors (I)
* Efficiency of Green LED
B LED * G Phosphor (530nm)
= 60% * 70% * 87% = ~ 37 %
>
G LED
= ~ 20 %
2 G LED + 1 B LED + 1 R LED
Why? Transition to indirect band-gap material
at above 0.53 of Al
Why? difficult to obtain high quality InGaN epi- layer
due to re-evaporation of In from growth surface
wider FWHM of green LED
and the subsequent low color purity
9/219
2. Phosphor Converted White LED : Need for Phosphors (I)
*
*
*
*
White를 위해 3.0 lm, 5.7 lm, 0.57 lm 이 필요함
R LED의 경우 85%, B LED의 경우 65 %만 사용
current ratio를 작게 가져가거나 or 2 G LED + 1 B, R LED
HB LED의 경우 I와 T에 따른 보상이 필요함
10/219
2. Phosphor Converted White LED : Need for Phosphors (II)
* efficiency vs. temperature
* efficiency vs. time (life time)
- same effect for PC white LED
- less effect for PC white LED
optical
feedback
11/219
2. Phosphor Converted White LED : Need for Phosphors (II)
12/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Parameters
Excitation WL
Absorption efficiency (Reflection)
Quantum efficiency
Stock shift
Luminance (Peak WL: Eye factor)
Emission color (Peak WL, FWHM)
Temperature dependency (Peak WL, Luminance)
Particle size
Scattering Particle
Surface modification
Illumination vs. backlight
Refractive index (Phosphor, Encapsulation material)
Gravity (Phosphor, Encapsulation material)
Phosphor mixing ratio (CCT, CIE, CRI, Color Gamut) & thickness
Structure of phosphor coating layer
Environment friendly
Phosphor degradation
Radiation damage of encapsulation (epoxy or silicone)
13/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry
2.0
1931 CIE X, Y, Z color matching function
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
555 nm
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
350
400
X = X() P() d
Y = Y() P() d
450
500
550
600
x = X / (X + Y + Z)
y = Y / (X + Y + Z)
Z = Z() P() d
lm/W
W/nm
650
700
750
u = 4X / (X + 15Y + 3Z)
v = 6Y / (X + 15Y + 3Z)
for uniform chromaticity coordinates
(color difference between two point)
Br = 680 Y() P() d
Photometry unit : lm, cd = lm/sr, lux = lm/m2, nit = cd/m2
14/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry
Consider one photon at each wavelength,
1.0
Br (Y)
0.9
0.8
cie x
0.7
cie x, cie y
0.6
0.5
0.4
cie y
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
400
450
500
550
600
650
700
WL(nm)
15/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : CIE (x,y) chromaticity diagram
all the colors perceivable by human eyes
cie x, y
0.9
520 nm
530 nm
0.8
540 nm
510 nm
550 nm
0.7
560 nm
0.6
570 nm
500 nm
580 nm
0.5
y
590 nm
0.4
600 nm
610 nm
620 nm
0.3
490 nm
0.2
480 nm
0.1
470 nm
460 nm
0.0
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
x
16/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : CIE (x,y) chromaticity diagram
17/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : CCT
same cct
v
u
y
standard light sources
(specific emission spectrum)
Different body color (R() S())
x
same cct, different (x,y)
18/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : Color Gamut (Backlight)
current ratio, phosphor ratio for white
0.8
0.7
0.6
cie y
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
NTSC : (0.14,0.08), (0.21,0.71), (0.67,0.33)
0.0
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
cie x
NTSC
CCFL + CF
B LED + R Ph + G Ph + CF
19/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : CRI (Illumination)
general color rendering index, Ra
color difference of each sample
objects (u,v) between under
standard light source and tested
light source
Ri = 100 – 4.6 Ei
Ei = 100 { [(uk,i – uk)-(uoi-uo)]2 + [(vk,i – vk)-(voi-vo)]2 }1/2
Ra = (R1 + ~ R5 ~ + R8 ) / 8
20/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : Color Purity
color purity = a / (a+ b)
one of problems
21/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : Color Mixing (di-chromatic)
22/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : Color Mixing (tri-chromatic)
case I
다음값은
입력치
결과치
입니다.
(1) 단색의 색좌표, 휘도 측정치를 입력하시오. 그리고, 측정시의 I, V 값은?
x
RED
GREEN
BLUE
y
0.714
0.074
0.135
0.286
0.656
0.049
Br(lm)
power(mW)
19.52
155.07
32.60
93.47
9.56
170.82
current(A) voltage(V)
0.35
2.90
0.35
3.50
0.35
3.50
(2) 단색의 R,G,B의 효율은 다음과 같읍니다.
lm/W
WPE(%)
EQE(%)
RED
=>
19.2
15.3
GREEN =>
26.6
7.6
BLUE =>
7.8
13.9
(3) White 색좌표 또는 원하는 구현색의 색좌표를 입력하시오.
x=
0.310 y=
0.310
(4) 단색 측정치가 삼색혼합시 유지된다면
이때, White 색좌표 또는 원하는 구현색의 색좌표를 내기 위한 R, G, B에 대한 current 값은
다음과 같읍니다.
ratio 1
ratio 2
current (A)
RED
0.310
0.074
0.135
RED
=
0.382
0.81
0.28
0.310
0.656
0.049
GREEN =
0.471
1.00
0.35
0.000626
1.000
1.000
1.000
BLUE =
0.147
0.31
0.11
GREEN
0.000773
BLUE
0.000241
0.714
0.286
1.000
0.310
0.310
1.000
0.135
0.049
1.000
0.714
0.286
1.000
0.074
0.656
1.000
0.310
0.310
1.000
(5) current가 위와 같으면, R,G,B의 휘도는 다음과 같읍니다.
lm
Br for W =
Br for R =
Br for G =
Br for B =
51.38
15.81
32.60
2.98
W (lm/W)
21.16
(6) x,y coordinate에서 삼색tube의 색재현영역(color gamut)은 다음과 같읍니다.
그리고, color purity는 다음과 같읍니다.
NTSC
color gamut =
0.183
116 %
R
G
B
0.67
0.21
0.14
0.33
0.71
0.08
23/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : values from measured spectrum
ca se I
corrected F
peak center
#
WL(nm)
2.93E+11 1.12E+11 2.97E+11
460
510
640
2.86E+17 1.50E+17 3.01E+17
B
G
R
x=
y
0.055
0.624
0.295
mW
122.0
58.1
94.0
lm
7.6
20.4
14.5
peak (nm)
460
510
640
lm
WPE(%)
EQE(%)
ratio 2
current (A) Br for
6.2
10.0
13.1
0.28
0.10 Br for
16.7
4.7
6.9
1.00
0.35 Br for
14.3
9.3
13.8
0.69
0.24 Br for
0.310
lm/W
B
G
R
current(A)
voltage(V)
0.35
3.50
0.35
3.50
0.35
2.90
W=
R=
G=
B=
W(lm/W) =
32.50 CG=
2.13
20.40
9.97
14.35
NTSC % =
0.164
104.1
50000.0
45000.0
40000.0
35000.0
30000.0
Int e nsi t y
B
G
R
0.310 y=
x
0.138
0.106
0.703
B
G
R
25000.0
20000.0
15000.0
10000.0
5000.0
0.0
350
400
450
500
550
600
650
700
750
800
WL ( nm)
B
G
R
B
G
R
24/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Basics of Radiometry and Photometry : values from simulated spectrum
ca se I
std. Dev.
peak center
intensity
WL(nm)
12
460
200
B
x=
B
G
R
ca se II
G
9
640
250
R
0.310 y=
std. Dev.
peak center
intensity
WL(nm)
y
0.036
0.656
0.286
mW
172.7
93.5
155.1
lm
7.8
32.6
19.5
peak (nm)
460
510
640
lm
WPE(%)
EQE(%)
ratio 2
current (A) Br for
6.4
14.1
18.3
0.27
0.10 Br for
26.6
7.6
11.0
1.00
0.35 Br for
19.2
15.3
22.9
0.78
0.27 Br for
lm/W
B
G
R
W=
R=
G=
B=
W(lm/W) =
12
460
200
B
x
0.143
0.074
0.714
B
G
R
0.310
current(A)
voltage(V)
0.35
3.50
0.35
3.50
0.35
2.90
x=
20
545
120
G
9
630
250
R
0.310 y=
x
0.143
0.298
0.702
B
G
R
y
0.036
0.676
0.298
mW
172.7
87.5
157.5
lm
7.8
52.7
29.6
lm/W
B
G
R
49.89 CG=
2.12
32.60
15.18
21.26
NTSC % =
0.186
117.6
peak (nm)
460
545
630
lm
WPE(%)
EQE(%)
ratio 2
current (A) Br for
6.4
14.1
18.3
0.44
0.15 Br for
43.0
7.1
11.0
1.00
0.35 Br for
29.1
15.5
22.9
0.83
0.29 Br for
0.310
current(A)
voltage(V)
0.35
3.50
0.35
3.50
0.35
2.90
W=
R=
G=
B=
W(lm/W) =
80.63 CG=
3.42
52.68
24.53
30.95
NTSC % =
0.158
100.3
12.0
10.0
8.0
Int e nsi t y
B
G
R
15
510
120
6.0
4.0
2.0
0.0
350
400
450
500
550
600
650
700
750
800
WL ( nm)
B
G
R
B
G
R
25/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Color Gamut
CCFL
White by CCFL + CF
Intensity (count)
Intensity (count)
White by CCFL
400
400
450
500
550
WL(nm)
600
650
450
700
500
550
600
650
700
WL(nm)
W CCFL + R CF
W CCFL + G CF
W CCFL + B CF
CCFL + CF
26/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Color Gamut
R, G, B LED
White by R, G, B LED + CF
Intensity (count)
Intensity (count)
White by R, G, B LED
400
450
500
550
600
650
700
400
450
R LED
G LED
B LED
500
550
600
650
700
WL(nm)
WL(nm)
White by RGB LED
W LED + R CF
W LED + G CF
W LED + B CF
RGB LED + CF
27/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Color Gamut
B LED + Y Ph
White LED + CF
Intensity (count)
Intensity (count)
White LED
400
400
450
500
550
WL(nm)
600
650
450
700
500
550
600
650
700
WL(nm)
W LED + R CF
W LED + G CF
W LED + B CF
W LED + CF
28/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Color Gamut
B LED + R,G Ph
White by B LED + R, G Ph
Intensity (count)
Intensity (count)
White by B LED + R, G Ph
400
450
500
550
600
650
700
750
800
400
450
500
CaS
SrGa2S4
550
600
650
700
750
800
WL(nm)
WL(nm)
B LED
W + R CF
W + G CF
W + R/ G/ B CF
W + B CF
29/219
3. Characteristics of Phosphors for White LED Application
Color Gamut
0.8
0.7
0.6
cie y
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
cie x
RGB LED
CCFL + CF
BLU system
NTSC
RGB LED
RGB LED + CF
B LED + Y Ph + CF
CCFL + CF
B LED + R,G Ph + CF
NTSC
B LED + Y Ph + CF
x
0.2505
0.2617
0.3234
0.3026
0.3062
y
0.2874
0.3063
0.3146
0.2705
0.2863
RGB LED + CF
B LED + R Ph + G Ph + CF
CCT (K) color gamut
0.158
14500
0.164
11000
0.151
6000
0.113
8400
0.111
7541
0.145
NTSC %
1.00
1.04
0.96
0.71
0.70
0.91
30/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* What & How?
- B light : converted to Yellow light by Phosphor
converted to Red and Green (Yellow) light by Phosphor
- UV light : converted to Red, Green, Blue light by Phosphor
* Key Factor for Producing White light?
- for General Lighting : color rendering index
- for BLU : color gamut
* Who (patent)? Phosphors for PC- White LED
- Nichia
- Osram Opto.(Siemens, Osram Lighting)
- Lumileds (Philips)
- Gelcore (GE)
- Toyoda
- LBG (LWB)
- Toshiba
- Matsushita
31/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
YAl5O12:Ce3+,Sm3+
* Commercially used Yellow Phosphor for B LED
- Nichia : YAG:Ce
TbAl5O12:Ce3+
- Osram Opto : TAG:Ce
(Ba,Sr,Ca)2SiO4:Eu2+
- Lumileds (Philips) : YAG:Ce (Nichia), YAG:Ce,Pr
- Gelcore (GE) : ?
- Cree : YAG:Ce (Nichia)
- Toyoda : YAG:Ce (Nichia)
- Rohm, Lite-on, Everlight, Vishay : TAG:Ce (Osram)
- Citizen : YAG:Ce (Nichia)
- Stanley : YAG:Ce (?)
- Samsung E.M. : TAG:Ce (Osram)
- Seoul S.C. : Ortho-silicate:Eu (LWB,Toyoda)
- Matsushita : ?
* Commercially used Red, Green Phosphor for B LED
- Strong Candidate : CaS:Eu, STG:Eu
- Degradation of Sulfide Phosphors ? Luminance ?
* Commercially used Phosphors for UV LED
- Toyoda : ZnS:Cu,Al / Halo-phosphate:Eu / LOS:Eu
32/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Licensing : PC - White LED
Samsung
E.M.
Rohm
Citizen
Osram
Everlight
Lumileds
Cree
Nichia
Liteon
Toyoda
Toshiba
UV LED + Phosphors
* Seoul S.C : Phosphor from LWG(Toyoda) + B LED chip from Cree
33/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Matsushita
1. Publication : EP1447853 (2004, 8)
2. Priority : 2001, 10
3. * 1항 : UV LED (350~410nm) + B Ph (400~500nm) + G Ph (500~550nm) + R Ph(600~660nm)
+ Y Ph (550~600nm)
* 2~8항 : Y Ph : (Sr1-a1-b1-xBaa1Cab1Eux)2SiO4, 0 a1 0.3, 0 b1 0.6, 0 ≺ x ≺ 1
B Ph : (M1-xEux)10(PO4)6Cl2, M = Ba, Sr, Ca, Mg
(M1-xEux)(N1-yMny)Al10O17, M = Ba, Sr, Ca & N = Mg, Zn & 0 y 0.05
G Ph : (M1-xEux)(N1-yMny)Al10O17, M = Ba, Sr, Ca & N = Mg, Zn & 0.05 y 1
(M1-xEux)2SiO4, M = Ba, Sr, Ca, Mg
R Ph : (Ln1-xEux)O2S, Ln = Sc, Y, La, Gd
34/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
LBG (LBW)
1. Publication : WO 02/054502 (2002, 7) (KR공개 2003-74641)
2. Priority : 2000, 12
3. * 1항 : UV or B LED +
(2-x-y)SrO x(BauCav)O (1-a-b-c-d)SiO2, aP2O5, bAl2O3, cB2O3, dGeO2 : yEu2+
* 형광체를 강조하여 1항에서 claim
* B Ph : alkaline earth aluminates:Eu2+, Mn2+
R Ph : Y(V, P, Si)O4:Eu2+, Y2O2S:Eu3+, Bi3+,
alkaline earth magnesium disilicate (M3-x-yMgSi2O8:Eu2+, Mn2+)
1. Publication : WO 02/054503 (2002, 7) with Toyota Gosei (KR공개 2003-91951)
2. Priority : 2000, 12
3. * 1항 : LED + Ph로 이루어진 발광장치에서 형광체는 ortho-silicate
* 3항(종) : ortho-silicate를 규정함.
(2-x-y)SrO x(BauCav)O (1-a-b-c-d)SiO2, aP2O5, bAl2O3, cB2O3, dGeO2 : yEu2+
* LED + Ph”로 이루어진 발광장치상의 구조 등에 대한 claim이 주를 이룸.
35/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Toyoda Gosei
1. Publication : KR1997-0030949 (1997, 6)
2. Priority : 1995, 11
3. * 1항 : Phosphor + UV
* Reject : 재심사 청구
1. Patent : US6791116 (2004, 9) with Matsushita
2. Priority : 2002, 4
3. * Scattering material과 phosphor를 함유한 diode 발광장치
1. Publication : JP2004-127988 (2004, 4) (WO 04/032251)
2. Priority : 2002, 9
3. * UV or Blue LED + Y, R, G, B Phosphor
* Y Ph = (2-x-y)BaO x(SruCav)O (1-a-b-c-d)SiO2, aP2O5, bAl2O3, cB2O3, dGeO2, : Eu2+
36/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Toyoda / Toshiba
* Near UV LED + R, G, B Ph ?
37/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Toshiba
1. Publication : JP2004-103443 (2004, 4)
2. Priority : 2002, 9
3. * B LED + Y, R Phosphors
1. Publication : JP2003-318447 (2003, 11)
2. Priority : 2002, 4
3. * LED (400~500 nm) + Ph 1 (500~600 nm) + Ph 2 (600~700 nm)
1. Publication : JP1999-246857 (1999, 9)
2. Priority : 1998, 2
3. * UV LED + R Ph
KASEI?
* 1항 : R Ph = (La1–x–yEuxSmy)2O2S, 0.01 x 0.15, 0.0001 y 0.03
* 형광체를 강조하여 1항에서 claim
* 5항 : La 대신 Y or Gd를 일부 함유
38/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Toshiba
1. Publication : JP2000-183408 (2000, 6)
2. Priority : 1998, 12
3. * UV LED + B Ph + O Ph (excited by B Ph)
* B Ph = M10(PO4)6Cl2:Eu2+
* O Ph = (Y,Gd)3Al5O12:Ce3+
1. Publication : JP2002-203991 (2002, 7)
2. Priority : 1997, 9
3. * UV LED + R, G, B Phosphors
39/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Publication : JP1996-36835 (1998, 2)
Nichia
2. Priority : 1996, 7
3. * 형광체 특허임
* (Y
1-p-q-r
GdpCeqSmr)3(Al1-sGas)5O12, 0 p 0.8, 0.003 q 0.2, 0.003 r 0.08, 0 s 1
1. Patent : US5998925 (1999, 12) (Family : US6069440, US6608332, US6614179, JP2927279)
2. Priority : 1996, 7
3. * 1항(독) : Garnet material, A3B5O12:Ce, A = Y, Lu, Sc, La, Gd, Sm & B = Al, Ga, In
* 2항 :Y와 Al을 함유하는 yttrium aluminum garnet material
* 3항 : (Re1-rSmr)3(Al1-sGas)5O12:Ce, 0 r 1, 0 s 1, Re = Y, Gd
1. Patent : US6069440 (2000, 5)
2. Priority : 1996, 7
3. * 1항(독) : Blue light 일부를 흡수할 수 있는 형광체
1. Patent : US6614179 (2003, 9)
2. Priority : 1996, 7
3. * 1항(독) : (Re1-rSmr)3(Al1-sGas)5O12:Ce, 0 r 1, 0 s 1, Re = Y, Gd
40/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Publication : US2004-135504 (2004,7)
Nichia
2. Priority : 2002, 3
3. * 형광체 자체가 1항이며, 연색성 증가위해 Red 성분의 보충을 갖는 형광체 조성
LxMyN(2/3x + 4/3y):R, LxMyOzN(2/3x + 4/3y – 2/3z):R
where, L = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn & M = Si (essential), C, Ge & R = Eu2+ (essential), RE
* LED : below 500 nm
Ph : 520 ~ 780 nm
1. Patent : JP3419280 (2003, 4)
2. Priority : 1996, 11
3. * 365 nm LED 400 nm, Red Ph
* aMgO bLi2O Sb2O3 : cMn
dMgO eTiO2 : fMn
jCaO kMO TiO2 : iPr, M = Zn, Mg, Sr, Ba
1. Publication : JP1998-112557 (1998, 4)
2. Priority : 1996, 10
3. * LED + (M,Eu,Q)O n(Al1-m,Bm)2O3, M = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn & 0 m 0.5 & 0.5 n 10
Q (co-activator) = Mn, Zr, Nb,… etc.
41/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Nichia
1. Publication : JP1999-046019 (1999,2)
2. Priority : 1997, 7
3. * Phosphor mounting by Ink jet method
JP : 2998696 (1999), 3036465 (2000), 2900928 (1999), 3065258 (2000)
JP Publication : 1998-154830, 1998-228249, 1998-233533, 1998-247750, 1999-199781
42/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Nichia
* YAG : (Y
sGas)5O12
1-p-q-r
GdpCeqSmr)3(Al1온도 특성 향상
Gd
Gd
43/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Nichia
* YAG : (Y
1-p-q
GdpCeq)3(Al1-sGas)5O12
44/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Nichia
* YAG : (Y
1-p-q
GdpCeq)3(Al1-sGas)5O12
45/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
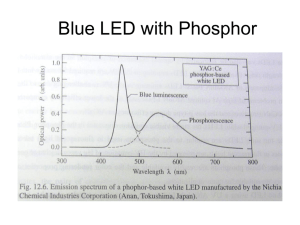
Nichia
When using YAG, low Ra at low CCT
For “High Ra” or “warm white”
: new red phosphor ! (655 nm)
46/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Nichia
High CRI – daylight white LED,
using shorter YAG and red phosphor
3.2 V / 20 mA
1.8 lm / 28.3 lm/W
4600 K (0.357/0.355)
Ra = 76.2
3.3 V / 20 mA
1.67 lm / 28.3 lm/W
4670 K (0.355/0.361)
Ra = 87.7
47/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Nichia
High efficacy or CRI – warm white LED,
using YAG and red phosphor
3.22 V / 20 mA
1.49 lm / 23.1 lm/W
2810 K (0.451/0.408)
Ra = 72.5
3.24 V / 20 mA
1.23 lm / 18.9 lm/W
2830 K (0.449/0.408)
Ra = 87.5
48/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Light for 21C : Stanley/Mitsubishi/Kasei/Yamaguch Univ.
* Near UV LED + R, G, B Ph
49/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Light for 21C : Stanley/Mitsubishi/Kasei/Yamaguch Univ.
* Near UV LED + R, G, B Ph
50/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Sharp
* Near UV LED + R, G, B Ph
CG : ~ 74 % of NTSC
450 mcd at 4 V /40 mA
51/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Patent : US6351069 (2002,2) (family : US6680569)
2. Priority : 1999, 2
Lumileds
3. * wavelength conversion : primary FL material, supplementary FL material (red)
* Y3Al5O12:Ce3+ + Y3Al5O12:Ce3+, Pr3+
* Y3Al5O12:Ce3+ + SrS:Eu2+
1. Patent : US6686691(2004,3)
2. Priority : 1999, 9
3. * composition comprising a mixture of a 1st and a 2nd phosphor,
each phosphor comprising a host sulfide material and rare earth dopant
* Especially, Blue LED
* SrGa2S4:Eu2+ + SrS:Eu2+ + CaS:Eu2+
SrGa2S4:Ce3+ + SrS:Ce3+ + CaS:Ce3+
1. Patent : US6642618 (2003, 11)
2. Priority : 2000, 12
3. * 5항 : white light by sol-gel glass (SiO2) layer containing (Sr,Ba,Ca)Ga2S4:Eu2+ + SrS:Eu2+
1. Patent : US 6603258 (2003, 8)
2. Priority : 2001, 4
3. * white light by LED (485 ~ 515nm) + (Sr,Ba,Ca)S:Eu2+ (600 ~ 620nm), 특히 SrS:Eu2+
52/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Patent : US6084250 (2000,7) by Philips (Family : US6051925, JP공개2000-509912)
2. Priority : 1997, 3
Lumileds
3. * 1항 : UV (300 ~ 370 nm) + B Ph (430~490 nm) + G Ph ( 520~570 nm) + R Ph (590~630 nm)
* 6항 : B Ph = BaMgAl10O17: Eu2+, G Ph = ZnS:Cu, R Ph = Y2O2S:Eu3+
* 7항 : Organic phosphor (dye)
1. Patent : US6717353 (2004, 4)
2. Priority : 2002, 10
3. * 1항 : 1st WL converting material comprising Sr-SiON:Eu2+ (or YAG:Ce) emitting 2nd WL light
* 2항 : UV and Blue light = 1st WL light
* 3항 : Green = 2nd WL light
* 4, 8항 : Red Ph = 2nd WL converting material (using 2nd WL lght),
(Sr1–a–b–cBabCac)2Si5N8:aEu2+
Blue Ph = 3rd WL converting material (using 1st WL light),
(Sr1–a–xBax)3MgSi2O8:aEu2+
1. Patent : US6417019 (2002, 7)
2. Priority : 2001, 4
3. * 1항 : white light by LED (380 ~ 500nm) + (Sr,Mg,Ba,Ca)(Ga,Al,In)2S4:Eu2+ (490 ~ 610 nm)
* LED/Phosphor structure (encapsulation, mounting)
53/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Patent : US6501102 (2002, 12)
Lumileds
2. Priority : 2002, 1
3. * 1항 : LED (below 460 nm)
+ 2nd, 3rd WL light from YAG, (Y,Ln)AG, (Y,Ln)(Al,Ga)G, SrS, SrGa2S4, NitridoSilicate
* 2항 : Ce3+, Eu2+ etc.
* Phosphor powder layer, Phosphor thin film, Substrate for light emitting structure
1. Patent : US6650044 (2003, 11)
2. Priority : 2000, 10
3. * Stencing method for phosphor layer
1. Patent : US6576488 (2003, 6)
2. Priority : 2001, 6
3. * Electrophoretic method for conformal coating
1. Patent : US6645652 (2003, 11)
2. Priority : 2001, 6
3. * Stencing, Electrophoresis method for phosphor layer
54/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds
1. Patent : US6590235 (2003, 7) (Family : US6204523)
2. Priority : 1998, 11
3. * Encapsulating material (silicone) for UV LED
1. Patent : US5813752, US5813753 (1998,9)
2. Priority : 1997, 5
3. * Enhanced efficiency by short wave pass filter between LEDs and phosphor layer
(reflecting visible light from phosphor layer)
1. Patent : US5959316 (1999,9) (by HP)
2. Priority : 1998, 9
3. * Uniform phosphor layer on the hemisphere transparent spacer
55/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds - Philips
56/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds - Philips
57/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds
* Blue LED + Y Ph (YAG:Ce, YAG:Ce,Pr)
* Blue LED + G Ph (SrGa2S4:Eu2+) + R Ph (SrS:Eu2+)
Resistance to humidity ?
Preventing coating ?
LCD BLU ?
58/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds
* Blue LED + Y Ph (YAG:Ce, YAG:Ce,Pr) + R Ph (CaS:Eu2+)
For Illumination ?
59/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds - Philips
*
60/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
*
Lumileds - Philips
61/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds
* UV LED + R, G, B Phosphors
62/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds
63/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Lumileds
64/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
*
SrCaS:Eu2+
Sarnoff
65/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
*
SrCaS:Eu2+
Sarnoff
66/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Osram Opto.
1. Patent : US6066861 (2000, 5) (Family : US6245259, 6277301, 6576930, 6592780, 6613247)
2. Priority : 1996, 9
3. * 1항 : WL (from UV, Blue, Green) converting casting composition
Resin (epoxy)
A3B5X12:M3+, A = Y, Ca, Sr & B = Al, Ga, Si & X = O, S & M = Ce, Tb
(YAG, Thiogallate, Orthosilicate) (not, Eu)
size 20 m (d 5 m)
* 7항 : YAG:Ce
* 10항 : Lighting emitting S.C. component = S.C. body (UV, Blue, green) + A3B5X12:M
1. Patent : US6245259 (2001, 6)
2. Priority : 1996, 9
3. * 1항 : WL (from UV, Blue, Green) converting casting composition
Resin (epoxy)
Ce doped phosphors
size 20 m (d 5 m)
* 7항 : YAG:Ce
* 10항 : Lighting emitting S.C. component = S.C. body (UV, Blue, green) + Ce doped phosphors
* 15항 : Yellow by Blue LED
* 16항 : Green, Red by Blue LED
67/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Osram Opto.
1. Patent : US6277301 (2001, 8)
2. Priority : 1996, 9
3. * 1항 : WL (from UV, Blue, Green) converting casting composition
Resin (epoxy)
Ce doped phosphors, garnet doped with rare earth, thiogallates doped with rare earth,
Aluminates doped rare earth, orthosilicates doped with rare earth
tempering above 200 oC
* 2항 : size 20 m (d 5 m)
* 11항(독) : White lighting emitting S.C. component =
S.C. body (UV, Blue, green) + Ce doped phosphors(blue to yellow) with epoxy
* 12항(독) : White lighting emitting S.C. component = S.C. body (UV, Blue, green)
+ garnet doped with rare earth, thiogallates doped with rare earth,
aluminates doped rare earth,
orthosilicates doped with rare earth (blue to green and red) with epoxy
68/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Patent : US6613247 (2003, 9)
Osram Opto.
2. Priority : 1996, 9
3. * 1항 : WL (from UV, Blue, Green) converting casting composition
Resin (epoxy)
garnet doped with rare earth, thiogallates doped with rare earth
aluminates doped rare earth, orthosilicates doped with rare earth
size 20 m (d 5 m)
* 7항 : YAG:Ce3+ phosphor
* 12항(독) : White lighting emitting S.C. component = S.C. body (UV, Blue, green)
+ garnet doped with rare earth, thiogallates doped with rare earth,
aluminates doped rare earth, orthosilicates doped with rare earth
* 17항 : White = Blue LED + yellow light by Ce doped phosphor
* 18항 : White = Blue LED + green and red light
1. Patent : US6669866 (2003, 12) (Family : US6552487)
2. Priority : 1999, 7
3. * 1항(독) : light source comprising emission from 420 to 490 nm and phosphor A3B5O12:Ce3+
A = Tb or one of Y, Gd, La, Lu & B = Al, Ga
* 2항 : Tb solely or predominantly (TAG)
69/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Osram Opto.
1. Patent : US6504179 (2003, 1)
2. Priority : 2000, 5
3. * 1항 : LED (300 ~ 470nm) + Eu activated calcium magnesium chlorosilicate (green phosphor)
Ce activated rare earth garnet (yellow phosphor)
* 2항 : Green (Ca8-x–yEuxMnyMg(SiO4)4Cl2)
* 3항 : Yellow ((Re)3(Al,Ga)5O12:Ce, 특히 YAG:Ce or TAG:Ce)
* 4항 : 특히, LED (330~370 nm) + phosphors (430~470, 490~525, 545~590 nm)
* 5항 : 특히, LED (430~470 nm) + phosphors (545~590, 490~525 nm)
1. Patent : US 6649946 (2003, 11) (Family : US 6682663)
2. Priority : 1999, 11
3. * 1항(독) : “Yellow to Red” emitting phosphor
MxSiyNz:Eu2+, M = La, Sr, Ba, Zn
* 8항 : LED + phosphors
* 9항 : LED = 420~470nm
70/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Osram Opto.
1. Patent : US6695982 (2004, 2)
2. Priority : 2000, 6
3. * 1항 : 형광체 제조 방법
AB2S4: D, A = Mg, Ca, Sr & B = Al, Ga, Y & D = Ce3+, Eu2+
1. Publication : US2004-0124758 (2004, 7)
2. Priority : 2000, 7
3. * 1항(독) : UV (370~420 nm) or Blue (420~480 nm)
+ MS:Eu2+ (M = Ba, Mg, Zn, Ca, Sr) containing one of Ba, Mg, Zn
+ MN2S4:Eu2+ or Ce3+ (M = Ba, Mg, Zn, Ca, Sr & N = Al, Ga, In, Y, La, Gd)
71/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* Blue LED + Y Ph (TAG:Ce)
Shorter YAG
Osram Opto.
* Blue LED + Y,G Ph (Y(Al,Ga)G:Ce or TAG:Ce) + R Ph ((AE)2Si5N8:Eu2+)
72/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* Near UV LED + R, G, B Ph
Osram Opto.
Sr4Al14O25:Eu2+ (~490 nm)
SrAl12O19:Eu2+ (~520 nm)
SrAl2O4:Eu2+ (~400 nm)
73/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Osram Opto.
74/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* YAG : (Y
1-p-q GdpCeq)3(Al1-sGas)5O12
Osram Opto : Siemens
Ga
Gd
75/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* YAG : (Y
1-p-q
GdpCeq)3(Al1-sGas)5O12
Osram Opto : Siemens
* f-d absorption or CT absorption
76/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* Potential R, G, B, Y Ph
Osram Opto : Siemens
77/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Patent : US6765237 (2004, 7)
GE or Gelcore
2. Priority : 2003, 1
3. * 1항 : 380~420nm LED + Blue Ph (BaMg2Al16O27:Eu2+) + Y Ph ((Tb1–x–yAxREy)3DzO12)
A = Y, La, Gd, Sm & RE = Ce etc & D = Al, Ga, In
* 15항 : B Ph = (Sr,Ba,Ca,Mg)5(PO4)3Cl:Eu2+
1. Patent : US6501100 (2002, 12)
2. Priority : 2000, 5
3. * 1항 : UV LED (370~405 nm) + Ph 1 (570~620 nm) + Ph 2 (480~520 nm)
* Ph 1 = APO:Eu2+,Mn2+, A2P2O7:Eu2+,Mn2+, A = Sr, Ca, Ba, Mg
Ph 2 = A4D14O25:Eu2+, (AD)8O13:Eu2+, A10(PO4)6Cl2:Eu2+, A2Si3O8 ACl2:Eu2+
A = Sr, Ca, Ba, Mg & D = Al, Ga
1. Patent : US6580097 (2003, 6) (Family : US6252254, US6469322)
2. Priority : 1998, 2
3. * 1항 : Blue LED + Ph 1 + Ph 2
* G Ph 1 = YBO3:Ce3+,Tb3+, BaMgAl10O17:Eu2+,Mn2+, (Sr,Ca,Ba)(Al,Ga)2s4:Eu2+,Y3Al5O12:Ce3+
* R Ph 2 = Y2O2S:Eu3+,Bi3+, YVO4:Eu3+,Bi3+, SrS:Eu2+, SrY2S4:Eu2+, CaLa2S4:Ce3+, (Ca,Sr)S:Eu2+
78/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Patent : US6469322 (2002, 10)
GE or Gelcore
2. Priority : 1998, 2
3. * 1항 : UV, Blue LED + Green Ph (LnBO3:Ce3+,Tb3+, Ln = Sc, Y, La, Gd, Lu)
* 9항 : Blue Ph ((Ba,Sr,Ca)5(PO4)3Cl: Eu2+,Mn2+) 함유
* 10항 : Red Ph 함유
1. Patent : US6791259 (2004, 9)
2. Priority : 2000, 8
3. * Scattering material 사용 (between LED & Phosphor material)
* size는 /3~ /2
1. Patent : US6685852 (2004, 2)
2. Priority : 2001, 4
3. * 1항 : UV LED (315~480nm, 바람직하게는 350~410nm) + 아래 Phosphor 가운데 2종
(1) Sr2P2O7:Eu2+,Mn2+
(2) (Ba,Sr,Ca)5(PO4)3(F,Cl,OH): Eu2+,Mn2+
(3) 3.5 MgO – 0.5 MgF2 – GeO2:Mn4+
(4) (Ba,Sr,Ca)5(PO4)3(Cl,OH): Eu2+
(5) (Ba,Sr,Ca)2MgAl16O27:Eu2+, (Ba,Sr,Ca)MgAl10O17:Eu2+, (Ba,Sr,Ca)Mg3Al14O25:Eu2+
(6) (5)에서 Mn2+를 co-activator로 사용
79/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Patent : US6621211 (2003, 9)
GE or Gelcore
2. Priority : 2000, 5
3. * 1항 : UV LED (360~420 nm)
(1) Ph = 575~620 nm : (Sr,Ca,Ba,Mg)PO:Eu2+,Mn2+, (Sr,Ca,Ba,Mg)2P2O7:Eu2+,Mn2+
(2) Ph = 495~550 nm : ASiO4:Eu2+, A2DSi2O7:Eu2+, AAl2O4:Eu2+, A = Sr, Ba, Ca & D = Mg, Zn
(3) Ph = 420~480 nm : Mg2Al16O27:Eu2+, (Sr,Ba,Ca)5(PO4)3Cl:Eu2+, Zn(Ba,Eu)O-6Al2O3,
BaAl12O19:Eu2+, KAl11O11:Eu2+
(4) Ph = 620~670 nm (optional): 3.5 MgO – 0.5 MgF2 – GeO2:Mn4+
1. Patent : US6616862 (2003, 9)
2. Priority : 2001, 5
3. * Mn2+ 첨가로 red shift
* UV LED (350~420 nm)
* 1항 : (Ba,Sr,Ca,Mg)5(PO4)3(F,Cl,OH):Eu2+,Mn2+ (orange color)
Optionally, add blue phosphors
1. Patent : US6596195 (2003, 7)
2. Priority : 2001, 6
3. * 1항(독) : 형광체를 claim, TAG, (Tb1–x–yAxREy)aDzO12, A = Y, La, Gd, Sm & D = Al,Ga
* 38항(독) : LED + phosphor
* 40항(독) : LED = 400~480 nm + phosphor
80/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
1. Patent : US6538371 (2003, 5)
2. Priority : 2000, 3
GE or Gelcore
3. * Blue LED + YAG:Ce3+
* 1항 : System color output을 향상시키는 방법 (CIE coord.에서 BBL과 line의 상관관계 이용)
1. Patent : US6522065 (2003, 2)
2. Priority : 2000, 3
3. * 1항 : UV LED + white phosphor
A2–2xNa1+xExD2V3O12, A = Ca, Ba, Sr, & D = Mg, Zn, & E = Eu3+, Sm3+
* (e.g.) 370 nm LED + Ca2–2xNa1+xEuxMg2V3O12
1. Patent : US6294800 (2001, 9) (Family: US6255670)
2. Priority : 1998, 12
3. * 1항 : Ca8Mg(SiO4)4Cl2:Eu2+,Mn2+를 포함하는 조성
* 2항 : 상기 G Ph와 R, B Ph를 포함하는 조성
* 3항 : UV LED (330 ~420 nm, 특히 355~365 nm)
* 6항 : G = Ca8Mg(SiO4)4Cl2:Eu2+,Mn2+,
R = Y2O3:Eu3+,Bi3+,
B = (Sr,Ba,Ca)5(PO4)3Cl:Eu2+ or BaMg2Al16O27:Eu2+
81/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
GE or Gelcore
{C}3[A]2(D)3O12
Y3Al5O12
tetrahedral site
octahedral site
dodecahedral site
Ga prefers tetrahedral site to larger octahedral site.
Expansion of structure.
Replacement to Ga provides longer Ce3+ - O distance.
Less crystal field. (centropoid shift, covalency ?)
Blue shift of Em. & Ex. spectrum.
* Replacement to Ga brings about decrease of emission intensity.
82/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
GE or Gelcore
Al5
Al4Ga1 Al3Ga2 Al2Ga3 Al1Ga4
similar thermal quenching
No emission at RT
crossover bet. d and f level
Photo-ionization
83/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
GE or Gelcore
Y3Al5O12
(garnet)
REAlO3
replacement to Large RE3+
(perovskite)
Secondary phase due to solubility
Quenching by energy transfer from Ce3+ to RE3+
Mainly, replacement to Gd (red shift) or Lu (blue shift).
When replacement to Tb,
f-d absorption of Tb3+ at 275 nm.
(checking by excitation spectrum of Ce3+)
Energy transfer from Tb3+ to Ce3+ (phonon assisted?)
i.e., no quenching
Red shift of both Em. And Ex. spectrum.
84/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
GE or Gelcore
TAG : no change of Q.E. at RT
significant change at high T
Overlap with 5D4 level of Tb3+
Energy transfer from Ce3+ to Tb3+
(i.e., back transfer)
Patent : US6596195 (2003, 7)
Using TAG phosphors
85/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* Blue or Near UV LED + Phosphors
For BLU ?
GE or Gelcore
For Illumination ?
86/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* Near UV LED + Phosphors
GE or Gelcore
Replace into B2O3?
or
?
What phosphor ?
87/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* Near UV LED + R, G, B Ph
GE or Gelcore
88/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
GE or Gelcore
* LED + white phosphor
Activator ?
?
89/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* Blue or UV LED + Phosphors
Phosphortech
* Excitation (absorption) : bandgap absorption or absorption by activators (Cu,A)
* Eg for ZnS : 3.7 eV (~335nm)
for ZnSe : 2.7 eV (~460nm)
90/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* Blue LED + Phosphors
Phosphortech
CRI?
91/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* UV LED + Phosphors
Phosphortech
92/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Review by C. Summers
* 254 Hg emission AC
no sulfide phosphor
* LED CW : decay time (fast – recycling)
ground state depletion
high order effect (quenching)
sulfide phosphor?
GIT, Phosphortech
* B LED high I & high T : color change of pump
change of excitation for ph (WL)
change of emission from ph (Intensity)
* UV LED better for phosphor development
patent for phosphor
better pump efficiency (n-UV)
tri color phosphor (emulation)
no involving in color mixing
N-UV or B LED?
Peak WL?
* For UV LED
Sr2SiO4:Eu2+ : 3.2 lm/W, Ra=68 vs. 2 lm/W, Ra=80 for YAG
– APL 82, 683, 2003
Ca10(PO4)6Cl2:Eu2+ : UV to Ph, Blue from Ph, Blue to YAG
– Jpn. JAP 41, L371, 2002
30 lm/W, Ra = 93 from B,Y,O phosphors
– IDW 817, 2000
AE silicon-nitride material for life time : small stoke shift due to rigid lattice
- Acta Cryst. C53, 1751, 1997
RE silicon-nitride, silicon oxy nitride
coating for sulfide phosphor : life time
93/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
GIT, Phosphortech
Review by C. Summers
* Lumileds : for Blue LED, STG and SS from 2000 (two phosphor) combinations
Ra > 90
94/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
GIT, Phosphortech
Review by C. Summers
* for Blue LED, YAG was broadly used.
Q. When Ce was excess,
efficiency or peak shift?
95/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
NIMS (Japan)
* Blue LED + Y Ph (Ca--SiAlON:Eu2+)
APL, V84, P5405, 2004
USP 6,776,927 (NIMS), USP 6657379 (Elektrische Gmbh)
96/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
* UV LED + Nano phosphors
Sandia
97/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Temperature Dependence
B LED
Due to I increase : band filling
Phosphor : more sensitive upon T
98/219
4. Phosphors Claimed, Studied and Used in LED Application
Temperature Dependence
Phosphor : more sensitive upon T
The reason for this behavior ?
several factors should be considered.
99/219