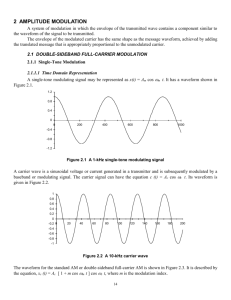
Amplitude modulation
advertisement

Amplitude Modulation Basic AM • Modulation – Amplitude – Spectrum • Carrier • Sideband v(t ) (1 m cosmt ) EC cosCt C C m – Modulation index • 0<m<1 • How to measure? – Modulated carrier vs baseband signal • What happens when m>1? Waveforms • Base Band and Modulation – m = 100% – m = 120% • Math • Real Spectrum • Double Side Band Full Carrier – Spectrum • LSB, USB, Carrier Efficiency • Efficiency in Using Bandwidth? – Two side bands • Efficiency in Using Power? – Carrier V 2 Ec2 (sin ct )2 Ec2 Pc R R 2R – Side band m 2 Pc Plsb Pusb 4 – Information in side band – Carrier for synchronization Variations of AM • Bandwidth Efficiency – Single Side Band – Vestigial Side Band • Power Efficiency – Reduced Carrier – Suppressed Carrier • Complication – Circuits: generation, tuning, detection – Filter, tone variation, carrier recovery AM Radio • Source – Audio, 20-20 kHz • Carrier Frequency – 525 – 1705 kHz • Performance – 5 kHz bandwidth – 250-500 km range – 50 µV sensitivity AM Radio Commercial AM Radio • Circuit Diagram Commercial Radio • Circuit Board Block Diagram Crucial Components • RF Amplifier – High dynamic range • Autodyne Oscillator and Mixer – Tuning • Loop Antenna – LC resonator • Intermediate Frequency Amplifiers – 455 kHz – Tank circuit (double tuner) with flat center band • Diode RF Rectifier – Envelope detection • Automatic Gain Control – Strong vs weak stations • Audio Amplifier • Speaker Heterodyne • Incoming RF vRF (t ) (1 m cosmt ) EC cosCt – RF amplifier – Bandpass filter • Local Oscillator • Mixer vLO (t ) ELO cos(C IF )t – Nonlinear device or balanced mixer vIF (t ) (1 m sin mt ) EC ELO cos(IF )t – Bandpass filter – Signal proportional to local oscillator strength • Intermediate Frequency (AM at 455 kHz) – No further tuning • EMI from Local Oscillator Detection • Baseband Signal • Coherent Detection – – – – – – vRF (t ) m A(t ) vRF (t ) (1 m A(t )) EC cosCt AM modulation vLO (t ) ELO cosCt Local oscillator vM (t ) (1 m A(t )) EC ELO cosCt cosCt Mixer vLP (t ) (1 m A(t )) EC ELO / 2 LP filter vO (t ) m A(t ) EC ELO / 2 AC coupling High sensitivity for low S/N Envelope Detection • Circuit – RF rectifier – Filter – RC time constant – Simple for high S/N • Waveform Detection • Square Law Detector – – – – Modulation Nonlinearity RF filter Low pass and AC coupling vRF (t ) (1 m A(t )) EC cosCt vsq (t ) (1 m A(t ))2 EC2 cos2 Ct vRF LF (t ) (1 m A(t ))2 EC2 / 2 vLF (t ) m A(t ) EC2 Performance • • • • Sensitivity Fidelity or Bandwidth Dynamic Range Selectivity – Adjacent channel • Image Rejection – IF • Spurious Response – Harmonics • Squelch • Noises – Static noise from transmission media – Motor boating noise from drift in frequency Lab and Projects • Virtual Laboratory – http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/load Category.do (Search: FM AM) – Matlab project • http://www.cse.ucsc.edu/classes/ee151/Winter01/ – Software Radio (http://www.wpi.edu/Pubs/E-project/Available/Eproject-042805-113037/unrestricted/DASR_MQP_REPORT.pdf) • Simple AM Projects • Experiments – Agilent 33120 AM modulation – MC1496 http://www.onsemi.com/pub/Collateral/AN531-D.PDF AM Transmitter • History • Block Diagram • Automatic Level Control – m<1 AM Modulator • Balanced Mixer • Other Circuit – Base band signal modulates oscillator current Power Amplifier Impedance Matching • Maximize Power to the Load • Impedance – Z=V/I • Change V – I Relation – Transformer • High current, low voltage • Low current, high voltage – RLC Networks • Frequency dependent impedance Impedance Matching • MIT Open Courseware – http://ocw.mit.edu/NR/rdonlyres/Electrical-Engineering-andComputer-Science/6-776Spring-2005/025E9FB7-46C3-471898EA-CBD23EEC9D98/0/lec4.pdf • Berkeley RLC Pi and T LC Network Calculator – http://bwrc.eecs.berkeley.edu/Research/RF/projects/60GHz/matc hing/ImpMatch.html • Role of Antenna – Impedance transformation between circuit and free space Short Wave Radio • Terrestrial Coverage, HAM – http://n5xu.ece.utexas.edu/hamradio/ • Regenerative Receiver Project – http://www.electronics-tutorials.com/receivers/regen-radio-receiver.htm HAM • http://www.arrl.org/hamradio.html • http://www.qsl.net/dl4yhf/ – Spectral analysis of audio signals • http://www.ac6v.com/ – Antenna projects • http://www.radio.org/linux/ – Linux HAM AM Stereo • Two Channels – L+R – L-R • Quadrature Amplitude Modulation – Sin, Cos: orthogonal – Increase Information Capacity Without Increasing Bandwidth • Motorola CQUAM System – Details – Chip Modern Application of AM • Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) • 8-VSB Digital Signaling AM Noise Analysis • DSBFC Signal and Noise e(t ) (1 m A(t )) EC cosCt nC cos(Ct ) nS sin(Ct ) – – – – – Baseband signal power: SM m2 A2 EC2 / 2 Carrier power: SC EC2 / 2 Noise spectral density: N0 / 2 Double sideband bandwidth: 2 2W 2 2 Total noise power: N 2W N0 nc / 2 ns / 2 • Coherent Detection eD (t ) (1 m A(t )) EC ELO / 2 nC ELO / 2 – In phase noise only S / N m2 A2 EC2 / 2WN 0 – S/N AM Noise Analysis • Envelope Detection – Signal Dominant Regime e(t ) [(1 m A(t )) EC ) nC ]2 ns2 (1 m A(t )) EC nC • Similar to coherent detection – Noise Dominant Regime • Noise large • Signal small with random phase e(t ) nC2 ns2 (1 m A(t )) EC cos • Numerical Analysis AM Review • • • • AM Waveform Modulation Index Limit Double Sideband, Full Carrier Detection Circuits – Coherent detection – Envelope detection • Variations – SSB, RC or SC – Vestigial sideband • AM Transmitter – Impedance matching – Efficiency