Variable Frequency Drives
advertisement
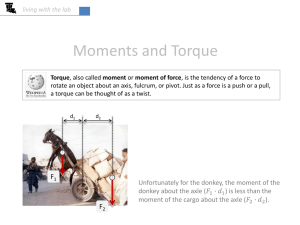
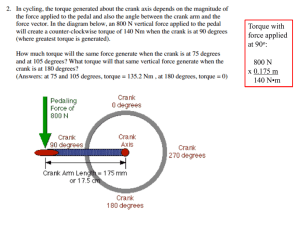
Application Types • Variable Torque • Constant Torque Variable Torque Affinity Laws: • Flow is proportional to speed. (Flow1 / Flow2) = (RPM1)/(RPM2) • Pressure is proportional to the square of the speed. (Press1 / Press2) = (RPM1)2 / (RPM2)2 • HP is proportional to the cube of the speed. (HP1 / HP2) = (RPM1 )3/ (RPM2)3 Variable Torque Curve Variable Torque Curve Region of continuous operation Region of intermittent operation Torque (Typical) 200% 100% 63% Continuous torque capability Peak torque capability Load torque Requirement 60 Speed in Hertz 120 Variable Torque - Flow Flow is proportional to speed. (Flow1 / Flow2) = (RPM1) / (RPM2) Flow Gallons/min 10000 RPM 1800 Second RPM 900 Second Flow 5000.00 Variable Torque - Pressure Pressure is proportional to the square of the speed. (Press1 / Press2) = (RPM1)2 / (RPM2)2 Pressure Lb/sq. in 1000 RPM 1800 Second RPM 3600 Second Pressure (lb/sq. in) 4000 Variable Torque - HP HP is proportional to the cube of the speed. (HP1 / HP2) = (RPM1)3 / (RPM2)3 Horsepower RPM 10 1800 Second RPM 3600 Second Horsepower 80.00 Energy Savings Using VFD’s Energy Savings Using VFD's Motor RPM HP Eff PF Amps Volts kW Rate / Hr 24 Hrs Annual Cost VFD 1750 30.0 88% 90% 35.47 460 25.43 0.06 $ 36.62 $ 13,366.96 RPM HP Eff PF Amps Volts kW Rate / Hr 24 Hrs $ Annual Cost $ 1750 30.0 89% 97% 32.54 460 25.15 0.06 36.21 $ 13,217 $ 1600 1500 22.9 18.9 89% 89% 97% 97% 24.87 20.49 460 460 19.22 15.84 0.06 0.06 27.67 $ 22.80 $ 10,101 $ 8,323 $ 1400 15.4 89% 97% 16.66 460 12.87 0.06 18.54 $ 6,767 $ Operating Costs Hrs % speed RPM HP Eff PF Amps Volts kW Rate / Hr Total $ Annual Cost $ 3 60% 1050 6.48 89% 97% 7.03 460 16.29 0.06 0.98 $ 357 $ 6 1.5 100% 75% 1750 1312.5 30.00 12.66 89% 89% 97% 97% 32.54 13.73 460 460 150.88 15.91 0.06 0.06 9.05 $ 0.95 $ 3,304 $ 348 $ 9 80% 1400 15.36 89% 97% 16.66 460 115.87 0.06 6.95 $ 2,538 $ 1300 12.3 89% 97% 13.34 460 10.31 0.06 14.84 $ 5,418 $ 1200 9.7 89% 97% 10.49 460 8.11 0.06 11.68 $ 4,261 $ 900 4.1 89% 97% 4.43 460 3.42 0.06 4.93 1,798 Formulas 3 80% 1400 15.36 89% 97% 16.66 460 38.62 0.06 2.32 $ 846 $ 1.5 90% 1575 21.87 89% 97% 23.72 460 27.50 0.06 1.65 602 HP2 = HP1 x ( RPM2/RPM1)3 kW = (E x I x PF x 1.732) / 1000 Amps = (746 x HP) /(1.732 x E x Eff x PF) Kw / Hr Rate $ 0.06 Voltage 460 Totals kW Rate / Hr 24 Hrs Annual Cost 365.08 0.06 $ $ 21.90 7,995.00 Variable Torque Applications • Irrigation Water Pumps • Downhole Water Pumps • Submersible Water Pumps • Domestic Water Pumps • Centrifugal Sewage Treatment Pumps • • • • Centrifugal Fans Blowers Air Handling Units Chillers Types of Three Phase AC Motors used on Pumps Horizontal foot mounted Close coupled Belt driven Gear reducer Available in NEMA MG1 Part 30 & NEMA MG1 Part 31 Vertical Hollow shaft Solid shaft Submersible Specialized winding process Available in NEMA MG1 Part 30 only Single Phase Motors IMPORTANT NOTICE!!!!! Single Phase Motor Cannot be used with a VFD Three Phase Motor with THREE Phase Input L1 L2 L3 T1 T2 T3 VFD is sized by the Full Load Amperage of the motor. Three Phase Motor with SINGLE Phase Input T1 L1 T2 T3 L2 Output Voltage is the same as Input Voltage. VFD is sized by the Full Load Amperage of the motor multiplied by 1.7 eg. For a 10HP motor with a FLA of 12 amps. The VFD size would be 12 x 1.7 = 20.4 amps Pump Packaging Options • Reactors line and load, Harmonic Filters, Sine Wave DV/DT Filters • Disconnect, fusible or non-fusible • Bypass system, Cam Switch, 2 contactor, 3 contactor • Serial communication HVAC protocols • Standard and custom door mounted controls; any combination • Pre-engineered packages – Nema 1, Nema 12, Sprinkler Proof and Nema 3R • Custom engineered packages Bypass Package Nema 3R • Options – OPE Keypad – Fusible disconnect – 3 Contactor Bypass – Line Reactor – Load Reactor – Forced Air Ventilation Pump Packages • Standard Enclosure Options: – Nema 1 – Nema 12 – Nema 3R – Sprinkler Proof – Wall Mount – Floor Mount WELLMAX • • • • • A USER FRIENDLY GRAPHICAL TOUCH SCREEN LCD with sensible wording for easy operation. Displays historical data of TORQUE, AMPS, and RPM (standard). You can zoom in & out to examine any data point of interest. An optional memory card will CONSTANTLY STORE DATA, which can be retrieved by the user. An optional four inch printer will be available for on the site printing of information. PUMPOFF CONTROL features will prolong the life of the pump by monitoring and maintaining an approximate FLUID LEVEL. SERIAL port available for COMMUNICATION. Optional interface available for MODBUS protocols. Option - A LOW COST SATELLITE COMMUNICATION link, which allows Internet viewing of 10 points of information as well as voice call out ability on alarm situations for $6 per day. WELLMAX CONTROLLER PUMPOFF CONTROLLER Constant Torque Curve Constant Torque • Torque remains constant up to the motor base speed. • HP is proportional to the speed. Constant Torque Applications • • • • • • Conveyors Compressors Positive Displacement Pumps Crushers Mixers Etc. Positive Displacement Pumps Constant Torque Load Region of intermittent intermitten operation Region egion of continuous operation eration Region of intermittent operation Torque (Typical) 200% 100% 63% Peak torque capability Continuous torque capability Load torque requirement 60 100 Speed in Hertz Constant Power Load Region of intermittent operation Region of continuous operation Field weakening region 200% Torque (Typical) Peak torque capability provided that the AC drive has adequate overload capability 100% Continuous torque capability limited by motor cooling 63% Load torque requirement 60 Speed in Hertz 100 Torque Derating Due to Motor Cooling F ie ld w e a k e n in g re g io n (T y p ic a l) T o rq u e 200% P e a k to rq u e c a p a b ility p ro v id e d th a t th e A C d riv e h a s a d e q u a te o v e rlo a d c a p a b ility 100% C o n tin u o u s to rq u e c a p a b ility lim ite d b y m o to r c o o lin g 63% 60 S p e e d in H e rtz 100 Torque Curve Below & Above 60 Hz, Constant Torque V/F Ratio Application Considerations • • • • • • • Motor voltage, HP & FLA specifications Load type, constant or variable torque Control system requirements Serial communication protocol Analog and digital input and outputs Harmonic considerations Nuisance tripping concerns Motor insulation protection Line & load filter options