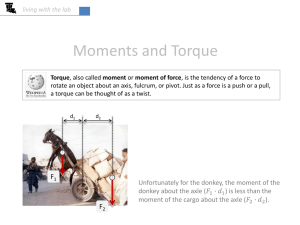
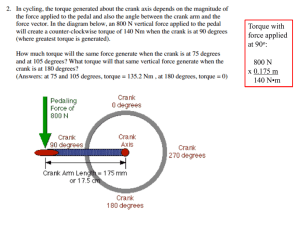
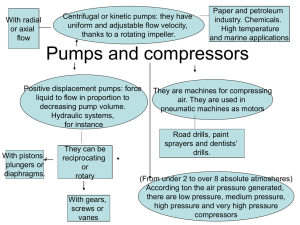
Energysavings
advertisement
TYPES OF LOAD automation4me 1 TYPES OF LOAD CONSTANT TORQUE LOAD : 100 TORQUE 80 NOTE:A CONSTANT TORQUE LOAD IS NOT NECESSARILY 100% LOAD 50 50 100 PERCENT SPEED automation4me 2 TYPES OF LOAD CONSTANT TORQUE LOAD : Positive Compressors Displacement Root Conveyors Blowers Pumps automation4me 3 TYPES OF LOAD VARIABLE TORQUE LOAD : TORQUE & POWER IN % 100 80 TORQUE 60 40 POWER 20 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 SPEED IN % automation4me 4 TYPES OF LOAD VARIABLE TORQUE LOAD ( Torque Varies as Square of Speed) automation4me Centrifugal CentrifugalPumps Fans 5 TYPES OF LOAD CONSTANT HORSEPOWER LOAD : 100 TORQUE HORSE POWER TORQUE 50 50 100 150 200 PERCENT SPEED automation4me 6 TYPES OF LOAD CONSTANT HORSEPOWER LOAD : • Lathe • Grinders • Winders • Coilers automation4me 7 ENERGY SAVING APPLICATIONS automation4me 8 Energy Savings Key Applications Areas – The Energy Guzzlers • Fans – AHU – Ventilation / Fresh Air – Exhaust – Cooling Tower Fans – ID / FD Fans • Pumps – Process Water – Pressure booster pumps • Compressors – Reciprocating, Screw, Centrifugal automation4me 9 FAN APPLICATION Air flow control of fan Outlet side damper automation4me Inlet side damper 10 Comparison of motor power for fan drive system 100 0 50 automation4me Airflow or motor speed (%) 100 11 Flow Control-Affinity Laws • Flow Speed • Pressure / Head Speed 2 • Power Speed 3 automation4me Benefits of Flow Control… 12 Fundamentals- Traditional Throttle Flow control is achieved by riding the pump or the fan curve… automation4me 13 Fundamentals- Evolution Flow control is achieved by riding the System Curve… automation4me 14 PRINCIPLE - ENERGY SAVING BY SPEED CONTROL OF PUMPS A E THROTTLE CONTROL ENERGY SAVING B PRESSURE = SHADED REGION = AREA (OEAD) - AREA (OFCD) F O C SPEED CONTROL D VOLUME automation4me 15 The energy saving effect to the pump type 2.0 1.0 0 0.5 1.0 Flow rate Q (P.U.) automation4me 16 PRINCIPLE - ENERGY SAVING BY SPEED CONTROL As Per Affinity Laws Flow (%) HP (%) Required 100 100 75 42 50 12.5 automation4me 17 automation4me 18 Compressors • Operates in a load/ unload cycle. Load 100% Time automation4me 20 Compressor–Load/Unload Control Conventional compressor system work between two set pressures, resulting in pressure generated being higher than the pressure required in the system. 110PSI PRESSURE 100PSI 20 PSI 90PSI MINIMUM SYSTEM PRESSURE REQUIRED TIME POWER 100% FULL LOAD POWER DURING LOAD CYCLE 20-30% OF FULL LOAD POWER DURING UNLOAD CYCLE LOAD UNLOAD automation4me TIME 21 Disadvantages of Traditional Compressor: Energy consumption as high as 20-30% of full load power during unload period. Pressure in the system is much more than the minimum system pressure required, resulting in extra power consumption and wear and tear of the mechanical system. 20PSI extra pressure in the system, results in 10% extra power consumption. DOL or star/delta starting sequence on a motor creates a power surge in electrical system. automation4me 22 Typical Schematic A I R AC MOTOR VARIABLE SPEED AC DRIVE AIR COMPRESSOR PRESSURE TRANSMITTER R E C E I V E R To Plant 4-20 mA/ 0-10V PRESSURE FEEDBACK SIGNAL 3 Ph./ 415V Supply automation4me 23 Advantages with Inverter Control: Variable pressure setting possible. Accurate pressure control. No unload cycle, thus reducing power consumption typically by 20 to 30% of full load power. Soft start with inverter control, power to the motor is increased progressively, avoiding peak power demand in the electrical system. automation4me 24