Electromagnetics Enhancements
advertisement

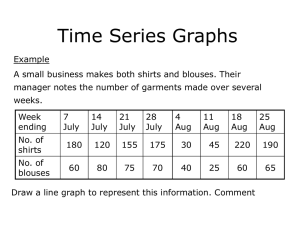
6. Electromagnetics Enhancements Electromagnetics Enhancements • Emag focus in ANSYS 5.7 is on high-frequency electromagnetics (discussed next). – LMATRIX (inductance calculation) improvements • Output array contains the NxN inductance matrix (as before) and a new N+1th column containing flux linkage values, with the I th row corresponding to the I th coil. – SENERGY (magnetic energy calculation) is more robust, accurate, and faster. NEW FEATURES 5.7 • Other Emag enhancements: Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-2 … Electromagnetics Enhancements • Other Emag enhancements (cont'd): – New diode element, CIRCU125 • To simulate a common or Zener diode. • Can be defined using the circuit builder. CIRCU125 NEW FEATURES 5.7 • Can interface with circuit element CIRCU124, transducer element TRANS126, and mechanical elements MASS21, COMBIN14, and COMBIN39 for coupled-field analyses. Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-3 High Frequency Electromagnetics Overview – RF/microwave problems (interior wave propagation) – Radiation and scattering problems (exterior wave propagation) • Available in ANSYS/Multiphysics and ANSYS/Emag HF products. NEW FEATURES 5.7 • In ANSYS, HF Electromagnetics is used to simulate the full wave electromagnetic phenomena. • HF solution is in the frequency domain. • No limit on the highest frequency allowed. Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-4 … High Frequency Electromagnetics Overview (cont'd) Major components of a HF FEA model Modal analysis CAD import Boundary conditions HF Elements New/enhanced Existing NEW FEATURES 5.7 Harmonic analysis materials HF Postprocessing Excitations Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-5 … High Frequency Electromagnetics Overview (cont'd) – New boundary conditions • PML (perfectly matched layer), impedance – New excitations • Waveguide ports; plane wave; surface magnetic field, surface electric field, and current density excitations NEW FEATURES 5.7 • ANSYS 5.7 takes a major leap in HF simulation capabilities with several new features and enhancements: – Elements • New HF118 element, enhancements to HF119 & HF120 – Solvers and postprocessing Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-6 HF Electromagnetics - New BC's PML Perfectly Matched Layer (PML) • Reduce the FEA domain significantly by replacing the outer computation domain (infinite) with an absorbing layers. • Required in many real world applications: – Exterior phenomena, e.g, antenna and EMC/EMI problems. NEW FEATURES 5.7 • Absorbing layers of elements used for the truncation of the HF FEA domain. – Interior phenomena, e.g, waveguides and transmission lines. Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-7 HF Electromagnetics - New BC's … PML • PML region is simply a layer (or layers) of elements placed at the boundary of the field domain. – Extend the material properties in the field region into PML – PML supports symmetry boundary conditions PML Surrounding field HF Device NEW FEATURES 5.7 • Elements used are 119 and 120 with KEYOPT(4) = 1. For example: ET,2,HF120,,,,1 Schematic of cross section of a 3D PML region Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-8 HF Electromagnetics - New BC's … PML • Recommendations: – Thickness of PML region > 0.25*wavelength. – Allow at least 4-5 layers of elements in surrounding field as buffer zone between device and PML. – Four elements through the thickness of PML region for - 50 Db attenuation. More attenuation can be obtained by adding more PML layers. PML2 NEW FEATURES 5.7 – PML boundary edges should be parallel to global Cartesian or Cartesian ESYS. ESYS2 PML1 Schematic of 1D PML layers ESYS1 PML3 ESYS3 Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-9 HF Electromagnetics - New BC's Impedance • Four types of impedance BC's are now available: – Far-field radiation boundary – PEC (perfect electric conductor) surface with dielectric coating – Non-PEC surface • Apply using SF family of commands air-dielectric Interface surface of non-perfect conductor dielectric non-perfect conductor conductor PEC with dielectric coating NEW FEATURES 5.7 – Air-dielectric boundary air far-field boundary Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-10 HF Electromagnetics - New Excitations Waveguide Ports • New parallel-plate waveguide – Can be used to simulate problems like micro-strip. – Z axis can be in either the wave propagation direction or the opposite direction. X-axis must be parallel to width of port. – Origin for rectangular waveguide is at center, different from 5.6. new y y x z Rectangular Waveguide y y x x NEW FEATURES 5.7 • All four types of waveguides x z Parallel-Plate Waveguide Circular Waveguide Coax Waveguide Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-11 HF Electromagnetics - New Excitations ...Waveguide Ports • Higher-order modes are now available at 5.7: RECT C IR C TEM P AR A TEM TEm n TEm n TE0n TM m n TM m n TM 0n NEW FEATURES 5.7 CO AX Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-12 HF Electromagnetics - New Excitations ...Waveguide Ports • HFPORT,Portnum,Porttype,Local,Mode,Portbc, VAL1,VAL2,VAL3,VAL4,VAL5 • Port boundary conditions by Portbc in HFPORT: – IMPD Matching the impedance of the single mode. – SEXT Terminating the port w/ PML layers. An invisible port to extract S-parameters. – SOFT Equivalent current excitation. Allow multiple ports & multiple modes. Can extract S-parameter. – HARD Fixed electromagnetic field at port. NEW FEATURES 5.7 • New HFPORT command replaces PORTOPT. Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-13 HF Electromagnetics - New Excitations ...Waveguide Ports • Schematics of four Portbc options for waveguides in HFPORT command port PML2 PML1 IMPD port incident wave SOFT HARD incident wave reflection wave incident wave incident wave NEW FEATURES 5.7 SEXT reflection wave Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-14 HF Electromagnetics - New Excitations Plane Wave • New PLWAVE command replaces PLANEWAVE: – PLWAVE, EX, EY, EZ, AngX, AngZ • AngX and AngZ are the angles of the wave to X-axis and Zaxis. – Used for scattering analysis in EMC/EMI analysis NEW FEATURES 5.7 • EX, EY and EZ are the electric field amplitudes in X, Y and Z directions. Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-15 HF Electromagnetics - New Excitations Source Terms • You can now specify the following excitation sources (using the BF family of commands): – Magnetic field (H) at a surface. – Current density (JS) at a point, line, surface, or volume. NEW FEATURES 5.7 – Electric field (EF) at a surface. Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-16 HF Electromagnetics Element Enhancements • New 2.5-D, 8-node HF118 element – Applicable for modal analyses (Block Lanczos). – Quadrilateral or triangular shapes. – Both 1st order and 2nd order available. – To calculate cutoff frequencies and propagating constants used together with HFEIGOPT. NEW FEATURES 5.7 – Extract eigenvalues of guided wave structures (waveguides or transmission lines). Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-17 HF Electromagnetics … Element Enhancements • HF119 (10-node tet) gets new 2nd-order option – Applicable to both modal and full harmonic analyses – Better accuracy compared with 1st order element, especially for complex geometry • HF120 (20-node brick) gets improved 2nd-order option – DOFs from 36/element to 54/element – Complete vector basis functions NEW FEATURES 5.7 – Keyopt(1) = 2 – Better accuracy for higher-order modes Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-18 HF Electromagnetics Solution and Postprocessing • Sparse solver is now the default (not frontal). – ICCG and FRONTAL also available as before – Harmonic analysis (Antype, harmic) HFSCAT,SCAT must be specified for RCS calculation – Modal analysis (Antype,modal) 3D or 2D modal analysis NEW FEATURES 5.7 • Choosing analysis types Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-19 HF Electromagnetics … Solution and Postprocessing • New commands to review far-field results: – PRHFFAR for listings RCS of a metal plate with incident plane wave NEW FEATURES 5.7 – PLHFFAR to display the electromagnetic far field, radar cross-section (RCS), and antenna pattern (PATT) Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-20 HF Electromagnetics … Solution and Postprocessing • New HFNEAR command to calculate near-field results (EF & H). • New PRHFFAR calculates/prints far field beyond FEA domain. • Other: – HFSYM to set symmetry planes for postprocessing calculations in near and far field NEW FEATURES 5.7 – Options to calculate at a specified point or along a path. – Current density can be shown graphically – Calculated parameters: • SPARM: magnitude and phase angle of S-parameter (both single and multiple ports) Training Manual 001419 15 Aug 2000 6-21