ONT - BSNL Durg SSA(Connecting India)
advertisement

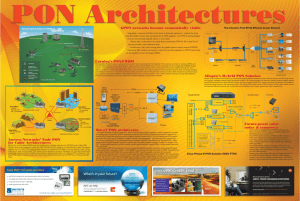
1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) FTTX Future of FTTH PON a Simple view Types of PON GPON Overview Fundamentals of GPON PON advantage Comparison Of PON With Other Broadband Access Technologies •FTTX is of 4 types: •FTTH: Fiber To The Home •FTTB: Fiber To The Building •FTTC: Fiber To The Curb FTTH •FTTN: Fiber To The Node •WHY CHOOSE FIBER? FTTC Superior Performance 2. Ease of Installation 3. Easy to Upgrade 4. Smaller size and lighter weight 1. FTTx FTTN FTTB FTTH access networks will provide ample bandwidth for 5, 10 and even 20 years or more. FTTH can redefine performance parameters to support future applications. An example of this is support for Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation or DBA. FTTH provide different bandwidth priorities to subscribers so that different application service requirements can be supported. For example, it may be critical for high-definition IP TV to have priority download of a time-sequenced video frame and not so critical for a user accessing email. All GPON suppliers must have programmable DBA. •In a PON system, a single fiber connects multiple customers to a single transceiver at the central office (CO). •The single fiber is split, using a passive optical splitter, to serve up to 32customers. • Not only does PON reduce the amount of fiber required, but a single transceiver serves multiple customers instead of requiring one per customer. Passive Optical Network. Facilitates another (higher bandwidth) broadband access technology Competes with and complements xDSL, cable modem and fixed wireless With a PON, optical fiber is deployed either all the way or almost all the way to the end user (VDSL) Passive because –- network only consists of passive light transmission components (fiber links, splitters and couplers) –- This creates great cost savings for the provider (more reliable and less costly to operate/troubleshoot) PONs use a Point-to-Multi-Point (P2MP) topology ODN – Optical Distribution Network – An ODN realizes the optical transmission from the OLT towards the users and vice versa. It utilizes passive optical components. OLT – Optical Line Termination – An OLT is the service provider endpoint of a PON and is placed in a CO or head end ONT – Optical Network Termination – An ONT is a device that terminates the PON and presents native service interfaces to the user. An ONT is typically located on the customer’s premises. ONU – Optical Network Unit – An ONU is the PON-side half of the ONT, terminating the PON, and may present one or more converged interfaces, such as xDSL or Ethernet, toward the user. An ONU typically requires a separate subscriber unit to provide native user services such as telephony telephony, Ethernet data, or video. There are various types of PONs. The general technology is the same. The differences are in the specifications and upper layer protocols. – APON – ATM based PON uses ATM encapsulation of the transported data. – BPON – Broadband PON succeeded APON and also uses ATM encapsulation. Supports superior features, higher speeds and was standardized by the ITU-T. – EPON or GE-PON – Ethernet PON uses Ethernet for data encapsulation. Standardized by the IEEE in mid-2004. -GPON or Giga PON – Gigabit PON uses a new Generic Encapsulation Method (GEM) transport layer that supports ATM, Ethernet and TDM data transport. GPON 2,5GB EPON 1,25GB 1000 SPEED [MB/s] BPON 622MB APON 155MB 100 PON 1990 1992 54MB 1994 1996 1998 2000 YEARS 2002 2004 2006 2008 Gigabit PON is an attractive FTTH broadband access network technology because it meets the needs of carriers world-wide. GE-PON (EPON) has successfully demonstrated this approach and is being deployed in high volume in Asia. It is an access method transported by optical fiber, FTTx. Is a point to multipoint access, one central point can reach from 32 to 128 premises. There are only two types of equipments the OLT (central) and the ONT’s (in customer premises) It includes all of the ingredients for market success –a consumer base that is eager to adopt a much faster and more comprehensive set of high-speed services, Optical Line Terminal(OLT) Optical Splitter ONT ONT ONT The Optical Line Terminal (OLT) • Acts as the central aggregation element. • Located in the Core Data Center. • Replaces multiple L2 switches. • Can aggregate thousands of end users. Optical Line Terminal(OLT) Optical Splitter ONT ONT ONT Passive Optical Network (PON) • Completely passive infrastructure • Single fiber (32:1) carries multiple wavelengths • 2.48 Gbps downstream • 1.24 Gbps upstream Serve Remote Bldgs Up to 20Km Optical Line Terminal(OLT) Optical Splitter ONT (32:1) ONT ONT Passive Optical Splitter Feeding FDH •Rack Mount or Cassette versions • Splits single fiber up to 32 ways • Can be located in the IDF/TR, under a raise floor, in a ceiling zone box, or in a manhole. • The further the splitter is extended to the desk, the greater the savings in fiber infrastructure . Optical Line Terminal(OLT) Optical Splitter ONT ONT ONT Optical Network Terminals (ONT) • Terminates the fiber at the end user • Provides Data, VoIP, IP Video services • Some models also provide native POTS • Desktop and MultiDesk Unit models shared infrastructure translates to lower cost per customer • minimal number of optical transceivers • feeder fiber and transceiver costs divided by N customers • Greenfield per-customer cost similar to UTP passive splitters translate to lower cost • can be installed anywhere • no power needed • essentially unlimited MTBF fiber data-rates can be upgraded as technology improves • initially 155 Mbps • then 622 Mbps • now 1.25 Gbps • soon 2.5 Gbps and higher Edge Switches vs. Passive Fiber Splitter ADVANTAGES These include a long-term life expectancy of the fiber infrastructure, lower operating costs through the reduction of “active components, support for greater distances between equipment nodes most importantly, much greater bandwidth. DSL-certain megabits per sec, FTTH pon 1 to 2.5Gbps Since Pon uses only passive components • it has low power requirements • less no of technicians • cost savings up 40 t0 60% • Savings mainly result from lower customer contacts associated with service orders and trouble reporting, outside plant operations, central office operations, and network operations. It provides high bandwidth for high-speed Internet access, video on demand,IPTV and voice over IP (VoIP) .