ANSI TIA EIA 570
advertisement

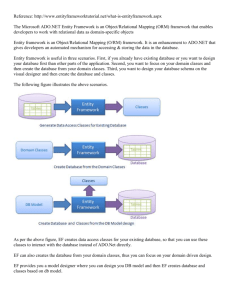
ANSI/TIA 570B Residential Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard Updated Dec 2013 PRGodin ©PRGodin @gmail.com 1 Introduction Originally a standard for small commercial buildings the 570B standard has migrated to primarily address residential installations. Communication infrastructures are still relatively new in the residential construction market but have become common for new construction. 2 General Requirements Communication cabling infrastructures in singledwelling residences need to support a wide variety of communication requirements. The cabling structure needs to address: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Voice Data Video Security Whole-home audio Control system 3 Source: ANSI-TIA-EIA-570 Standard Single Dwelling Residence Infrastructure 4 Grades of Residential Cabling Grade 1: Basic ◦ Provides for basic telecommunication services. Minimum: One 4-pair UTP (Cat5e or better) One 75Ω Coax Grade 2: Intermediate ◦ Provides for basic to intermediate service needs. Minimum: Two 4-pair UTP (Cat5e or better) Two 75Ω Coax Optional 2-fiber optical cabling 5 Some Definitions Demarcation point: Point where ownership of the hardware changes Distribution Device (DD): Central facility used to connect outlets within the residence and to the service providers ADO Cable: Connectorized cable assembly used to connect between the demarcation point and the DD. 6 Typical 570B Residential Installation Source: ANSI-TIA-EIA-570 Standard 7 The Distribution Device (DD) The DD may consist of: ◦ Passive cross-connections ◦ Active cross-connections ◦ A combination of passive & active cross-connections The DD is installed within the tenant’s space in a centralized location that is easy to access The DD should be capable of handling all communication requirements 8 Space for the DD There is a guideline for space to allocate for the DD The DD can be installed either on a backboard or between wall studs. Multiple interconnected DDs may be used within the same space DDs usually require electrical service 9 DD Space Allocation Chart Source: ANSI-TIA-EIA-570 Standard 10 Outlet Cables Cables are run from the DD to the telecom outlets in a star topology. Cables shall not exceed 90 meters, with an additional 10 meters for patch cords and jumpers. Recognized cables: ◦ 4pr UTP (cat 5e or better) ◦ Coax RG-6 (RG59 for CCTV only) foil & braid ◦ Optical fiber (50, & 62.5 MM, SM) 11 Room Requirements Minimum of one outlet location for each of these rooms: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Kitchen Bedroom Family Room Den/Study Room Additional outlets should be installed where: ◦ there is more than 3.7 meters (12ft) along a continuous wall ◦ There is more than 7.6 meters (25ft) along a broken wall 12 Examples of Room Outlet Location Source: ANSI-TIA-EIA-570 Standard 13 Cable Pathways Efforts should be made to conceal the cabling within the walls of the building especially in new construction and remodeling. image: howto.techworld.com 14 Special Case Cabling Alarm, Control and other cables may fall under the jurisdiction of local and national codes and laws. The standard provides installation suggestions but is not meant to overrule specific legal and performance requirements. 15 Special Case: Alarm/Security Cable Security alarm systems may consist of: ◦ Sensors ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Motion, breakage or shock detectors Door and window contacts Sound & Pressure sensors Water & temperature sensors Smoke, heat and CO2 sensors Control panels Entry keypads and manual activators 1 and/or 2-way audio and/or video Alerting devices (siren, strobes, bells, etc) Remote (personal) devices Door and window latch operators Lighting control Remote connection 16 Alarm/Security Systems Cable Should be run in a physical star topology. Daisychaining some devices may be the standard connection method but it is not recommended. Fire systems are subject to regulation by the US NEC. Typical security systems cable: ◦ 16 or 18 AWG stranded or 22 AWG solid conductors ◦ 4 conductor (active devices) or 2 conductor (passive devices) 17 Video Cabling RG 59 for baseband video (such as CCTV) RG 6 for broadband (CATV, Satellite) Cat 5e/6 may be used with a balun 18 Home Audio Location of the audio systems is important for performance quality and ease of control. Follow manufacturer recommendations for installation locations and requirements Three areas of control: ◦ Headend (DD) to distribution device ◦ Distribution device to volume control ◦ Volume control to the speaker 19 20 Source: ANSI-TIA-EIA-570 Standard Audio Cable Headend (DD) to distribution: ◦ one cat 5e/6 ◦ 4 conductor speakers for left and right ◦ 2 conductors for control Distribution to Volume control & Volume control to speakers ◦ one cat 5e/6 ◦ 4 conductors for 1 or 2 speakers 21 Audio Cable AWG The AWG is based on the wattage of the speakers and the length of the cable. Conductors should be red(+) and black(-), and for 4conductors should include white(+) and green(-). Source: ANSI-TIA-EIA-570 Standard 22 Control Systems Climate control, lighting control and other home automation: ◦ Recommend following manufacturer’s recommendations for cabling ◦ The standard recommends running a can 5e/6 between the active elements of the system to “accommodate a large variety of climate control options”. 23 Multi-Dwelling & Campus Infrastructures Multi-dwelling buildings may have a single services demarcation and redistribute the service to the individual dwellings. Services Provider(s) ADO/DD ADO/DD Unit 1 ADO/DD Unit 2 ADO/DD Unit 4 Entrance Facility ADO/DD Common Equipment Room Unit 3 ADO/DD Unit 5 ADO/DD Unit 6 ADO/DD Unit 7 Unit 8 24 Distances The Entrance Facility should be connected to a separate common Equipment Room. This room should permit shared access for services and for the building management’s services. If the distance from the ER to the furthest dwelling is more than 150 meters the service provider should be advised. Limitations between the DD an outlets in the dwelling are limited to a maximum of 90 meters. 25 Larger Multi-Dwelling & Campus Infrastructures If there are a large number of floors or units a CTR, or Common Telecommunications Room, should be located on each floor or on each 3rd floor. Services Provider(s) ADO/DD ADO/DD ADO/DD CTR Unit 1 Unit 2 ADO/DD ADO/DD Unit 3 ADO/DD CTR Unit 4 Entrance Facility Unit 5 Common Equipment Room ADO/DD Unit 6 ADO/DD Unit 7 Unit 8 26 Campus Telecommunication Requirements Campus environments may consist of separate buildings. Interconnecting backbones should be contained within conduit, aerially or within interconnecting tunnels. Building entrance protection must be implemented where required 27 Backbone Cabling Multi-conductor copper Multi-pair 100Ω UTP Series 6 & 11 coax (RG6 triple and quad shield and RG11) Series 59 coax (CCTV only) Other coaxial (“hardline”) Fiber Optics (50 & 62.5MM, SM) 28 Telecommunications Outlet Telephone outlet with mounting studs permitted 8 position mod jacks that meet the 568 standards (may be used with 6 pos plugs) Coax F connectors Recommendation is that patch cords be factory made. 29 Other Issues All firestop requirements must be followed Secondary protection must be installed Grounding must be implemented 30 Electromagnetic Noise Data communications cable must be run with at least 2 inches of separation from a parallel power cable within a wall and 6 inches of separation from cables going to active security devices. Security cable must maintain at least 6 inches of separation from power cables. Audio cable should have at least 12 inches of separation from data communication cable Typically 12” of separation is recommended in all cases. 31 Testing and Administration Testing should follow the 568C standards Administration should follow the 606B standards. Pathways planning should follow the 569B standard. 32 Conclusion The 570B standard addresses small installations and installations for residential units. These installations typically make use of a greater variety of communication requirements. The standard relies on other standards for administration, testing, cable performance and documentation. END prgodin @ gmail.com 33