PPTX
advertisement

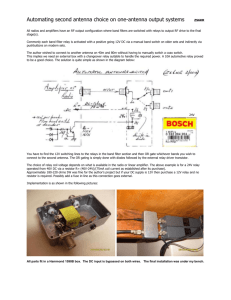
Yossef Oren, Dvir Schirman, and Avishai Wool: Tel Aviv University ESORICS 2013 Introduction Contactless smartcards Attack motivation System design Experimental results Attack scenarios Conclusions Passive tags Communication based on inductive coupling Transmit back data using load modulation Nominal operation range – 5-10 cm Contactless smartcards are being used in a variety of security oriented applications: Access control Payment E-voting Smart ID card Passports All of them assume the tag is in proximity of the reader If a communication between the reader and the tag could be established from a longer range – the proximity assumption would be broken Our goal – build a device (a.k.a “Ghost”) which allow a standard tag to communicate with a standard reader from a distance of more than 1m HF Re RFI D ad er 5 cm HF R T a FI D g Relay attack – extending the nominal communication range between a reader and a tag using a relay channel between two custom made devices (“Ghost” & “Leech”) [KW05, Han05, FHMM11, SC13] Extended range Leech – a device that allows to read a standard tag from a distance of 30 cm [KW06] Design principles: Two separate antennas: ▪ A large loop antenna for downlink ▪ A mobile monopole HF antenna for uplink Active load modulation for uplink transmission PC based relay An open source & open hardware evaluation board for ISO14443 Can emulate a tag or a reader Based on NXP PN532 www.openpcd.org A relay & a Leech were not part of this research, but necessary for the whole system Relay channel between two OpenPCD2 boards was implemented inside a single PC Using libnfc’s nfc-relay-picc – designed to overcome relay timing limitations Leech was based on an unmodified OpenPCD2 Receiving antenna: a 39 cm loop antenna designed for prior Leech project Matching circuit: Based on NXP’s app note LNA: Mini-Circuits’ ZFL-500LN Active load modulation: Producing the spectral image created by load modulation by means of a standard AM modulator Ghost OpenPCD2 modification: LOADMOD pin was enabled – outputs modulated subcarrier (847.5 kHz) The above signal was connected to a detector, in order to extract coded bitstream The bitstream was pulse modulated on a 14.4075 MHz carrier signal The HF signal was pre-amplified (MiniCircuits’ ZHL-32A) & power amplified (RMItaly KL400) Transmitting antenna: Broadband helically wound monopole antenna We use the magnetic near field emitted from the antenna Downlink experiment: Maximal downlink range was tested with a homemade diode detector ~ 1.5m Using a spectrum analyzer as a detector a range of ~3.5m was measured Jamming By transmitting a continuous signal on 14.4075 MHz the reader can be jammed Since we couldn’t measure uplink range independently from downlink system, maximal Jamming range was measured in order to evaluate the performance of the uplink system By transmitting a 29 dBm signal, a jamming range of 2 m was achieved The measured range was highly sensitive to the surrounding environment E-voting Using a range extended Ghost and a relay attack, an adversary can mount several attacks on Israel’s proposed e-voting system Allows the attacker complete control over previously cast votes Access control By using a range extended Ghost and a relay setup the attacker can open a secured door without being detected by a guard / security camera We offer a car mounted range extension setup for ISO 14443 RFID systems We successfully built a prototype working from 1.15 m (more than 10 times the nominal range) Extending the nominal communication range of contactless smartcards form a severe threat on the system’s security Combining with a relay attack the presented device can allow adversary to mount his attack without being detected