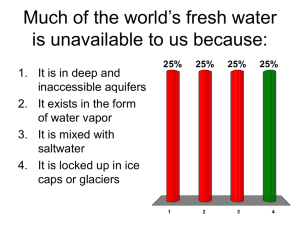
click to save-HYDRO POWER PLANT

INTRODUCTION
HYDRO POWER
1) One of the most widely used renewable source of energy for generating electricity on large scale basis is hydropower
2) The power obtained from river or ocean water is called as hydropower
3) Hydropower is the renewable source of energy since water is available in large quantities from rain, rivers, and oceans and this is will be available for unlimited time to come
HISTORY
- Nearly 2000 years ago the Greeks used water wheels to grind wheat into flour
- In the 1700's, hydropower was broadly used for milling of lumber and grain and for pumping irrigation water
- Appleton, Wisconsin became the first operational hydroelectric generating station in the United States, in 1882, producing 12.5 kilowatts (kW) of power
- The total electrical capacity generated was equivalent to 250 lights
- The largest and last masonry dam built by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation was the Roosevelt Dam in Arizona between 1905-1911; its power output has increased from 4,500 kW to 36,000 kW
- Still in use today, Niagra Falls was the first hydropower site developed for a vast quantity of electricity
TYPES OF HYDRO POWER PLANT
1) Water wheels
2) Hydro power plants
3) Wave energy from oceans
4) Tidal energy
5) Damless hydro power
Based on Quantity of Water Available
1) Run-off river hydro plants with pond
2) Run-off river hydro plants with pond
3) Reservoir hydroelectric power plants
Based on the Head of Water Available
1) Low head hydroelectric power plants
2)Medium head hydroelectric power plants
3) High head hydroelectric power plants
Based on the Nature of Load
1) Base load hydroelectric power plants
2) Peak load hydroelectric power plants
PRINCIPLE OF HYDRO POWER PLANT
WATER CYCLE
The continuous cycle in which water changes from water vapor in the atmosphere to liquid water through condensation and precipitation and then back to water vapor through evaporation, transpiration, and respiration
Water cycle in nature:
Water surface evaporation
Precipitation of clouds
Collected back to the oceans
VAPORATION
PRECIPITION
RAIN
Water cycle in the hydraulic power plant
Water energies: Kinetic energy , Potential energy
PROCESS / STAGES
1) Water in reservoir
2) Fall in turbine blade
3) Shaft rotation
4) Electric generation
5) Flow back of water
COMPONENT AND WORKING OF HYDRO POWER PLANT
1) Dam
What is dam
Location
Classification of dams
Storage dams
Diversion dams
Detention dams
Overflow dams
Rockfill dams
Gravity dams
Dam structure and design
Gravity dam
Storage dams
To impound water
Purpose - Irrigation
- Flood control
- Power generation
Diversion dams
For diversion
To provide sufficient pressure
Detention dams
To Minimize the effect of sudden floods
To trap sediment
Overflow dams
They carry water discharge over their crests
Rockfill dams
Rock instead of earth
Embankment dams hold back water by the force of gravity acting upon their mass
Gravity dams
Most gravity dams are made from concrete, a mixture of port land cement, water, and aggregates
They are much thicker at the base than the top
2) Water reservoir
Place behind the dam
Height of water
Potential energy
3) Intake or control gates
Gates inside of the dam.
Inlet gates
4) The penstock
To carries the water
Controlled by the control gates
5) Water turbines
Convert HYDROLIC energy to MECHANICAL energy
6) Generators
Convert MECHANICAL energy in ELECTRICAL energy
7) Transformer
Converts the alternating current to high voltage current.
Two coils: the supply coil and the outlet coil.
Voltage required for various applications is 110V or 230V.
Numbers of turns in outlet coil are double of supply coil, the voltage produced is also double.
8) Tailrace
Pipeline to drain the water
The potential energy of water in the tailrace has been used to generate electricity
CASE STUDY OF “HIRAKUND DAM”
INTRODUCTION
Built across the Mahanadi river
Located about 15 km from Sambalpur in the state of Orissa in India.
HISTORY
Built in 1956
Length is about (26 km)
It was the first major multipurpose river valley project started after India's independence.
Construction history
Project was proposed by Sir M. Visveswararya
Foundation stone was laid by sir HOWTHRONE LEWIS on 15 march 1946
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru laid the first batch of concrete on 12 April 1948.
The dam was completed in 1953 and was formally inaugurated by
Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru on 13 January 1957
The total cost of the project was Rs. 100.02 crores (in 1957).
Power generation along with agricultural irrigation started in 1956, achieving full potential in 1966
Geography
Hirakund is located at 21°31′N 83°52′E21.52°N 83.87°E
It has an average elevation of 160 meters (524 feet)
Demographics
As of 2001 India census Hirakund had a population of 26,397
Hirakund has an average literacy rate of 70%
Power generation
Nearly about 307 MW
Structure
The Hirakud Dam is a composite structure of earth, concrete and masonry
Ten km north of Sambalpur, it is the longest major earthen dam in the world
The main dam has an overall length of 4.8 km spanning between two hills; the Lamdungri on the left and the Chandili Dunguri on the right.
It also forms the biggest artificial lake in Asia, with a reservoir holding 743 km² at full capacity, with a shoreline of over 640 km..
People affected from the Dam Construction
Nearly 1.5 lakh people got affected by the Hirakud project.Nearly 22,000 family were displaced under the Hirakud dam project, an amount of Rs 12 crores was provided for payment of compensation to the affected people
Details
Total length of Dam : 15,748 Feet or 4800 Meter
Concrete Dam : 3,937 Feet or 1200 Meter
Earth Dam : 11,811 Feet or 3600 Meter
Left Dyke : 32,274 Feet or 9837 Meter
Right Dyke : 35,299 Feet or 10759 Meter
Maximum Height of Masonary Dam :200 Feet or 61 Meter
Maximum Height of Earth Dam :195 Feet or 59.5 Meter
Catchment Area : 83,400 km²
Total Power Capacity :275.5 MW
SALIENT FEATURES
(A)
(a)
(b)
HYDROLOGICAL :-
Catchment
Rain fall(mm)
(B)
-
-
83400 Sq. Kms (32200 sq miles)
Original Revised
DAM AND RESERVOIR
Top dam level R.L 195.680M.
(R.L.642 ft.)
Dead storage level R.L 197.830 M (R.L 590 Ft)
(c) SPILLWAY
Spillway capacity 42450 cumecs (15 lakhs cusecs)
Crest level - R.L. 185.928 M ( R.L. 610 ft.)
(D) POWER GENERATION:
Installed Capicity
At Burla - 5 x 37.5
2x24.0 = 235.50 MW
At Chiplima - 3x24 = 72.00 MW
Total = 307.50 MW
ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES OF
HYDRO POWER PLANT
Advantages
1) No fuel required
2) Cost of electricity is constant
3) No air-pollution is created
4) Long life
5) Cost of generation of electricity
6) Can easily work during high peak daily loads
7) Irrigation of farms
8) Water sports and gardens
9) Prevents floods
DISADVANTAGES
1) Disrupts the aquatic ecosystems
2) Disruption in the surrounding areas
3) Requires large areas
4) Large scale human displacement
5) Very high capital cost or investment
6) High quality construction
7) Site specific
8) Effects on environment
9) Safety of the dams