A Decision Process Dr. Asit K Patro Disaster Management
advertisement

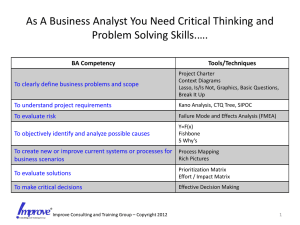
Hazard Identification Techniques on Chemical Emergency Planning Dr. Asit K Patra Disaster Management Institute Bhopal Terminology 1. Hazard: A chemical or physical condition that has the potential for causing damage to people, property and the environment. Example: Chlorine storage in Water treatment Plant LPG storage in Bottling plant Pressurised pipeline carrying Natural Gas 2. Risk: A measure of human injury/economic loss in terms of both the incident likelihood and the magnitude of loss or injury Relation between Hazard and Risk Terminology 3. Risk Analysis -A Quantitative or qualitative estimate of risk. 4. Risk Assessment Process of utilising Risk Analysis results with respect to a reference. 5. Disaster/Emergency Serious disruption of life, injury/death Affected large number of people and area Mobilisation of resources in case of those necessary during normal operation. Terminology 6. On-site and Off-site On-site: Consequences are confined within the plant premises Off-site: Consequences crosses the plant boundary. On-site Planning: As per Schedule 11 of MS&IHC Rules Off-site Planning: As per Schedule 12 of MS&IHC Rules Accident Outcomes (i) Fire: Pool, Jet, Flash, Fireball (ii) Explosion : BLEVE, VCE, Dust Explosion (iii) Release of Toxic gas/vapour BLEVE AN INDUSTRY AFTER VCE POOL-FIRE JET- FIRE Parameters to study Consequences of Accidental Release Scenarios (A) Fire : Thermal Radiation (Various damage levels) (B) Explosion : Overpressure (Various damage levels) (C) Toxic Release : Concentration (Various damage levels) A. Through Specific Checklist: B. Qualitative review : OSHAS/MSDS Identification Techniques of Potential Hazards C. Quantitative or Semi-Qualitative Method: HAZOP/FMEA/FTA/LOPA/Dow Fire & Explosion Index Etc. HAZOP = HAZard and OPerability Study Method for identifying (and assessing) HAZOP- a hazard identification tool problems that may represent risks to personnel or equipment, or prevent efficient operation Systematic and qualitative method based on the use of guide- words Multi- disciplinary team effort *** Qualitative and Quantitative INTENTION Procedure of HAZOP DEVIATION CAUSES CONSEQUENCES HAZARDS OPERATING DIFFICULTIES Process HAZOP Guide Words HAZOP Flow Chart HAZOP Work-sheet - An analysis of the system/plant equipment, their failure modes, effect of each failure mode on the system/plant. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) • Failure Mode – Description of how equipment fails (open, closed, on, off, leak etc.) • Effect of Failure Mode - System response or accident resulting from the equipment failure. IDENTIFY ELEMENTS OF SYSTEM IDENTIFY FUNCTIONS IDENTIFY FAILURE MODES PROCEDURE OF FMEA IDENTIFY EFFECTS OF FAILURE MODE IDENTIFY POSSIBLE CAUSES IDENTIFY EFFECT ON THE SYSTEM IDENTIFY EFFECT ON OTHER SYSTEMS FINAL RISK ASSESSMENT TAKE ACTION TO REDUCE RISK When to use Design : FMEA can be used to identify additional protective features those can be readily incorporated into the design. Construction: FMEA can be used to evaluate equipment changes resulting from field modifications. Operation: FMEA can be used to evaluate an existing facility and identify existing single features those represent potential accidents as well as to supplement more detailed hazard assessment such as HAZOP or FTA. FMEA identifies single failure modes and is not efficient in identifying combinations of equipment failures that lead to accidents. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) - A Tool in Risk Analysis FAULT TREE ANALYSIS (FTA) - A technique to estimate incident frequencies. A tool to find out the contribution of equipment failure and human /operator error in an accident event. - A Logic gate based graphical representation of the interrelationships between equipment failure and a specific accident Consequence Zones (Overpressure/Radiation flux/Toxicity) • Red Zone: – Collapse of Buildings ,Distortion in Steel Structure. – Complete Burning of human Body. – Lethal for 50% of healthy people (Toxic Release). • Orange Zone: – Partial Collapse of Buildings, Slight distortion in Steel Structure. – Third degree burns to human body. – Immediately dangerous to life & health(Toxic Release). • Blue Zone: – Second degree burns to human body if unable to reach in cover within 20 seconds. – Breakage of Window panes, Projectile limit. – Short term Exposure Limit.(Toxic Release). Planning : Engineering, Administrative and Legal PREVENTION PREPAREDNESS RESPONSE RECOVERY For Further Information, Please contact: asitkpatro@gmail.com Thanks