Adaptation technologies in agriculture, experiences from
advertisement

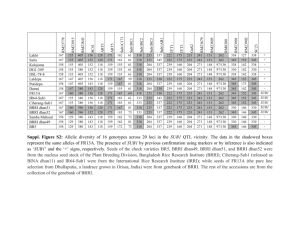
Adaptation Technologies in Agriculture: Experiences from Bangladesh Expert Meeting on Technology Road Maps 25 March 2013 Bonn, Germany Golam Rabbani Bangladesh Centre for Advanced Studies (BCAS) Outline of the Presentation Background Climate Induced Major Hazards How climate change currently affects agriculture practices (including the coast of Bangladesh) Adaptation Technologies for Agriculture (Crop-Rice) in Government of Bangladesh Adaptation Policy and Strategy of the Bangladesh Some examples of Adaptation technology in Agriculture in Bangladesh Background Bangladesh is one of the climate related disaster prone countries of the world Climate Change reduces rice production in Bangladesh by an average 3.9 % each year (World Bank, 2010) 4°C increase in temperature would have a sever impact on food production in Bangladesh, resulting in a 28 percent reduction for rice and a 68 per cent reduction for wheat (BCAS, BIDS and BUP, 1996) Bangladesh losses about 0.5 million tones of rice annually as a result of floods (Paul and Rashid, 1993) Salinity affected 1.1 million ha of land (soil) in the coast Farmers are adapting with local and innovative technologies (advantage and disadvantages) Drought Cyclone Storm surge, salinity Climate Induced Major Hazards That Affect Agriculture Sector in Bangladesh Flood Water logging Bank Bank erosion Erosion Mazumder, 2011 Climate Induced Major Hazards That Affect Bangladesh • River flood • Flash flood • Tidal surge Affected/Exposed Areas: • Nearly 80 % areas of the country is low-lying • Recent floods affected 30-69 % areas • Standing crops damage 5 Climate Induced Major Hazards Rice Production (Tons) That Affect Bangladesh Loss and Damage of Rice production in four study villages in the coast (Before and After Cyclone Aila in 2009) 2369 1063 134 0 Year 2008 Year 2009 Year 2010 Year Year 2011 Climate Induced Major Hazards That Affect Bangladesh Source: BWDB Climate Induced That Affect Bangladesh Sea Level Rise Major Hazards Climate Induced Major Hazards That Affect Bangladesh Salinity Intrusion in agriculture fields (SOIL) Salinity intrusion increased by 27 % from 1973 to 2009 (SRDI, 2010) Farmers are extremely challenged with salinity After Cyclone Aila (2009), many farmers couldn’t cultivate rice for three consecutive years How climate change induced hazards currently affects agriculture practices in the coast of Bangladesh Vulnerability to LIVELIHOOD • Damages of crops, fisheries and livestock • No freshwater for crops • Reduced yields • loss of crops Cyclone and Storm surge Late and lack of rainfall • Overflows surface water resources • Low level of water in ponds and mini ponds • Water quality and quantity • Lack of freshwater for irrigation • Reduce crop production due to salinity in soil Tidal surge and Salinity intrusion • Salinity in surface water • Vulnerability to LIVELIHOODS • Heavy rainfall in short time cause damage to crop • Excessive rainfall submerge the vegetables and crops for several days excessive rainfall (sky flood!) • huge surface runoff • Quality of water deteriorates Impacts on Agriculture sector Climate Change Impacts on water sector Adaptation Technologies for Agriculture (Crop-Rice and Wheat) in Bangladesh Climate Change Current Adaptation Technologies for Crop Agriculture key Elements (e.g. Rice and wheat ) Hard Technology Temperature variations Soft Technology Heat tolerant variety Training/capacity Early morning flowering variety building Improve irrigation system/ supplementary Crop irrigation Irrigation rotation patterns efficiency (magic pipe Awareness raising technology) Changing crop varieties Erratic rainfall Submergence tolerant varieties Awareness raising Early warning system Capacity building Short term variety Change of cropping pattern Adaptation Technologies in Agriculture (Crop-Rice and Wheat) in Bangladesh Climate Change Current Adaptation Technologies for Crop Agriculture key Elements (e.g. Rice and wheat ) Hard Technology Drought Soft Technology Drought tolerant variety Awareness raising Rainwater harvesting for lean period Capacity building Excavation and re-excavation of water Irrigation efficiency channels, mini ponds for irrigation Change tilling practices Drip irrigation system Flood Flood tolerant variety Awareness raising Infrastructure e.g. flood control Capacity building Seed preservation Crop forecasting Early warning system Salinity Saline tolerant variety Infrastructure Awareness raising (protection of agriculture Capacity building land from intrusion of sea water) Adaptation Technologies in Agriculture (Crop-Rice) in Bangladesh Climate Tolerant Rice Varieties Climate Related Stress Flood (submergence) Salinity in Climate Tolerant Popular Growth Duration Average Yield Rice Variety (Ton/Ha) (days) BRRI dhan 51 142-154 4 BRRI dhan 52 145-155 4.5 145 4.5 BRRI dhan 41 148 4.5 BRRI 28 140 6.0 BR 23 150 5.5 BRRI dhan 27 115 4 BRRI dhan 47 152 6.0 130-135 5.0 145 7.0 118 4.5 soil, surface BRRI dhan 40 and ground water BINA-8 Drought BRRI dhan 55 (also saline tolerant) BRRI dhan 33 “Saline Tolerant Varieties” as the effective adaptation option for Rice Farming in the most vulnerable Coastal Zone in Bangladesh Popular saline tolerant Rice varieties Crop Season Months Salinity tolerant level (ds/m) BRRI 28 Boro Dec-May 1-4 BRRI dhan 40 Aman June-Dec 8-10 BRRI dhan 41 Aman June-Dec 8-10 BRRI 23 Aman June-Dec 8-10 BRRI dhan 47 Boro Dec-May 8-10 Boro and Aman Dec-May/ June-Dec 12-14 BINA-8 key Adaptation Technologies in Crop Agriculture in Bangladesh Stress (flood, drought and salinity) tolerant varieties Short duration crops Innovative farming practices (floating gardens, irrigation efficiency) Crop diversification Changing/shifting cropping pattern Adjustments in irrigation system (excavation of mini-ponds, supplementary irrigation) Cropping intensity (1, 2, 3, 4……crops in a year) 15 Adaptation Policy and Strategy of the Government of Bangladesh Integrated Coastal Zone Management Plan 2005 National Adaptation Programmes of Action (NAPA) 2004/2005 Bangladesh Climate Change Strategy and Action Plan (BCCSAP, 2009) Food security, social protection and health Comprehensive Disaster Management Infrastructure Mitigation and low carbon development Research and knowledge management Capacity and institutions 16 Current Adaptation Governance: Conceptual Framework Trusty Board • Managing fund and selection of adaptation projects • 15 members MoEF Adaptation Actions/Projects Line Ministries Policy and Strategy •BCCSAP • NAPA CCT Climate Finance CTF Technical Committee • review and recommendation of adaptation projects Evaluation Team BCRRF High Level Committe e NGO/CSOs Communities DoE Department s/Institutes Implementing Organizations Some examples of Adaptation technology in Agriculture in Bangladesh Technology Case-1. Floating Gardens (Vegetable Farming) • Adaptation technology in practice: Flood Prone Areas • Floating Bed Preparation – Collection of materials (waterhyacinth and other aquatic vegetation) – Making a floating bed (May to July) • Farming crops and season – Mostly vegetables, both summer and winter – Ball or cushion like structure – Seedling raising Some examples of Adaptation technology in Agriculture in Bangladesh Technology Case-1. Floating Gardens (Vegetable Farming) • Growing vegetables – Vegetables growing People also grow vegetables for own consumption and sell surplus to the market • Income – Women earns 5 USD/Day (May-June) for preparing “Dolla” (small ball shaped structure) – Farmer earns 200 to 2000 USD/season depending on the size of the floating bed Some examples of Adaptation technology in Agriculture in Bangladesh Technology Case-2. Saline Tolerant Rice Variety • Adaptation Technology in practice: Coastal Zone • Saline Tolerant Rice Variety – BRRI 28 (mid 1990s to 2008) – BRRI dhan 47 is saline resistant variety – BRRI 47 can resist 8-10 dS/m (moderate level of salinity) – About 5 tons/ha – Duration about 150 days Source: Some examples of Adaptation technology in Agriculture in Bangladesh Technology Case 3. Traditional Adaptation Technology • Homestead Vegetable Garden on raised plinth • Most of the farmers now practice vegetable farming Some examples of Adaptation technology in Agriculture in Bangladesh Technology Case 3. Traditional Adaptation Technology • Vegetable farming at different level (adapting different degree of salinity) of raised plinth • Traditional practices in coastal areas • Mainly own consumption • Alternate livelihoods option under saline condition Some examples of Adaptation technology in Agriculture in Bangladesh Technology Case 3. Traditional Adaptation Technology • Adaptation technology in practice: Drought Prone Areas • Adjustments in irrigation for both rice and vegetable cultivation • improve irrigation efficiency in water scarcity areas • small water reservoir in the agriculture fields for irrigation Mini ponds supplementary irrigation Adaptation Projects in Agriculture Sector • Bangladesh Climate Change Trust Fund • Bangladesh Climate Resilience Fund Adaptation Projects in Agriculture Budget (USD) 1 Innovation & Extension of rice based technology to reduce the adverse impact of climate change. 0.75 Million 2 Stress tolerant rice, wheat, pulses & oil seed production, processing & distribution project 3.1 Million 3 Innovation of Sustainable Crop System for Drought Prone 0.75 Million and Coastal/saline Area to Face Climate Change Impact. 4 Innovation of various Crop System for Drought Prone and Coastal/saline Area to Face Climate Change Impact 0.6 Million 5 Agriculture Adaptation in Climate Risk Prone Areas 22.5 Million Thank you