Chapter 17: Water Use and Management
advertisement

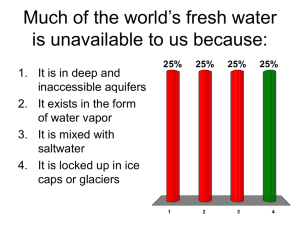
Chapter 17: Water Use and Management Surface Water, Bosnia 17.1 Water Resources • The hydrologic cycle constantly redistributes water • Water supplies are unevenly distributed The Hydrologic Cycle 17.2 Major Water Compartments • Oceans hold 97 percent of all water on earth • Glaciers, ice, and snow contain most surface fresh water (69%) • Groundwater Stores Large Resources (30%) • Rivers, lakes, and wetlands cycle quickly (1%) • The atmosphere is among the smallest of compartments (1 ppm) 17.3 Water Availability And Use • Many Countries Suffer Water Scarcity And Water Stress • Water Consumption Is Less Than Withdrawal – Withdrawal: What’s Taken Out. Much May Return Quickly To Source – Some Returned Water May Be Degraded – Consumed: Not Easily Returnable To Source – Very Little Water Is Actually Destroyed – What Is Destroyed Is Easily Reconstituted 17.3 Water Availability And Use • Water Use Is Increasing • Agriculture Is The Greatest Water Consumer Worldwide – Water Recycles Quickly But Not Necessarily Where It Came From • Domestic And Industrial Water Use Are Greatest In Wealthy Countries 17.4 Freshwater Shortages • • • • • Many people lack access to clean water Groundwater is being depleted Climate change threatens water supplies Rivers are shrinking Would you fight for water? All-Time Life Savers • • • • • • • • Clean Water Food Preservation Antiseptics Antibiotics Vaccination Surgery Green revolution Mosquito Control Green Bay Case Study Deep Aquifers of the Green Bay Area Green Bay Piezometric Surface 1957 1960 Green Bay Piezometric Surface 1957 2003 The Russian Radioactive Waste Injection Program Center-Pivot Irrigation Center-Pivot Irrigation Some Places Have Too Much Water Soluble Rocks Karst in Wisconsin Geothermal Systems: Mammoth Hot Springs, Yellowstone Yellowstone Canyon Old Faithful Geyser, Yellowstone 17.5 Dams And Diversions • Dam failure can be disastrous • Dams often displace people and damage ecosystems • Dams kill fish • Sedimentation limits reservoir life • What Do You Think? Should We Remove Dams? – Near end of useful life – Too small to contribute meaningfully Banqiao Dam Failures, China, 1975 • Built 1950’s for power and flood control • Hydrologist critical of design was sacked, reinstated, and sacked again • Designed to survive 1000 year flood (30 cm = 12 inches rain per day) • In 1975, >2000 year flood occurred – 19 cm (8 inches) in one hour – 106 cm (40 inches) in one day Banqiao Dam Failures, China, 1975 • August 1975: Cold Front collides with Super Typhoon Nina • Delay in opening gates because of communications failures and concern about downstream flooding • Gates blocked by sediment • August 8, 12:30 AM: Dam upstream fails – Designed for 500 year flood but exceeded capacity Banqiao Dam Failures, China, 1975 • August 8, 1 AM, Banqiao Dam overtopped and failed • Precipitated the failure of 62 dams • Flood wave 10 km wide, 3-7 m high, moving 50 km/hour • Numerous dams opened by air strikes to control flow Banqiao Dam Failures, China, 1975 • One commune of 9600 people was entirely annihilated • 26,000 people died from flooding • 145,000 died from subsequent epidemics and famine. • 9 days after the flood a million people were still stranded • About 6,000,000 buildings collapsed • Details declassified in 2005 Banqiao Dam After Failure 17.7 Increasing Water Supplies • • • • Desalination Provides Expensive Water Domestic Conservation Can Save Water Recycling Can Reduce Consumption Prices And Policies Have Often Discouraged Conservation (Encouraged Waste) • What Can You Do? Saving Water And Preventing Pollution Desalination • Passive Distillation – Slow • Active Distillation – Energy Intensive • Reverse Osmosis – Energy Intensive – Fragile Filters Reverse Osmosis