Powerpoint
advertisement
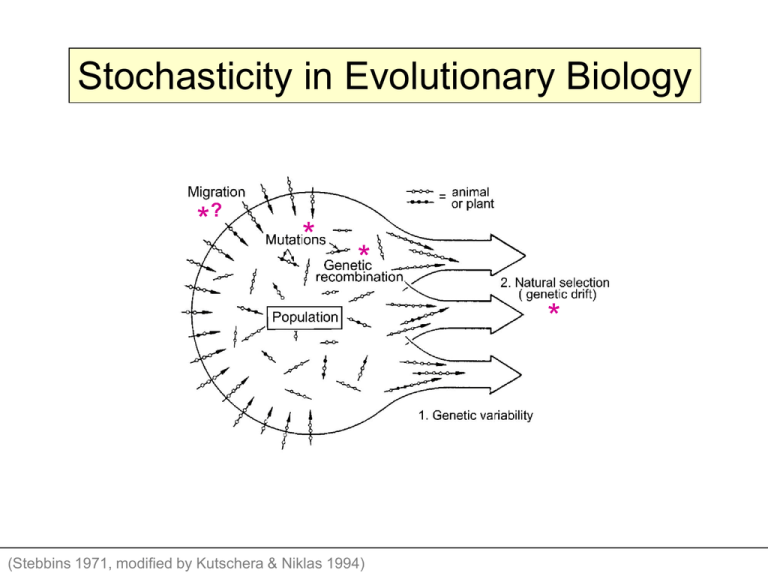
Stochasticity in Evolutionary Biology * ? * * * (Stebbins 1971, modified by Kutschera & Niklas 1994) “When we look at the plants and bushes clothing an entangled bank, we are tempted to attribute their proportional numbers and kinds to what we call chance. But how false a view is this!” “…the idea that chance begets order…” (Peirce 1893, quoted in Beatty 1984) Random with respect to… Beatty, J. 1984. Chance and natural selection. Philosophy of Science 51:183-211. Key insight into evolution: Particulate inheritance Deterministic effects: genes to genotypes to phenotypes Fisher Wright Haldane Particulate Inheritance (Mendel) + Evolution by Natural Selection (Darwin) = The Modern Synthesis Population genetics theory built from scratch 4 processes: Drift (N), Mutation (m), Gene Flow (m), Selection (s) Consensus on theoretical possibilities, and the “right” model structure Disagreement on the relative importance of different processes in Nature *? The Evolutionary Modern Synthesis * * * (Stebbins 1971, modified by Kutschera & Niklas 1994) * Processes with stochastic elements Consensus on theoretical possibilities, and the “right” model structure Disagreement on the relative importance of different processes in Nature The Molecular Revolution: Evolution at the level of proteins/DNA Why so much variation? Shouldn’t it get edited out by natural selection? Maybe much of this variation isn’t even “seen” by natural selection The neutral theory of molecular evolution: Mutation, Drift, Gene flow Mootoo Kimura Many DNA changes do not alter the amino-acid composition of a protein Some (many?, few?) amino acid substitutions don’t alter the function of a protein The neutral theory of molecular evolution is operational (in a way that the ecological theory is not) Each one of these loci (some neutral, some not) has the exact same demographic history (i.e., drift, migration) The neutral theory of molecular evolution is operational An example: Selective sweeps Okay, so all these processes are happening in Nature… but what is their relative importance? Does the answer really matter? On relative importance: Beatty, J. 1984. Chance and natural selection. Philosophy of Science 51:183-211. The importance (or not) of debates about relative importance Beatty, J. (1997) Why do biologists argue like they do? 64:S432-S443. The reason evolutionary biology seems to rest on more solid theoretical footing than ecology, is because evolutionary biologists agree on the theoretical framework, not the relative importance of different processes. …about ecological communities Everything you need to know… Global community Speciation Drift Selection Dispersal Regional community Dispersal Speciation Drift Selection Dispersal Dispersal Local Community Speciation Drift Selection Note: Extinction results from drift & selection What about macroevolution? Darwin’s first phylogeny The Tree of Life Project http://tolweb.org/tree/ Stephen J. Gould and “contingency” A critique of assuming determinism A critique of assuming gradualism Replaying Life’s Tape “I call this experiment “replaying life’s tape.” You press the rewind button…go back to any time and place in the past…Then let the tape run again and see if the repetition looks at all like the original” Contingency (= stochasticity?) “any replay of the tape would lead evolution down a pathway radically different from the road actually taken” Are the shapes of phylogenies different from random expectation? Are the shapes of phylogenies different from random expectation? Looks like we got null models from evolution too (in addition to neutral models) Lessons for Community Ecology: • Can neutral theory be “operationalized”? • Perhaps we can at least agree on a conceptual framework (mine, of course) • Can we skip past the mind-numbingly obvious aspects of the selection-neutrality debate? • Where is the “relative importance” approach going to get us? •Building models and empirical studies to be more comparable to one another. • Getting drift into models of selection…to come next week