Histology for Pathology
Male Genital Tract
Theresa Kristopaitis, MD
Associate Professor
Director of Mechanisms of Human Disease
Kelli A. Hutchens, MD, FCAP
Assistant Professor
Assistant Director of Mechanisms of Human Disease
Loyola Stritch School of Medicine
Male Reproductive System Histology Objectives
• Describe the pathway for sperm conduction through the genital ducts.
• Testis
– On a cross section of testis identify seminiferous tubules and interstitial
connective tissue.
– Name the two types of cells in the seminiferous tubules - spermatogenic
(germ) and supporting (Sertoli cells).
– Explain the function of Sertoli cells.
– On an H&E stained section, identify interstitial cells of Leydig and explain
their function.
• Prostate Gland
– On a section of the prostate, identify prostate glands and stroma.
– Identify corpora amylacea (prostatic secretions) and explain their
significance.
– On a high power view of the prostate describe the epithelium that lines the
glands.
• Penis
– On a cross section of the penis identify the corpora cavernosa, corpora
spongiosum, urethra and epidermis.
I.
II.
III.
IV.
V.
VI.
Spermatozoa leave the
seminiferous tubules via
the tubuli recti
From the tubuli recti to the
rete testis and efferent
ductules which lead to the
extratesticular ducts
Ductus epididymis
Ductus / Vas deferens
Ejaculatory ducts of the
prostate
Urethra
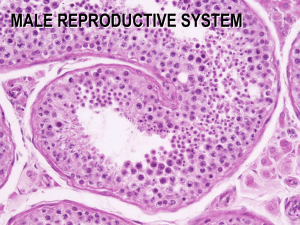
Seminiferous Tubules
• Consist of germinal epithelium and basement
membrane
– Epithelium contains various stages of spermatogenic
cells and supporting cells = Sertoli Cells
• Sertoli cells provide blood-testis barrier, secrete fructose,
androgen binding protein, anti-Mullerian hormone, inhibin,
and activin
• Connective tissue in between tubules contains
tubuli recti, vessels, and Leydig cells
– Leydig / interstitial cells secrete testosterone
Seminiferous tubule
Germinal
Epithelium
Sertoli Cell
Leydig cell
Prostate
Composed of branched
tubuloalveolar glands
Lumens often contain
prostatic secretions =
corpora amylacea
Corpora
amylacea
High power view of gland with its simple columnar epithelium that is highly
folded creating an irregular lumen.
Penis
Full cross section image: University of Michigan Medical School
Histology website
urethra
Corpora Cavernosa
Corpora spongiosum
Corpora Cavernosa of the Penis