Photomorphogenesis 1
advertisement

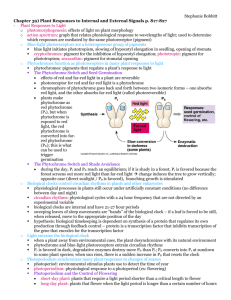
Photomorphogenesis (control of growth & development by light) • Environmental signals (light, temperature and gravity) are important signals for plant development • Light affects many aspects of plant development, for example: 1. 2. 3. 4. required for proper leaf development inhibits stem elongation in the emerging seedling promotes flowering (photoperiodism) promotes (or inhibits) seed germination Molecular Biol. of Leaf Development • Leaf development is light-dependent in angiosperms Arabidopsis Dark-grown Light-grown cotyledon • Chloroplast development is the signature feature: hypocotyl proplastids > (etioplasts) >chloroplasts (plastid number per cell increases) • Light controls expression of important chloroplast proteins Skotomorphogenesis – seedling development in darkness Barley (Hordeum vulgare) 7-10 days old Older cells (etioplasts) Young cells w/proplastids light CF1- α, β subunits of ATP synthetase PSI - photosystem I Chl-apoproteins PSII – photosystem II Chl-apoproteins Pchlrd – protochlorophyllide reductase LHCII- light-harvesting Chl-apoproteins of PSII LS - large subunit of RuBPCase SS – small subunit of RuBPCase From J. Mullet & colleagues several steps light + NADPH aminolevulinic acid -------------> protochlorophyllide Chlorophyllide Chl Pchlrd Step in chlorophyll synthesis that requires light Pchlrd (Protochlorophyllide reductase) – enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of protochlorophyllide; it over-accumulates in darkgrown plants, and is down-regulated by light. Protochlorophyllide Chlorophyllide Protein synthesis and select mRNA levels in plastids from dark-grown barley and after illumination. D – psbA gene product, other proteins were described in a preceding slide From J. Mullet & colleagues Regulation of Plastid Proteins by Light 1. Light induction of the chloroplast-encoded proteins is mainly at the translational and post-translational (i.e., protein stability) levels John Mullet Nuclear-encoded Cab/lhc mRNAs are not present in dark-grown plants. They are induced by white light or pulses of red light, & inhibited by pulses of far-red light. N-H. Chua and colleagues Transcription run-off in isolated nuclei of selected genes from dark-grown barley, and after the indicated light treatments. rbcS – small subunit of RuBPCase cab/lhc – light-harvesting Chlapoproteins of PSII pcr- protochlorophyliide reductase Klaus Apel Regulation of Plastid Proteins by Light 1. Light induction of the chloroplast-encoded proteins is mainly at the translational and post-translational (i.e., protein stability) levels 2. Regulation of the nuclear-encoded genes (e.g., rbcS, cab/lhc, and pcr ) is mainly at transcription - light can down-regulate (pcr) as well as up-regulate - transcriptional control also mediated by Phytochrome How does light control gene transcription and plastid development ?: The photoreceptor(s) Plants See: - Light Intensity - Light Direction - Colors PHYTOCHROME (PHY) Some major phytochrome-controlled processes: 1. Surface seed germination 2. Inhibition of stem elongation in young seedlings 3. Promoting leaf development in young seedlings 4. promotes stomatal opening Phy exists in two interconvertible forms: Pr - inactive, absorbs mainly red light (660 nm) Pfr - active, absorbs far-red light (730 nm) Pfr Pr slowly in dark More Phytochrome properties : 1. Protein subunit of 125,000 Daltons (~1100 amino acids). 2. Chromophore is a linear tetrapyrrole, attached covalently to a cysteine. 3. Native Phy is a dimer. 4. Has His-kinase activity. The “Red Far-Red” test for Phy control: Pulse of red light response Pulse of far-red light no response Pulse of red light pulse of far-red no response - 5 Phytochrome (PhyA-PhyE) genes - Have overlapping functions, based on mutant analysis - Vary with respect to the light intensity or light quality required for activation: - e.g., far-red responses are mediated by Phy A - Can form heterodimers • • • • absorb in the 350-450 nm range a.k.a. Cryptochrome Cryptochrome gene (Cry) identified using genetic approach (Cashmore & colleagues): - hy4 mutant of Arabidopsis chromophore = flavin (FAD) Tony Cashmore