Molecular Biology of the Cell
advertisement

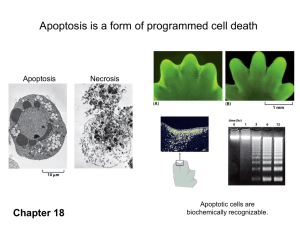
Chapter 18 Apoptosis Copyright © Garland Science 2008 M18.1 Apoptosis 건강한 성인: Billions of cells die every hour Programmed cell death(PCD): idea in 1970s acceptance (20년) :apoptosis (PCD의 한종류) Two distinct forms of cell death apoptosis Cell shrinks, Cytoskeletin collapses, 핵막 분해, DNA 절단 Apoptic body-chemically altered:macrophage necrosis Swell Burst Spilling their contents Eliciting inflammatory response Programmed cell death morphology in tobacco cells. Programmed cell death eliminates unwanted cells Sculpting the digits in the developing mouse paw by apotosis 1. 2. 3. 4. 불필요 세포/조직/기관제거 세포수 조절 (간세포 분열/phenobarbital) Quality control: B-/T-lymphocyte cell 제거 골수세포: 백혈구 제거 Figure 18-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Apoptotic Cells Are Biochemically Recognizable Markers of apoptosis TUNEL technique Phosphatidylserine: 세포막 안쪽 바깥: Annexin V로 검출 “eat me” signal “Don’t eat me” signal Figure 18-4a Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Apoptotic Cells Are Biochemically Recognizable Markers of apoptosis Positively charged 형광색소 : 미토콘도리아 inner membrane 의 안쪽 Cytochrome C: released from the intermembrane space of mitochondria Figure 18-4b Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Apoptosis Depends on an Intracellular Proteolytic Cascade That Is Mediated by Caspases Caspase: Procaspase activation during apoptosis Figure 18-5a Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Apoptosis Depends on an Intracellular Proteolytic Cascade That Is Mediated by Caspases Procaspase activation during apoptosis Caspase recruitment domain: activation complex Cytoskeleton Cell-cell adhesion proteins endonuclease Figure 18-5b Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Cell-Surface Death Receptors Activate the Extrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis The extrinsic pathway of apoptosis activated through Fas death receptors Tumor necrosis fctor receptor familiy Figure 18-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) DISC: Death-inducing signaling complex Decoy receptor FLIP blocking protein The Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis Depends on Mitochondria Release of cytochrome c from mitochondria during apoptosis bind procaspase-activating adapter protein(Apaf) apoptosome 형성 Recruit initiator procaspase proteins (procaspase-9) Figure 18-7 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) The Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis Depends on Mitochondria The intrinsic pathway of apoptosis Figure 18-8 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Apoptosis 효소? Bcl2 Proteins Regulate the Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis The three classes of Bcl2 Figure 18-9 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Bcl2 Proteins Regulate the Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis The role of BH123 pro-apoptotic Bcl2 proteins(mainly Bax and Bak) in the release of mitochondrial intermembrane proteins in the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis Figure 18-10 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Bax, Bak • Bax – Bound to mitochondrial outer membrane • Bak – Located in cytosol, transport into mitochondira after apoptotic signaling • Both work on ER and nuclear membrane, activated by ER stress release Ca++ and intrinsic apoptotic pathway Bcl2 Proteins Regulate the Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis How pro-apoptotic BH3-only and anti-apoptotic Bcl2 proteins regulate the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis Figure 18-11a Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Bcl2 Proteins Regulate the Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis How pro-apoptotic BH3-only and anti-apoptotic Bcl2 proteins regulate the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis Figure 18-11b Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Bid is the link between the two pathways • Death receptor extrinsic pathway • The initiator caspase, caspase-8 cleasve Bid producing tBid • tBid translocates to mitochondria inhibit bcl2 Bid: a proapoptotic BHS-3-only protein IAPs Inhibit Caspases A proposed model for the roles of IAPs and anti-IAPs in the control of apoptosis in mammalian cells IAP: Inhibitor of apoptosis first identified from vaculovirus. Figure 18-12a Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) IAPs Inhibit Caspases A proposed model for the roles of IAPs and anti-IAPs in the control of apoptosis in mammalian cells Figure 18-12b Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Extracellular Survival Factors Inhibit Apoptosis in Various Ways The role of survival factors and cell death in adjusting the number of developing nerve cells to the amount of target tissue Figure 18-13 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Extracellular Survival Factors Inhibit Apoptosis in Various Ways Three ways that extracellular survival factors can inhibit apoptosis Figure 18-14 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Bak/bax double mutant in mouse • Cannot activate intrinsic apoptosis • But without survival signal, nutrient import is not efficient • Autophagedie from starvation Figure Q18-1 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) UV illumination to human Hela Cells within 24h apoptosis in all cells from 6 h after illumination to 24 h Slow apoptosis? or Gradual apoptosis in cell population? Figure Q18-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008) Apoptosis (2010) 15:249–256 Apoptotic-like regulation of programmed cell death in plants • Protoplast condensation, nuclear condensation, fragmentation • A central regulatory role for the mitochondria • The degradation of the cell and its contents by PCD associated proteases. • Caspase-like – Study using caspase inhibitor, substrate – Lack in caspase ortholog from Arabidopsis genome • No evidence that cyt c can directly activate AL-PCD proteases. • No Bcl2 family homologs identified • Involvement of chloroplast? Schematic representation of AL-PCD MMP: mitochondrial membrane permeablization PTP: the perability transition pore Caspase-independent DNA degradation • Endo G – No homolog in plant – Mito IMS contain strong Mg2+ dependent nuclease activity • AIF/monodehydroascorbate reductase – 5 homologs in Arabidospsis – Antioxidant pathway – DNA-binding defective AIF fails to induce cell death Metacaspases • 9 metacaspases in Arabidopsis • Arginine instead of Aspartic acid • No caspase substrate clevage, no inhibition by caspase inhibitors • Involvement in PCD of Arabidopsis • Natural substrates? – TSN(Tudor staphylococcal nuclease) in Norway spruce (유럽가문비) – hTSN: caspase substrate, involved in PCD